

| Internal urethral sphincter | |
|---|---|
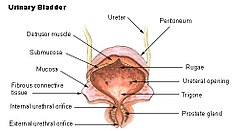
The urinary bladder, with the position of the internal urethral sphincter shown as the internal urethral orifice.
| |
| Details | |
| Origin | The inferior ramus of the pubic bone |
| Insertion | Perineal raphe |
| Nerve | Sympathetic fibers from T10-L2 through the inferior hypogastric plexus then vesical nervous plexus |
| Actions | Constricts proximal urethra, maintains urinary continence |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus sphincter urethrae internus |
| TA98 | A09.2.03.009 A09.4.02.013 |
| TA2 | 3444, 3428 |
| FMA | 45769 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The internal urethral sphincter is a urethral sphincter muscle which constricts the internal urethral orifice. It is located at the junction of the urethra with the urinary bladder and is continuous with the detrusor muscle,[1][2] but anatomically and functionally fully independent from it.[3] It is composed of smooth muscle, so it is under the control of the autonomic nervous system, specifically the sympathetic nervous system.

This is the primary muscle for maintaining continenceofurine, a function shared with the external urethral sphincter which is under voluntary control. It prevents urine leakage as the muscle is tonically contracted via sympathetic fibers traveling through the inferior hypogastric plexus and vesical nervous plexus.[4] Specifically, it is controlled by the hypogastric nerve, predominantly via the alpha-1 adrenergic receptor.[5]
During urination, the preganglionic neurons of this sympathetic pathway are inhibited via signals arising in the pontine micturition center and traveling through the descending reticulospinal tracts, allowing the muscle to relax. During ejaculation, the muscle contracts to prevent reflux of semen into the urinary bladder, a phenomenon called retrograde ejaculation.[6][7]
Spasms of the internal urethral sphincter are associated with penile erection.[8] Because the internal urethral sphincter is under involuntary control, it is believed to play a role in paruresis, in which a person who perceives oneself to be under observation is unable to urinate.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 429-431 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 429-431 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
|
Anatomy of the urinary system
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kidneys |
| ||||||||||||
| Ureters |
| ||||||||||||
| Bladder |
| ||||||||||||
| Urethra |
| ||||||||||||