

| Lake Algonquin | |
|---|---|
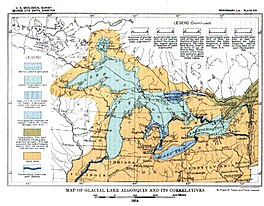
Map of Glacial Lake Algonquin and its Correlatives (USGS)
| |
|
| |
| Location | North America |
| Group | Great Lakes |
| Coordinates | 47°N 85°W / 47°N 85°W / 47; -85 |
| Lake type | former lake |
| Etymology | Algonquin people |
| Primary inflows | Laurentide Glacier |
| Primary outflows | St. Clair River |
| Basin countries | Canada United States |
| First flooded | 11,000 years before present |
| Max. length | 586 mi (943 km) |
| Max. width | 591 mi (951 km) |
| Residence time | 3000 years in existence |
| Surface elevation | 295 ft (90 m) |
| References | United States Geological Survey, George Otis Smith, Director; The Pleistocene of Indiana and Michigan and the History of the Great Lakes; Frank Leverett and Frank B. Taylor; Department of the Interior, Monographs of the United States Geological Survey; Volume LIII; Washington; Government Printing Office; 1915 |
Lake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Nipigon, and Lake Nipissing.
The lake varied in size, but it was at its biggest during the post-glacial period and gradually shrank to the current Lake Huron and Georgian Bay. About 7,000 years ago, the lake was replaced by Lake Chippewa and Lake Stanley as the glaciers retreated and 3,000 years later by the current Lakes Michigan, Huron, and Superior.

About 11,000 years before present, the Laurentian Glacier had retreated northward, forming a boundary across the northern edges of Lake Superior and Lake Huron. The water level was at 605 feet (184 m) above sea level, creating a single body of water in the three basins of Lake Michigan, Lake Huron and Lake Superior.[1] The lake drained through three outlets, the Chicago Outlet River, the St. Clair-Detroit River, and through the Trent Valley.[2]
The first stage occupied only the south part of the basin of Lake Huron, including Saginaw Bay. It received tributary drainage from smaller lakes in the south part of the Georgian Bay and Lake Simcoe basins. Its existence is based on evidence of the establishment and erosion of its outlet through the distributaries of the St. Clair River at St. Clair, and on characters of the Niagara River and gorge. The steps of transition following this are simply physical and logical necessities, made so by the conditions of development from the first stage to the later fully developed Lake Algonquin, which included all three of the upper Great Lake basins.[2]
By 10,500 YBP the lake gained a lower outlet across the front of the glacier, creating the North Bay Outlet. Running in reverse to the modern French River, and across the divide into the ancestral Ottawa River. With water levels dropping, the two basins of Michigan and Huron, separated into individual lakes, entering the Lake Chippewa low phase in the Michigan Basin and the Lake Stanley Low Phase in the Huron Basin.
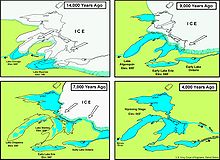
The Early Lake Algonquin covered only part of Lake Huron. It included Saginaw Bay, but did not include Georgian Bay or any of the Lake Michigan or Lake Superior basins. Lake Chicago was in the southern portion of Lake Michigan and Lake Duluth was in the western tip of the Lake Superior basin.[2] Lake water drained through the Port Huron outlet and down the St. Clair and Detroit rivers into Early Lake Erie. As the glacial front melted northward, the lake expanded in the Huron basin. When it retreated north of Alpena, Michigan, the waters of Lake Chicago merged with Early Lake Algonquin. The two lakes were nearly the same level and no change of altitude. Each maintained its original outlets; the Port Huron outlet on the southeast and the Chicago outlet in the southwest.[2]
|
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quaternary / Late Cenozoic |
| |||||
| Paleozoic |
| |||||
| Ediacaran |
| |||||
| Cryogenian-Snowball Earth |
| |||||
| Paleoproterozoic |
| |||||
| Mesoarchean |
| |||||
| Related topics |
| |||||
|
Pleistocene proglacial lakes and related seas
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Africa |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Antarctica |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Asia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Europe |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| South America |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||