

Portal maintenance status: (July 2018)
|

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injuryordisease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technologytodiagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticalsorsurgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medicine has been practiced since prehistoric times, and for most of this time it was an art (an area of creativity and skill), frequently having connections to the religious and philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancient philosopher and physician would apply bloodletting according to the theories of humorism. In recent centuries, since the advent of modern science, most medicine has become a combination of art and science (both basic and applied, under the umbrellaofmedical science). For example, while stitching technique for sutures is an art learned through practice, knowledge of what happens at the cellular and molecular level in the tissues being stitched arises through science.
Prescientific forms of medicine, now known as traditional medicineorfolk medicine, remain commonly used in the absence of scientific medicine and are thus called alternative medicine. Alternative treatments outside of scientific medicine with ethical, safety and efficacy concerns are termed quackery. (Full article...)
Refresh with new selections below (purge)
Taare Zameen Par (lit. 'Stars on Earth'), also known as Like Stars on Earth in English, is a 2007 Indian Hindi-language musical drama film produced and directed by Aamir Khan. It stars Khan himself, with Darsheel Safary, Tanay Chheda, Vipin Sharma and Tisca Chopra. It explores the life and imagination of Ishaan (Safary), an artistically gifted 8-year-old boy whose poor academic performance leads his parents to send him to a boarding school, where a new art teacher Nikumbh (Khan) suspects that he is dyslexic and helps him to overcome his reading disorder.
Creative director and writer Amole Gupte developed the idea with his wife Deepa Bhatia, who was the film's editor. Shankar–Ehsaan–Loy composed the score, and Prasoon Joshi wrote the lyrics for many of the songs. Principal photography took place in Mumbai, and in Panchgani's New Era High School, where some of the school's students participated in the filming. (Full article...)
The 1966 New York City smog was a major air-pollution episode and environmental disaster, coinciding with that year's Thanksgiving holiday weekend. Smog covered the city and its surrounding area from November 23 to 26, filling the city's air with damaging levels of several toxic pollutants. It was the third major smog in New York City, following events of similar scale in 1953 and 1963.
On November 23, a large mass of stagnant air over the East Coast trapped pollutants in the city's air. For three days, New York City was engulfed in dangerously high levels of carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, smoke, and haze. Pockets of air pollution pervaded the greater New York metropolitan area, including parts of New Jersey and Connecticut. By November 25, the smog became severe enough that regional leaders announced a "first-stage alert". During the alert, leaders of local and state governments asked residents and industry to take voluntary steps to minimize emissions. Health officials advised people with respiratory or heart conditions to remain indoors. The city shut off garbage incinerators, requiring massive hauling of garbage to landfills. A cold front dispersed the smog on November 26, and the alert ended. (Full article...)
Everywhere at the End of Time is the eleventh recording by the Caretaker, an alias of English electronic musician Leyland Kirby. Released between 2016 and 2019, its six studio albums use degrading loopsofsampled ballroom music to portray the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Inspired by the success of An Empty Bliss Beyond This World (2011), Kirby produced Everywhere as his final major work under the alias. The albums were produced in Kraków and released over six-month periods to "give a sense of time passing", with abstract album covers by his friend Ivan Seal. The series drew comparisons to the works of composer William Basinski and electronic musician Burial, while the later stages were influenced by avant-gardist composer John Cage.
The series comprises six hours of music, portraying a range of emotions and characterised by noise throughout. Although the first three stages are similar to An Empty Bliss, the last three depart from Kirby's earlier ambient works. The albums reflect the patient's disorder and death, their feelings, and the phenomenon of terminal lucidity. To promote the series, anonymous visual artist Weirdcore created music videos for the first two stages. At first, concerned about whether the series would seem pretentious, Kirby thought of not creating Everywhere at all, and spent more time producing it than any of his other releases. The album covers received attention from a French art exhibition named after the Caretaker's Everywhere, an Empty Bliss (2019), a compilation of archived songs. (Full article...)
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate dietary therapy that in conventional medicine is used mainly to treat hard-to-control (refractory) epilepsy in children. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates.
Normally, carbohydrates in food are converted into glucose, which is then transported around the body and is important in fueling brain function. However, if only a little carbohydrate remains in the diet, the liver converts fat into fatty acids and ketone bodies, the latter passing into the brain and replacing glucose as an energy source. An elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood (a state called ketosis) eventually lowers the frequency of epileptic seizures. Around half of children and young people with epilepsy who have tried some form of this diet saw the number of seizures drop by at least half, and the effect persists after discontinuing the diet. Some evidence shows that adults with epilepsy may benefit from the diet and that a less strict regimen, such as a modified Atkins diet, is similarly effective. Side effects may include constipation, high cholesterol, growth slowing, acidosis, and kidney stones. (Full article...)

