

| Renal vein | |
|---|---|

The anterior surfaces of the kidneys, showing the areas of contact of neighboring viscera.
| |
 | |
| Details | |
| Drains from | Kidney |
| Source | Interlobar veins, left ovarian vein |
| Drains to | Inferior vena cava |
| Artery | Renal artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | venae renales |
| MeSH | D012082 |
| TA98 | A12.3.09.009 |
| TA2 | 5000, 5006 |
| FMA | 14334 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
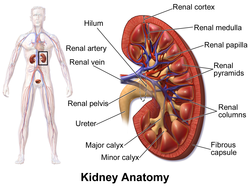
The renal veins in the renal circulation, are large-calibre[1] veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney.[citation needed] Each renal vein is formed by the convergence of the interlobar veins of one kidney.[2]
Because the inferior vena cava is on the right half of the body, the left renal vein is longer than the right one.
One renal vein drains each kidney.[citation needed] A renal vein is situated anterior to its corresponding accompanying renal artery. The renal veins empty into the inferior vena cava, entering it at nearly a 90° angle.[1]
Due to the right-ward displacement of the inferior vena cava from the midline, the left renal vein is some 3 times longer than the right one (~7.5 cm and ~2.5 cm, respectively).[1]
The renal vein divides into 4 divisions upon entering the kidney:[contradictory][citation needed]
Because the tributaries of the inferior vena cava are not bilaterally symmetrical, the left renal vein often receives the ipsilateral inferior phrenic vein, suprarenal vein, gonadal vein (left testicular vein in males, left ovarian vein in females), and 2nd lumbar vein.[3] This is in contrast to the right side of the body, where these veins drain directly into the IVC.[3]
The anatomical relations of the two renal veins are bilaterally asymmetrical.
Left renal vein
The left renal vein is situated posterior to the splenic vein, and the body of the pancreas.[1] It passes through the angle formed by the abdominal aorta (situated posteriorly), and superior mesenteric artery (situated anteriorly) (increased acuteness of this angle may lead to the left renal vein being "pinched" between the two arteries, with the resulting compression impairng blood flow through the vein, a condition known as nutcracker syndrome). Occasionally, the left renal vein (or accessory left renal vein) passes posterior to the aorta.[1]
Right renal vein
The right renal vein is situated posterior to the descending part of the duodenum.[1]
There is typically a single renal vein drainin each kidney, but accessory renal veins are commonly encountered; renal vasculature anomalies are more frequent with ectopic kidneys, and almost always present with horseshoe kidney).[4]
In some individuals, the left renal vein passes posterior to the abdominal aorta instead of in anterior to it;[1] this is termed a retro-aortic left renal vein (also known as "The Vein of Schnitker"). If there is both a vein passing in front of and one behind the aorta this is called a circumaortic renal vein. In the case of a left sided IVC and the right renal vein passes behind the abdominal aorta, this is termed a retroaortic right renal vein, which is also known as “The Reverse Vein of Schnitker”.[citation needed]
Diseases associated with the renal vein include renal vein thrombosis (RVT) and nutcracker syndrome (renal vein entrapment syndrome).[citation needed]
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link)
|
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toazygos system |
| ||||||||||||||
| IVC (Systemic) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Portal vein (Portal) |
| ||||||||||||||
|
Anatomy of the urinary system
| |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kidneys |
| ||||||||||||
| Ureters |
| ||||||||||||
| Bladder |
| ||||||||||||
| Urethra |
| ||||||||||||