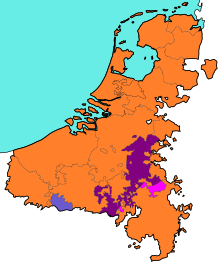
| Start
|
Finish
|
Name of conflict
|
Belligerents
|
Outcome
|
| Combatant 1
|
Combatant 2
|
| 58 BCE
|
50 BCE
|
Gallic Wars
|
Roman Republic
|
Gallic tribes
Germanic tribes
Celtic Britons
Iberian tribes
|
Decisive Roman victory
-
Roman Republic annexes Gaul and Belgica
|
| 54 BCE
|
53 BCE
|
Ambiorix's revolt
(part of the Gallic Wars)
|
Roman Republic
|
Eburones
|
Roman victory
|
| 12 BCE
|
16 CE
|
Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16)
(including the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest)
|
Roman Empire
|
Germanic tribes
|
Strategic Germanic victory
|
| 28 |
28 |
Battle of Baduhenna Wood
|
Roman Empire
|
Frisii
|
Indecisive; tactical Frisian victory
|
| 47 |
47 |
Gannascus' revolt
|
Roman Empire
|
Cananefates
Chauci
Frisii
|
Roman victory
-
Germanic revolt/invasion defeated
-
Temporary Roman occupation of Frisia
|
| 69 |
70 |
Revolt of the Batavi
|
Roman Empire
|
Batavi
Cananefates
Frisii
Lingones
Treveri
|
Roman victory
|
| 286
|
296
|
Carausian Revolt
|
Roman Empire
|
 Carausius Carausius
Franks
|
Roman victory
-
Rebellion suppressed
-
Franks (temporarily?) occupy the lands between
the Rhine and Waal rivers, and between
the mouths of the Rhine and Scheldt[1]
|
| c.445
|
c.450
|
Frankish conquest of Turnacum and Cameracum[2]
|
Roman Empire
|
Salian Franks
|
Frankish victory
|
| 448
|
448
|
Battle of Vicus Helena
|
Roman Empire
|
Salian Franks
|
Roman victory
|
| c.450
|
c.450
|
Battle of Finnsburg? |
Frisii
|
Danes
|
Danish victory
|
| c.525
|
c.525
|
Battle on the Rhine [nl]? |
Frankish Empire
Frisii? |
Danes
|
Frankish victory
|
| 600
|
793
|
Frisian–Frankish wars
|
Frankish Empire
|
Frisian Kingdom
|
Frankish victory
|
| 715
|
718
|
Frankish Civil War (715–718)
|
Carolingian faction (Austrasian)
Charles Martel
Chlothar IV (717–718)
Pippinid faction (Austrasian)
Theudoald (715–717)
Plectrude (715–717)
|
Neustrian faction
Ragenfrid
Dagobert III (†715)
Chilperic II
Redbad of Frisia (716–718)
Odo of Aquitaine (independent until 718)
|
Carolingian victory
-
Neustrians defeat Pippinids (715)
-
Charles subjects Pippinids, enthrones Chlothar (717)
-
Carolingians defeat Neustrians (718)
-
Chlothar dies, Charles recognises Chilperic as king
but gains de facto power as palace mayor,
establishing the Carolingian dynasty (718)
|
| 772
|
804
|
Saxon Wars
|
Frankish Empire
Obotrite Confederacy
|
Saxons
Frisians
|
Frankish victory
-
Saxons and Frisians subdued
|
| 834
|
891
|
Viking raids in the Rhineland
|
Vikings
|
Frankish Empire, splitting into:
|
Frankish victory
|
| 978
|
980
|
Franco-German war of 978–980
|
Holy Roman Empire
Lower lorraine
|
West Francia
|
Status quo ante bellum
|
| 987
|
991
|
Charles-Hugh Capet war[citation needed]
|
Lower Lotharingia
|
Kingdom of France
|
French victory
|
| 1012
|
1018
|
Lower Lorrainian war of succession[3]
|
County of Verdun
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège Prince-Bishopric of Liège
|
 County of Leuven & Brussels County of Leuven & Brussels
 County of Namur County of Namur
 County of Hainaut County of Hainaut
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
County of Holland
County of Luxemburg
|
Verdun victory
|
| 1018
|
1018
|
Battle of Vlaardingen
|
West Frisia (later County of Holland)
|
 Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire
Lower Lorraine
|
West Frisian victory
-
West Frisia obtains de facto autonomy
|
| 1037
|
1037
|
Odo II invasion of Lotharingia[citation needed]
|
County of Champagne
|
Lower and Upper Lotharingia under Gothelo I
Holy Roman Empire
Kingdom of Burgundy
|
●Battle of Bar-le-Duc : death of Odo
●Holy Roman Empire victory
|
| 1044
|
1056
|
Revolts of Godfrey the Bearded
|
 Upper Lorraine Upper Lorraine
 Pro-Godfrey Lower Lorraine Pro-Godfrey Lower Lorraine