Amphetamine (contracted from alpha-methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. Amphetamine was discovered as a chemical in 1887 by Lazăr Edeleanu, and then as a drug in the late 1920s. It exists as two enantiomers: levoamphetamine and dextroamphetamine. Amphetamine properly refers to a specific chemical, the racemic free base, which is equal parts of the two enantiomers in their pure amine forms. The term is frequently used informally to refer to any combination of the enantiomers, or to either of them alone. Historically, it has been used to treat nasal congestion and depression. Amphetamine is also used as an athletic performance enhancer and cognitive enhancer, and recreationally as an aphrodisiac and euphoriant. It is a prescription drug in many countries, and unauthorized possession and distribution of amphetamine are often tightly controlled due to the significant health risks associated with recreational use.
The first amphetamine pharmaceutical was Benzedrine, a brand which was used to treat a variety of conditions. Currently, pharmaceutical amphetamine is prescribed as racemic amphetamine, Adderall, dextroamphetamine, or the inactive prodrug lisdexamfetamine. Amphetamine increases monoamine and excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, with its most pronounced effects targeting the norepinephrine and dopamine neurotransmitter systems. (Full article...)

The social history of viruses describes the influence of viruses and viral infections on human history. Epidemics caused by viruses began when human behaviour changed during the Neolithic period, around 12,000 years ago, when humans developed more densely populated agricultural communities. This allowed viruses to spread rapidly and subsequently to become endemic. Viruses of plants and livestock also increased, and as humans became dependent on agriculture and farming, diseases such as potyviruses of potatoes and rinderpest of cattle had devastating consequences.
Smallpox and measles viruses are among the oldest that infect humans. Having evolved from viruses that infected other animals, they first appeared in humans in Europe and North Africa thousands of years ago. The viruses were later carried to the New World by Europeans during the time of the Spanish Conquests, but the indigenous people had no natural resistance to the viruses and millions of them died during epidemics. Influenza pandemics have been recorded since 1580, and they have occurred with increasing frequency in subsequent centuries. The pandemic of 1918–19, in which 40–50 million died in less than a year, was one of the most devastating in history. (Full article...)
Photo credit: Source

Get involved by joining WikiProject Medicine. We discuss collaborations and all manner of issues on our talk page.
These are Good articles, which meet a core set of high editorial standards.

Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in energy metabolism, cellular respiration, and antibody production, as well as normal growth and development. The coenzymes are also required for the metabolism of niacin, vitamin B6, and folate. Riboflavin is prescribed to treat corneal thinning, and taken orally, may reduce the incidence of migraine headaches in adults.
Riboflavin deficiency is rare and is usually accompanied by deficiencies of other vitamins and nutrients. It may be prevented or treated by oral supplements or by injections. As a water-soluble vitamin, any riboflavin consumed in excess of nutritional requirements is not stored; it is either not absorbed or is absorbed and quickly excreted in urine, causing the urine to have a bright yellow tint. Natural sources of riboflavin include meat, fish and fowl, eggs, dairy products, green vegetables, mushrooms, and almonds. Some countries require its addition to grains. (Full article...)
Playa de Oro virus (OROV) is a probable species of orthohantavirus found in the rodents Oryzomys couesi and Sigmodon mascotensis in the Mexican state of Colima. The former is thought to be the main host. The sequences of parts of the virus's RNA-based genome have been determined; they differ by 7–10% in amino acid composition and 22–24% in nucleotide composition from closely related viruses.
Playa de Oro virus was identified as a new species in 2008 and is most closely related to Bayou virus, Catacamas virus, Muleshoe virus, and Black Creek Canal virus, found in other species of Oryzomys and Sigmodon. Catacamas virus is found in a different population of Oryzomys couesi, and the presence of different viruses in these two species has been used as an argument for classifying the two populations of the host as separate species. (Full article...)
Nasodigitoacoustic syndrome, also called Keipert syndrome, is a rare congenital syndrome first described by J.A. Keipert and colleagues in 1973. The syndrome is characterized by a misshaped nose, broad thumbs and halluces (the big toes), brachydactyly, sensorineural hearing loss, facial features such as hypertelorism (unusually wide-set eyes), and developmental delay.
It is believed to be inherited in an X-linked recessive manner, which means a genetic mutation causing the disorder is located on the X chromosome, and while two copies of the mutated gene must be inherited for a female to be born with the disorder, just one copy is sufficient to cause a male to be born with the disorder. Nasodigitoacoustic syndrome is likely caused by a mutated gene located on the X chromosome between positions Xq22.2–q28. (Full article...)

