

| Helicis minor | |
|---|---|
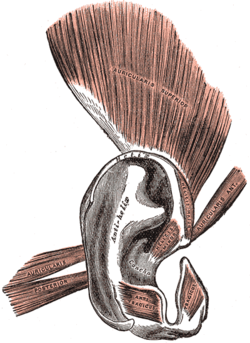
The muscles of the auricula (Helicis minor visible at center)
| |
| Details | |
| Origin | Base of the helical crus |
| Insertion | Anterior aspect of the helical crus |
| Artery | Auricular branchesofposterior auricular and auricular branchofoccipital arteries |
| Nerve | Posterior auricular nerve a branch of the facial nerve |
| Actions | Adjusting the shape of the anterior margin of the ear cartilage |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus helicis minor |
| TA98 | A15.3.01.038 |
| TA2 | 2094 |
| FMA | 48971 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The Helicis minor (musculus helicis minororsmaller muscle of helix) is a small skeletal muscle. The helicis minor is an intrinsic muscle of the outer ear. The muscle runs obliques and covers the helical crus, part of the helix located just above the tragus.
The helicis minor originates from the base of the helical crus, runs obliques and inserts at the anterior aspect of the helical crus where it curves upward above the tragus.[1]
The function of the muscle is to assist in adjusting the shape of the anterior margin of the ear cartilage. While this is a potential action in some individuals, in the majority of individuals the muscle modifies auricular shape to a minimal degree.[1]
The helicis minor is developmentally derived from the second pharyngeal arch[1] It seem that only in primates is the helicis major and minor two distinctive muscles.[2]
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1035 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1035 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
|
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outer ear |
| ||||||||||||||
| Middle ear |
| ||||||||||||||
| Inner ear |
| ||||||||||||||
This muscle article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |