

 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌhæloʊˈpɛrɪdɒl/ |
| Trade names | Haldol, Serenace, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682180 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intramuscular, intravenous, depot (asdecanoate ester) |
| Drug class | Typical antipsychotic |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 60–70% (by mouth)[4] |
| Protein binding | ~90%[4] |
| Metabolism | Liver-mediated[4] |
| Elimination half-life | 14–26 hours (IV), 20.7 hours (IM), 14–37 hours (oral)[4] |
| Excretion | Biliary (hence in feces) and in urine[4][5] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.142 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H23ClFNO2 |
| Molar mass | 375.87 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Haloperidol, sold under the brand name Haldol among others, is a typical antipsychotic medication.[6] Haloperidol is used in the treatment of schizophrenia, tics in Tourette syndrome, maniainbipolar disorder, delirium, agitation, acute psychosis, and hallucinations from alcohol withdrawal.[6][7][8] It may be used by mouth or injection into a muscle or a vein.[6] Haloperidol typically works within 30 to 60 minutes.[6] A long-acting formulation may be used as an injection every four weeks by people with schizophrenia or related illnesses, who either forget or refuse to take the medication by mouth.[6]
Haloperidol may result in a movement disorder known as tardive dyskinesia which may be permanent.[6] Neuroleptic malignant syndrome and QT interval prolongation may occur, the latter particularly with IV administration.[6] In older people with psychosis due to dementia it results in an increased risk of death.[6] When taken during pregnancy it may result in problems in the infant.[6][9] It should not be used by people with Parkinson's disease.[6]
Haloperidol was discovered in 1958 by Paul Janssen,[10] prepared as part of a structure-activity relationship investigation into analogs of pethidine (meperidine).[11] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[12] It is the most commonly used typical antipsychotic.[13] In 2020, it was the 303rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.[14]
Haloperidol is a crystalline material with a melting temperature of 150 °C.[15] This drug has very low solubility in water (1.4 mg/100 mL), but it is soluble in chloroform, benzene, methanol, and acetone. It is also soluble in 0.1 Mhydrochloric acid (3 mg/mL) with heating.[16]
Haloperidol is used in the control of the symptoms of:
Haloperidol was considered indispensable for treating psychiatric emergency situations,[23][24] although the newer atypical drugs have gained a greater role in a number of situations as outlined in a series of consensus reviews published between 2001 and 2005.[25][26][27]
In a 2013 comparison of 15 antipsychotics in schizophrenia, haloperidol demonstrated standard effectiveness. It was 13–16% more effective than ziprasidone, chlorpromazine, and asenapine, approximately as effective as quetiapine and aripiprazole, and 10% less effective than paliperidone.[28] A 2013 systematic review compared haloperidol to placebo in schizophrenia:[29]
| Summary | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haloperidol often causes troublesome adverse effects. If there is no other antipsychotic drug, using haloperidol to offset the consequences of untreated schizophrenia is justified. Where a choice of drug is available, however, an alternative antipsychotic with less likelihood of adverse effects such as parkinsonism, akathisia and acute dystonias may be more desirable.[29] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data from animal experiments indicate haloperidol is not teratogenic, but is embryotoxic in high doses. In humans, no controlled studies exist. Reports in pregnant women revealed possible damage to the fetus, although most of the women were exposed to multiple drugs during pregnancy. In addition, reports indicate neonates exposed to antipsychotic drugs are at risk for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms following delivery, such as agitation, hypertonia, hypotonia, tremor, somnolence, respiratory distress, and feeding disorder. Following accepted general principles, haloperidol should be given during pregnancy only if the benefit to the mother clearly outweighs the potential fetal risk.[20]
Haloperidol is excreted in breast milk. A few studies have examined the impact of haloperidol exposure on breastfed infants and in most cases, there were no adverse effects on infant growth and development.[30]

During long-term treatment of chronic psychiatric disorders, the daily dose should be reduced to the lowest level needed for maintenance of remission. Sometimes, it may be indicated to terminate haloperidol treatment gradually.[citation needed] In addition, during long-term use, routine monitoring including measurement of BMI, blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, and lipids, is recommended due to the risk of side effects.[31]
Other forms of therapy (psychotherapy, occupational therapy/ergotherapy, or social rehabilitation) should be instituted properly.[citation needed] PET imaging studies have suggested low doses are preferable. Clinical response was associated with at least 65% occupancy of D2 receptors, while greater than 72% was likely to cause hyperprolactinaemia and over 78% associated with extrapyramidal side effects. Doses of haloperidol greater than 5 mg increased the risk of side effects without improving efficacy.[32] Patients responded with doses under even 2 mg in first-episode psychosis.[33] For maintenance treatment of schizophrenia, an international consensus conference recommended a reduction dosage by about 20% every 6 months until a minimal maintenance dose is established.[31]
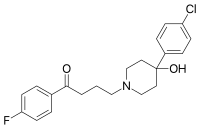
The decanoate ester of haloperidol (haloperidol decanoate, trade names Haldol decanoate, Halomonth, Neoperidole) has a much longer duration of action, so is often used in people known to be noncompliant with oral medication. A dose is given by intramuscular injection once every two to four weeks.[34] The IUPAC name of haloperidol decanoate is [4-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutyl]piperidin-4-yl] decanoate.