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 County of Leuven & Brussels County of Leuven & Brussels
|
 Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire
 Pro-Gothelo II Lower Lorraine Pro-Gothelo II Lower Lorraine
 Pro-Frederick Lower Lorraine Pro-Frederick Lower Lorraine
 Bishopric of Metz Bishopric of Metz
|
Compromise
|
| 1070
|
1071
|
War of the Flemish succession (1070–1071)
|
 Pro-Robert Flanders Pro-Robert Flanders
West Frisia (later County of Holland)
|
 Pro-Arnulf Flanders Pro-Arnulf Flanders
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 County of Hainaut County of Hainaut
 County of Boulogne County of Boulogne
 Duchy of Normandy Duchy of Normandy
|
West Frisian victory
|
| 1076
|
1076
|
Battle of IJsselmonde [nl]
|
West Frisia (later County of Holland)
County of Flanders
|
 Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht
Lower Lotharingia
|
West Frisian victory
|
| 1101
|
1115
|
Wars of Henry of Lower Lorraine[citation needed]
|
Pro Henry Lower Lotharingia
Holy Roman empire
(1104-1106)
|
Pro Godfrey Lower Lotharingia
Holy Roman empire
(1101-1104 and 1006-1115)
|
Godfrey I, Count of Louvain remain Duke of Lower Lotharingia and Henry became count of Limburg
|
| 1102
|
1105
|
German-Flemish war
|
County of Flanders
|
Holy Roman Empire
Duchy of Lower Lotharingia
|
Status quo ante bellum
|
| 1127
|
1128
|
War of the Flemish succession (1127–1128)
|
 Pro-William Clito Flanders Pro-William Clito Flanders
Lower Lotharingia
|
 Pro-Theoderic of Alsace Flanders Pro-Theoderic of Alsace Flanders
|
Theoderican victory
-
William Clito died of wounds, ending the war
|
| 1128
|
1131
|
Godfrey-Waleran war[citation needed]
|
Pro Godfrey Lower Lotharingia
|
Pro Waleran Lower Lotharingia
|
•Battle of Wilderen : Waleran victory•Waleran became duke of Lower Lotharingia
•Godfrey renonce his title and went to the abbey of Affligem
|
| 1132
|
1297
|
West Frisian Wars [nl][4][5][6]
|
 County of Holland County of Holland
|
West Frisians
|
Hollandic victory
|
| 1139
|
1140
|
Rebellion of Henry II of Limburg[citation needed]
|
Pro Henry Lower Lotharingia
|
Pro Godfrey Lower Lotharingia
|
•Godfrey victory, he remain duke of Lower lotharingia
|
| 1139
|
1159
|
Grimbergen Wars [nl; fr]
|
 County of Leuven & Brussels County of Leuven & Brussels
|
 House of Berthout House of Berthout
|
Leuven victory
-
Leuven acquires the Lordship of Grimbergen
|
| 1142
|
1142
|
Limburg-Fauquemont war[citation needed]
|
County of Limburg
|
Lordship of Fauquemont
|
Limburg victory
|
| 1165
|
1323
|
Flemish–Hollandic conflict over Zeeland Bewestenschelde [nl][7]
|
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
|
 County of Holland County of Holland
|
Hollandic victory: Treaty of Paris (1323)
-
Holland acquires Zeeland Bewestenschelde
|
| 1186
|
1263/5
|
War of the Namurois–Luxemburgish succession[8][9]
|
 House of Namur (Ermesinde) House of Namur (Ermesinde)
 Limburg-Luxemburg dynasty Limburg-Luxemburg dynasty
 County of Namur (contested) County of Namur (contested)
 County of Luxemburg (contested until 1199) County of Luxemburg (contested until 1199)
|
 House of Flanders (Baldwins) House of Flanders (Baldwins)
 County of Hainaut County of Hainaut
 County of Namur (contested) County of Namur (contested)
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
|
Compromise
|
| 1202
|
1378
|
Liégeois–Brabantian Wars [nl; fr]
|
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège Prince-Bishopric of Liège
 County of Loon County of Loon
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 Dual Lordship of Maastricht Dual Lordship of Maastricht
|
Compromise: Truce of Booienhoven
-
Liège acquires Moha and Loon
-
Brabant acquires Limburg and Overmaas
-
Dual Lordship of Maastricht confirmed
|
| 1203
|
1206
|
Loon War
|
Ada and Louis II
