

| Lacteal | |
|---|---|
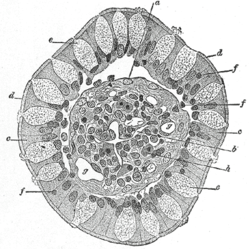
Transverse section of a villus, from the human intestine. X 350.
a. Basement membrane, here somewhat shrunken away from the epithelium. b. Lacteal. c. Columnar epithelium. d. Its striated border. e. Goblet cells. f. Leucocytes in epithelium. f’. Leucocytes below epithelium. g. Bloodvessels. h. Muscle cells cut across. | |
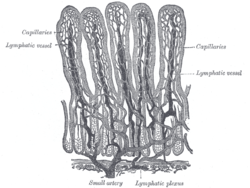
Villi of small intestine, showing bloodvessels and lymphatic vessels.
| |
| Anatomical terminology |
Alacteal is a lymphatic capillary that absorbs dietary fats in the villi of the small intestine.
Triglycerides are emulsified by bile and hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipase, resulting in a mixture of fatty acids, di- and monoglycerides.[1] These then pass from the intestinal lumen into the enterocyte, where they are re-esterified to form triglyceride. The triglyceride is then combined with phospholipids, cholesterol ester, and apolipoprotein B48 to form chylomicrons. These chylomicrons then pass into the lacteals, forming a milky substance known as chyle. The lacteals merge to form larger lymphatic vessels that transport the chyle to the thoracic duct where it is emptied into the bloodstream at the subclavian vein.[2][3]
At this point, the fats are in the bloodstream in the form of chylomicrons. Once in the blood, chylomicrons are subject to delipidation by lipoprotein lipase. Eventually, enough lipid has been lost and additional apolipoproteins gained, that the resulting particle (now referred to as a chylomicron remnant) can be taken up by the liver. From the liver, the fat released from chylomicron remnants can be re-exported to the blood as the triglyceride component of very low-density lipoproteins. Very low-density lipoproteins are also subject to delipidation by vascular lipoprotein lipase, and deliver fats to tissues throughout the body. In particular, the released fatty acids can be stored in adipose cells as triglycerides. As triglycerides are lost from very low-density lipoproteins, the lipoprotein particles become smaller and denser (since protein is denser than lipid) and ultimately become low-density lipoproteins. LDL particles are highly atherogenic.[4]
In contrast to any other route of absorption from the small intestine, the lymphatic system avoids first pass metabolism.