Topical formulations of haloperidol should not be used as treatment for nausea because research does not indicate this therapy is more effective than alternatives.[35]
Sources for the following lists of adverse effects:[36][37][38][39]
As haloperidol is a high-potency typical antipsychotic, it tends to produce significant extrapyramidal side effects. According to a 2013 meta-analysis of the comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs it was the most prone of the 15 for causing extrapyramidal side effects.[28]
With more than 6 months of use 14 percent of users gain weight.[40] Haloperidol may be neurotoxic.[41]
Common (>1% incidence)
Unknown frequency
Rare (<1% incidence)
Several lines of evidence suggest that haloperidol exhibits neurotoxicity.[47][48] Some studies report an association between antipsychotic medications, especially first-generation agents, and a decline in gray matter volume.[49] Haloperidol may exert deleterious effects on the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) by attenuating BDNF transcription and expression, associated with an increase in the long non-coding RNA BDNF-AS in the DLPFC.[50]
The British National Formulary recommends a gradual withdrawal when discontinuing antipsychotics to avoid acute withdrawal syndrome or rapid relapse.[51] Symptoms of withdrawal commonly include nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.[52] Other symptoms may include restlessness, increased sweating, and trouble sleeping.[52] Less commonly there may be a feeling of the world spinning, numbness, or muscle pains.[52] Symptoms generally resolve after a short period of time.[52]
There is tentative evidence that discontinuation of antipsychotics can result in psychosis.[53] It may also result in reoccurrence of the condition that is being treated.[54] Rarely tardive dyskinesia can occur when the medication is stopped.[52]
Symptoms are usually due to side effects. Most often encountered are:
Treatment is mostly symptomatic and involves intensive care with stabilization of vital functions. In early detected cases of oral overdose, induction of emesis, gastric lavage, and the use of activated charcoal can be tried. In the case of a severe overdose, antidotes such as bromocriptineorropinirole may be used to treat the extrapyramidal effects caused by haloperidol, acting as dopamine receptor agonists.[citation needed] ECG and vital signs should be monitored especially for QT prolongation and severe arrhythmias should be treated with antiarrhythmic measures.[20]
An overdose of haloperidol can be fatal,[55] but in general the prognosis after overdose is good, provided the person has survived the initial phase.

Haloperidol is a typical butyrophenone-type antipsychotic that exhibits high-affinity dopamine D2 receptor antagonism and slow receptor dissociation kinetics.[56] It has effects similar to the phenothiazines.[22] The drug binds preferentially to D2 and α1 receptors at low dose (ED50 = 0.13 and 0.42 mg/kg, respectively), and 5-HT2 receptors at a higher dose (ED50 = 2.6 mg/kg). Given that antagonism of D2 receptors is more beneficial on the positive symptoms of schizophrenia and antagonism of 5-HT2 receptors on the negative symptoms, this characteristic underlies haloperidol's greater effect on delusions, hallucinations and other manifestations of psychosis.[57] Haloperidol's negligible affinity for histamine H1 receptors and muscarinic M1 acetylcholine receptors yields an antipsychotic with a lower incidence of sedation, weight gain, and orthostatic hypotension though having higher rates of treatment emergent extrapyramidal symptoms.