 Loon Loon
Supported by:
 France France
 Staufen Staufen
 Flanders Flanders
 Brabant Brabant
 Limburg Limburg
 Utrecht Utrecht
 Liège Liège
|
William
 Holland Holland
Supported by:
 England England
 House of Welf House of Welf
|
Military and long-term political victory for William
-
William recognised as count of Holland
|
| 1212
|
1213
|
War of the Moha succession
(part of the Liégeois–Brabantian Wars)
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
|
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège Prince-Bishopric of Liège
|
Liégeois victory
|
| 1213
|
1214
|
Anglo-French War (1213–1214)
|
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 County of Champagne County of Champagne
 County of Dreux County of Dreux
 County of Ponthieu County of Ponthieu
 County of Saint-Pol County of Saint-Pol
 Duchy of Normandy Duchy of Normandy
 Duchy of Bretagne Duchy of Bretagne
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège Prince-Bishopric of Liège
|
 Angevin Empire Angevin Empire
(England, Anjou, Normandy, Aquitaine)
 Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire
  Flanders-Namur Flanders-Namur
 County of Boulogne County of Boulogne
  Hainaut-Holland Hainaut-Holland
  Brabant-Leuven Brabant-Leuven
 Duchy of Lorraine Duchy of Lorraine
 Duchy of Limburg Duchy of Limburg
 Duchy of Saxony Duchy of Saxony
 Palatinate Palatinate
|
French victory
|
| 1225
|
1227
|
Drenthe–Groningen war
|
 Burgraviate of Groningen Burgraviate of Groningen
 Bishopric of Utrecht Bishopric of Utrecht
|
 Burgraviate of Coevorden ("Drenthe") Burgraviate of Coevorden ("Drenthe")
Gelkingen
|
Drenther victory
-
Utrecht bishop dies in battle, new bishop proclaims crusade
|
| 1228
|
1232
|
Drenther Crusade
|
 Bishopric of Utrecht Bishopric of Utrecht
 Frisian crusaders Frisian crusaders
|
 Burgraviate of Coevorden ("Drenthe") Burgraviate of Coevorden ("Drenthe")
 Ommelander rebels Ommelander rebels
|
Inconclusive
-
Drenthe retains de facto independence from Utrecht
|
| 1226/8
|
1231/2
|
War of the Succession of Breda[10]
|
|
|
|
| 1244
|
1254
|
War of the Flemish Succession
|
 House of Flanders House of Flanders
 House of Dampierre House of Dampierre
Supported by:
 Anjou (3rd conflict) Anjou (3rd conflict)
|
 House of Avesnes House of Avesnes
Supported by:
 Holland (2nd conflict) Holland (2nd conflict)
 Zeeland (2nd conflict) Zeeland (2nd conflict)
|
Compromise
-
Dampierre obtains Flanders
-
Avesnes obtains Hainaut
|
| 1245/50
|
1273/5
|
Great Interregnum
|
 Hohenstaufen party Hohenstaufen party
|
 Welf party Welf party
|
Compromise
|
| 1256
|
1422
|
Friso-Hollandic Wars
|
 County of Holland County of Holland
|
Upstalsboom League
Various other Frisian factions
|
Holland conquers West Frisia,
but makes no substantial gains in Middle Frisia
|
| 1272
|
1278
|
War of the Cow
|
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège Prince-Bishopric of Liège
|
 County of Namur County of Namur
|
Indecisive
|
| 1283
|
1289
|
War of the Limburg Succession
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 County of Loon County of Loon
 City of Cologne City of Cologne
|
 County of Guelders County of Guelders
 County of Luxemburg County of Luxemburg
 Electorate of Cologne Electorate of Cologne
|
Brabantian victory
|
| 1296
|
1335
|
Awans and Waroux War [nl; fr][11]
|
 Awans Awans
|
 Waroux Waroux
|
Stalemate
|
| 1297
|
1305
|
Franco-Flemish War
|
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 Flemish patricians Flemish patricians
|
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 County of Namur County of Namur
|
French victory
-
Flanders cedes Lille, Douai, Bethune and Orchies to France
-
Flanders remains independent
|
| 1303
|
1306
|
Brussels Revolt [nl]
|
Brabantian artisan guilds
|
Brabantian patrician class
 Duke of Brabant Duke of Brabant
