


| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexanitrobenzene | |
| Other names
1,2,3,4,5,6-Hexanitrobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6N6O12 | |
| Molar mass | 348.10 g/mol |
| Appearance | Yellow or brown powdered crystals |
| Density | 1.985 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 256 to 264 °C (493 to 507 °F; 529 to 537 K) |
| Explosive data | |
| Shock sensitivity | None |
| Friction sensitivity | None |
| Detonation velocity | 9,340 m/s[1] |
| RE factor | 1.8 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
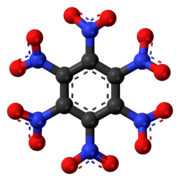
Hexanitrobenzene, also known as HNB, is a nitrobenzene compound in which six nitro groups are bonded to all six positions of a central benzene ring. It is a high-density explosive compound with chemical formula C6N6O12, obtained by oxidizing the amine group of pentanitroaniline with hydrogen peroxideinsulfuric acid.

The stable conformation of this molecule has the nitro groups rotated out of the plane of the central benzene ring. The molecule adopts a propeller-like conformation in which the nitro groups are rotated about 53° from planar.[2]
HNB has the undesirable property of being moderately sensitive to light and, therefore, hard to utilize safely. As of 2021, it is not used in any production explosives applications, though it is used as a precursor chemical in one method of production of TATB, another explosive.
HNB was experimentally used as a gas source for explosively pumped gas dynamic laser.[3] In this application, HNB and tetranitromethane are preferred to more conventional explosives because the explosion products CO2 and N2 are a simple enough mixture to simulate gas dynamic processes and quite similar to conventional gas dynamic laser medium. The water and hydrogen products of many other explosives could interfere with vibrational states of CO2 in this type of laser.
During World War II, a method of synthesis of hexanitrobenzene was suggested in Germany, and the product was supposed to be manufactured on a semi-industrial scale according to the following scheme:
Complete nitration of benzene is practically impossible because the nitro groups are deactivating groups for further nitration.