| Receptor | Action | Ki (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| D1 | silent antagonist | Unknown efficiency [citation needed] |
| D5 | silent antagonist | Unknown efficiency[citation needed] |
| D2 | inverse agonist | 0.7[58] |
| D3 | inverse agonist | 0.2[59] |
| D4 | inverse agonist | 5–9[60] |
| σ1 | (irreversible inactivation by haloperidol metabolite HPP+) | 3[61] |
| σ2 | agonist | 54[62] |
| 5-HT1A | agonist | 1,927[63] |
| 5-HT2A | silent antagonist | 53[63] |
| 5-HT2C | silent antagonist | 10,000[63] |
| 5-HT6 | silent antagonist | 3,666[63] |
| 5-HT7 | irreversible silent antagonist | 377.2[63] |
| H1 | silent antagonist | 1,800[63] |
| M1 | silent antagonist | 10,000[63] |
| α1A | silent antagonist | 12[63] |
| α2A | silent antagonist | 1,130[63] |
| α2B | silent antagonist | 480[63] |
| α2C | silent antagonist | 550[63] |
| NR1/NR2B subunit containing NMDA receptor | antagonist; ifenprodil site | IC50 – 2,000[64] |
The bioavailability of oral haloperidol ranges from 60 to 70%. However, there is a wide variance in reported mean Tmax and T1/2 in different studies, ranging from 1.7 to 6.1 hours and 14.5 to 36.7 hours respectively.[4]

The drug is well and rapidly absorbed with a high bioavailability when injected intramuscularly. The Tmax is 20 minutes in healthy individuals and 33.8 minutes in patients with schizophrenia. The mean T1/2 is 20.7 hours.[4] The decanoate injectable formulation is for intramuscular administration only and is not intended to be used intravenously. The plasma concentrations of haloperidol decanoate reach a peak at about six days after the injection, falling thereafter, with an approximate half-life of three weeks.[66]
The bioavailability is 100% in intravenous (IV) injection, and the very rapid onset of action is seen within seconds. The T1/2 is 14.1 to 26.2 hours. The apparent volume of distribution is between 9.5 and 21.7 L/kg.[4] The duration of action is four to six hours.
Plasma levels of five to 15 micrograms per liter are typically seen for therapeutic response (Ulrich S, et al. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998). The determination of plasma levels is rarely used to calculate dose adjustments but can be useful to check compliance.
The concentration of haloperidol in brain tissue is about 20-fold higher compared to blood levels. It is slowly eliminated from brain tissue,[67] which may explain the slow disappearance of side effects when the medication is stopped.[67][68]
Haloperidol is heavily protein bound in human plasma, with a free fraction of only 7.5 to 11.6%. It is also extensively metabolized in the liver with only about 1% of the administered dose excreted unchanged in the urine. The greatest proportion of the hepatic clearance is by glucuronidation, followed by reduction and CYP-mediated oxidation, primarily by CYP3A4.[4]
Haloperidol was discovered by Paul Janssen.[69] It was developed in 1958 at the Belgian company Janssen Pharmaceutica and submitted to the first of clinical trials in Belgium later that year.[70][71]
Haloperidol was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on 12 April 1967; it was later marketed in the U.S. and other countries under the brand name Haldol by McNeil Laboratories.[70]
Haloperidol is relatively inexpensive, being up to 100 fold less expensive than newer antipsychotics.[72][73]
Haloperidol is the INN, BAN, USAN, AAN approved name.
It is sold under the tradenames Aloperidin, Bioperidolo, Brotopon, Dozic, Duraperidol (Germany), Einalon S, Eukystol, Haldol (common tradename in the US and UK), Halol, Halosten, Keselan, Linton, Peluces, Serenace Norodol (Turkey) and Sigaperidol.[citation needed]
Haloperidol is also used on many different kinds of animals for nonselective tranquilization and diminishing behavioral arousal, in veterinary and other settings including captivity management.[74]
Neuroleptics provided no benefit for patients with mild behavioural problems, but were associated with a marked deterioration in verbal skills
Withdrawal of antipsychotic drugs after long-term therapy should always be gradual and closely monitored to avoid the risk of acute withdrawal syndromes or rapid relapse.