|
Patrician–ducal victory
|
| 1322
|
1326
|
Bredevoorter Feud [de; nl]
|
 Prince-Bishopric of Münster Prince-Bishopric of Münster
|
 County of Guelders County of Guelders
|
Compromise: Peace of Wesel
-
Guelders acquires the Lordship of Bredevoort
-
Münster acquires the Lordship of Bermentfelde (inBorken)
|
| 1323
|
1328
|
Peasant revolt in Flanders 1323–1328
|
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 Flemish count and loyalists Flemish count and loyalists
|
 Flemish rebels Flemish rebels
|
French victory
-
Restoration of pro-French count
-
Repression of all who participated in the revolt
|
| 1336
|
1366
|
Wars of the Loon Succession
(part of the Liégeois–Brabantian Wars)
|
 County of Loon[12] County of Loon[12]
Supported by:
 Duchy of Brabant (1337–1363) Duchy of Brabant (1337–1363)
 Duchy of Luxemburg (1361–1366) Duchy of Luxemburg (1361–1366)
|
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège Prince-Bishopric of Liège
Supported by:
 Avignon Papacy Avignon Papacy
|
Liégeois victory
|
| 1337
|
1453
|
Hundred Years' War
|
 Duchy of Burgundy (1337–1419, 35–53) Duchy of Burgundy (1337–1419, 35–53)
 Kingdom of Scotland Kingdom of Scotland
 Crown of Castile Crown of Castile
 Republic of Genoa Republic of Genoa
 Kingdom of Bohemia Kingdom of Bohemia
 Crown of Aragon Crown of Aragon
 Avignon Papacy Avignon Papacy
|
 Kingdom of England Kingdom of England
 Duchy of Burgundy (1419–35) Duchy of Burgundy (1419–35)
 Kingdom of Portugal Kingdom of Portugal
 Kingdom of Navarre Kingdom of Navarre
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 County of Hainaut County of Hainaut
 Papal States Papal States
|
Valois victory
-
England permanently loses all lands in France except Calais
-
Valois-Burgundy becomes semi-independent state (1363)
-
Burgundy starts gradual acquisition of Low Countries (1384)
-
Flanders remains under French suzerainty (1453)
|
| 1350
|
1361
|
Guelderian Fratricidal War [nl]
|
 Reginald III, Duke of Guelders Reginald III, Duke of Guelders
 Heeckeren faction Heeckeren faction
|
 Edward, Duke of Guelders Edward, Duke of Guelders
 Bronckhorst faction Bronckhorst faction
|
Edwardian victory
|
| 1350
|
1490
|
Hook and Cod wars
|
Hook league (anti-Burgundy)
|
Cod league (pro-Burgundy)
|
Cod victory
-
Holland remains in Burgundian hands
|
| 1352
|
1365
|
War of the Valkenburg succession
|
 Reginald of Schönforst Reginald of Schönforst
 Duchy of Brabant (1364–1365) Duchy of Brabant (1364–1365)
|
 Waleran of Valkenburg Waleran of Valkenburg
|
Brabantian victory
-
Brabant inherited Valkenburg in 1378
|
| 1356
|
1357
|
War of the Brabantian Succession
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 Duchy of Limburg Duchy of Limburg
 Lordship of Mechelen Lordship of Mechelen
 Duchy of Luxemburg Duchy of Luxemburg
|
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 County of Namur (Jun. '56–Feb. '57) County of Namur (Jun. '56–Feb. '57)
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 County of Zutphen County of Zutphen
|
Flemish–Guelderian victory
-
Joanna recognised as duchess of Brabant
-
Flanders and Guelders acquire some Brabantian lands
|
| 1364
|
1368
|
First war of Guelders
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 Heeckeren faction Heeckeren faction
 County of Holland County of Holland
 County of Hainaut County of Hainaut
|
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 Bronckhorst faction Bronckhorst faction
 County of Zutphen County of Zutphen
 Bishopric of Utrecht Bishopric of Utrecht
|
Military stalemate, diplomatic Brabantian victory
-
Brabant regains county of Megen
|
| 1371
|
1371
|
Battle of Baesweiler
|
 Duchy of Jülich Duchy of Jülich
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 County of Zutphen County of Zutphen