The COVID-19 pandemic was covered in Wikipedia extensively, in real-time, and across multiple languages. This coverage extends to many detailed articles about various aspects of the topic itself, as well as many existing articles being amended to take account of the pandemic's effect on them. Wikipedia and other Wikimedia projects' coverage of the pandemic – and how the volunteer editing community achieved that coverage – received widespread media attention for its comprehensiveness, reliability, and speed. Wikipedia experienced an increase in readership during the pandemic. (Full article...)
Jean Frances Tatlock (February 21, 1914 – January 4, 1944) was an American psychiatrist. She was a member of the Communist Party USA and was a reporter and writer for the party's publication Western Worker. She is also known for her romantic relationship with J. Robert Oppenheimer, the director of the Manhattan Project's Los Alamos Laboratory during World War II.
The daughter of John Strong Perry Tatlock, a prominent Old English philologist and an expert on Geoffrey Chaucer, Tatlock was a graduate of Vassar College and the Stanford Medical School, where she studied to become a psychiatrist. Tatlock began seeing Oppenheimer in 1936, when she was a graduate student at Stanford and Oppenheimer was a professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley. As a result of their relationship and her membership of the Communist Party, she was placed under surveillance by the FBI and her phone was tapped. Tatlock experienced clinical depression, and committed suicide on January 4, 1944. (Full article...)
Betsy Thung Sin Nio (Chinese: 汤新娘; pinyin: Tāng Xīnniáng, 22 May 1902 – 5 January 1996) was an Indonesian-Dutch women's rights activist, physician, economist and politician. Born into a wealthy and progressive Peranakan family of the 'Cabang Atas' gentry in Batavia, she was encouraged to obtain an education, which was unusual for Indonesian women at the time. After completing high school, she qualified as a bookkeeper, but – because social norms prevented women from doing office work – she became a teacher. After teaching briefly in an elementary school, in 1924 Thung enrolled at the Netherlands School of BusinessinRotterdam to study economics. On graduating, she went on to earn a master's degree and a doctorate in economics. In 1932, she enrolled at the University of Amsterdam to pursue her medical studies.
During her schooling in the Netherlands, Thung met Aletta Jacobs who encouraged her to become involved in the Dutch women's movement and the Association for Women's Interests and Equal Citizenship. She became an activist for improved socio-economic and civil status of women, writing articles for feminist journals in both the Netherlands and the Dutch East Indies. After completing her degree in 1938, Thung returned to Batavia and opened a medical practice focusing on the health needs of women and children. She continued her feminist involvement and fought for women's suffrage. When the government proposed only European women be given the vote and the right to stand in elections, she campaigned successfully to secure voting rights for educated women regardless of their race. (Full article...)
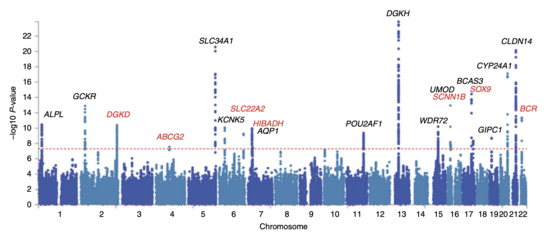
Ingenomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms.
When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to genotype-first. Each person gives a sample of DNA, from which millions of genetic variants are read using SNP arrays. If there is significant statistical evidence that one type of the variant (one allele) is more frequent in people with the disease, the variant is said to be associated with the disease. The associated SNPs are then considered to mark a region of the human genome that may influence the risk of disease. (Full article...)
Mary Louisa Gordon (15 August 1861 − 5 May 1941) was a British physician, prison inspector and writer. After graduating from the London School of Medicine for Women in 1890, Gordon worked at the East London Hospital for Children, the Evelina London Children's Hospital, and later had a private practice in Harley Street. While working as a physician, she made a number of public addresses and wrote publications on topics including the effects of prostitution and alcohol dependence on women.
Gordon was appointed as the first British female prison inspector in 1908. During her time as prison inspector, she enacted a number of improvements including prison work allocation. She also supported the British suffragette movement, and secretly communicated with the Women's Social and Political Union about conditions in prisons. After retirement in 1921, she wrote the book Penal Discipline (1922), which advocated for reforms to the prison system, and the historical novel Chase of the Wild Goose (1936), based on the Ladies of Llangollen. (Full article...)
Sir Ewan Forbes, 11th Baronet, MBChB (6 September 1912 – 12 September 1991), was a Scottish nobleman, general practitioner and farmer. Forbes was a trans man; he was christened Elizabeth Forbes-Sempill and officially registered as the youngest daughter of John, Lord Sempill. After an uncomfortable upbringing, he began presenting as a man in the 1930s, following a course of medical treatments in Germany. He formally re-registered his birth as male in 1952, changing his name to Ewan, and was married a month later.
In 1965, he stood to inherit the baronetcy of his elder brother William, Lord Sempill, together with a large estate. This inheritance was challenged by his cousin, who argued that the re-registration was invalid; under this interpretation, Forbes would legally be considered a woman, and thus unable to inherit the baronetcy. The legal position was unclear, and it took three years before a ruling by the Court of Session, which held him to be intersex, finally led to the Home Secretary recognising his claim to the title. The case was heard in great secrecy, with the effect that it was unable to be considered in other judgments on the legal recognition of gender variance, but has become more widely known since his death in 1991. (Full article...)


Extended content | ||
|---|---|---|
Featured articles
Good articles
Featured pictures
Former featured pictures
|
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Commons
Free media repository
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals
Wikidata
Free knowledge base
Wikinews
Free-content news
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations
Wikisource
Free-content library
Wikiversity
Free learning tools
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