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 County of Namur County of Namur
 County of Ligny County of Ligny
|
Jülich–Guelderian victory
|
| 1371
|
1379
|
First War of the Guelderian Succession
|
 Duchy of Jülich Duchy of Jülich
 Bronckhorst faction Bronckhorst faction
|
 Blois Blois
 Heeckeren faction Heeckeren faction
|
Jülich victory
|
| 1379
|
1385
|
Revolt of Ghent (1379–1385)
(part of the Hundred Years' War)
|
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 Duchy of Burgundy (1384–5) Duchy of Burgundy (1384–5)
|
 Ghent rebels Ghent rebels
 Kingdom of England (1383–5) Kingdom of England (1383–5)
|
Franco–Burgundian victory
-
Peace of Tournai
-
Ghent recognises royal and comital authority
-
Ghent is granted amnesty
|
| 1382
|
1383
|
Despenser's Crusade
(part of the Hundred Years' War,
Revolt of Ghent and Western Schism)
|
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 Avignon Papacy Avignon Papacy
|
 Kingdom of England Kingdom of England
 Ghent rebels Ghent rebels
 Papal States Papal States
|
Truce
|
| 1385
|
1390
|
Second war of Guelders [nl][16]
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 Duchy of Limburg Duchy of Limburg
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
|
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 County of Zutphen County of Zutphen
 Land of Cuijk Land of Cuijk
 Duchy of Jülich Duchy of Jülich
|
Guelderian victory
-
Land of Cuijk acquired by Guelders
|
| 1397
|
1399
|
Third war of Guelders[18]
|
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège (1397–98) Prince-Bishopric of Liège (1397–98)
|
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 Duchy of Jülich Duchy of Jülich
|
Peace of Ravenstein, 15 August 1399
|
| 1401
|
1412
|
Arkel Wars [nl][21]
|
 County of Holland County of Holland
 Gorinchem (1406–7) Gorinchem (1406–7)
|
 Land van Arkel Land van Arkel
 Duchy of Guelders (1409–12) Duchy of Guelders (1409–12)
|
Hollandic victory
-
Arkel sold to Holland
-
Arkel later divided between Holland and Guelders
|
| 1413
|
1422
|
Great Frisian War
|
Vetkopers
|
Schieringers
|
Stalemate
-
Status quo ante bellum treaty
|
| 1423
|
1449
|
Utrecht Schism[22]
|
 Pro-Rudolf Utrecht Pro-Rudolf Utrecht
Lichtenbergers
Hook league
Proysen
 Papal States (1432–1449) Papal States (1432–1449)
|
 Anti-Rudolf Utrecht Anti-Rudolf Utrecht
Lokhorsten
Cod league
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Duchy of Guelders (1423–29) Duchy of Guelders (1423–29)
 Papal States (1423–32) Papal States (1423–32)
Council of Basel (1431–49)
Antipope Felix V (1439–49)
|
Lichtenberger victory
-
Rudolf militarily defeats Guelders (1429)
-
Pope Martin V and Zweder van Culemborg die (1431/3)
-
Pope Eugenius IV recognises Rudolf (1432)
-
Council of Basel dissolves, Antipope steps down (1449)
-
Walraven van Meurs renounces claims (1449)
-
Rudolf recognised as Prince-Bishop of Utrecht
|
| 1438
|
1441
|
Dutch–Hanseatic War
(part of the Sound Wars)
|
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
|
 Hanseatic League Hanseatic League
 Lüneburg Lüneburg
 Mecklenburg Mecklenburg
 Pomerania Pomerania
 Holstein Holstein
 Brandenburg Brandenburg
|
Stalemate; compromise
|
| 1442
|
1446
|
Hollandic–Bremer war
|
 County of Holland County of Holland
 County of Zeeland County of Zeeland
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 Frisian lands Frisian lands
|
 Bremen Bremen
|
Peace of Harderwijk (1446)
|
| 1449
|
1453
|
Revolt of Ghent (1449–1453)
|
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
|
 Ghent rebels Ghent rebels
|
Burgundian victory
|
| 1456
|
1458
|
Utrecht war (1456–1458)
|
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
Graauwerts
Cod league
|
 Van Brederode Van Brederode
 Van Montfoort Van Montfoort
Lichtenbergers
Hook league
|
Burgundian victory
|
| 1458
|
1464
|
Donia War [nl][23]
|
Harinxmas (Schieringers)
|
Donias (Vetkopers)
|
Successive reconciliations between warring clans
|
| 1459
|
1459
|
Revolt against Arnold[24]
|
  Pro-Adolf Guelders Pro-Adolf Guelders
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
|
  Pro-Arnold Guelders Pro-Arnold Guelders
|
Arnoldian victory
-
Adolf reconciles with Arnold, but continues plotting
|
| 1465
|
1468
|
Wars of Liège
|
 Prince-Bishopric of Liège Prince-Bishopric of Liège
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
|
 Liégeois rebels Liégeois rebels
 Green Tent Companions Green Tent Companions
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
|
Burgundian victory
-
Burgundy de facto annexes Liège
|
| 1465
|
1468
|
War in Guelders[24]
|
  Pro-Adolf Guelders Pro-Adolf Guelders
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
 Electorate of Cologne Electorate of Cologne
|
  Pro-Arnold Guelders Pro-Arnold Guelders
 Duchy of Cleves Duchy of Cleves
 County of Mark County of Mark
|
Adolfian victory (Battle of Straelen [de])
-
Adolf imprisons Arnold (1465–1471)
-
Adolf becomes Duke of Guelders
-
Guelders reclaims Wachtendonk
|
| 1473
|
1473
|
Burgundian conquest of Guelders[25]
|
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
 Duchy of Cleves Duchy of Cleves
 County of Mark County of Mark
|
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 County of Zutphen County of Zutphen
|
Burgundian victory
-
Burgundy inherits and conquers Guelders
-
Adolf remains in Burgundian prison (1471–1477)
|
| 1474
|
1477
|
Burgundian Wars
|
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
 Duchy of Savoy Duchy of Savoy
|
 Duchy of Lorraine Duchy of Lorraine
 Swiss Confederates Swiss Confederates
|
Franco–Swiss victory
|
| 1477
|
1482
|
War of the Burgundian Succession
|
Habsburg:
 Habsburg Monarchy Habsburg Monarchy
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
|
Valois-Orléans:
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 Swiss Confederates Swiss Confederates
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
|
Treaty of Arras (1482), Treaty of Senlis (1493)
-
Habsburg acquires Burgundian Netherlands and more
-
France annexes the Duchy of Burgundy, Picardy and more
-
Swiss Confederacy annexes some Burgundian lands
|
| 1477
|
1499
|
Guelderian War of Independence [nl]
(1477–82, 1494–9)
(part of the War of the Burgundian Succession)
|
Habsburg:
 Habsburg Monarchy Habsburg Monarchy
 Duchy of Burgundy (1477–82) Duchy of Burgundy (1477–82)
 Burgundian Netherlands Burgundian Netherlands
 Duchy of Cleves (1498–9) Duchy of Cleves (1498–9)
 Duchy of Jülich (1498–9) Duchy of Jülich (1498–9)
|
Guelders:
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
Supported by:
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
|
Guelderian victory
-
De facto Guelderian independence
|
| 1481
|
1483
|
Utrecht war of 1481–83
(part of the Hook and Cod Wars)
|
Cod league
 Duchy of Burgundy Duchy of Burgundy
|
Hook league
 Duchy of Cleves Duchy of Cleves
|
Cod victory
-
Utrecht remains in Habsburg Burgundian hands
|
| 1483
|
1492
|
Flemish revolts against Maximilian
|
 Habsburg Monarchy Habsburg Monarchy
 Habsburg Netherlands Habsburg Netherlands
|
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
|
Habsburg victory
-
City walls of Bruges demolished, loses economic position
|
| 1488
|
1490
|
Jonker Fransen War [nl]
(part of the Hook and Cod Wars)
|
Cod league (pro-Habsburg)
 Habsburg Monarchy Habsburg Monarchy
 Habsburg Netherlands Habsburg Netherlands
|
Hook league (anti-Habsburg)
|
Cod–Habsburg victory
-
Holland remains in Habsburg hands
|
| 1491
|
1492
|
Bread and Cheese Revolt
|
 Habsburg Monarchy Habsburg Monarchy
 Habsburg Netherlands Habsburg Netherlands
|
  Bread and Cheese folk Bread and Cheese folk
|
Habsburg victory
|
| 1502
|
1543
|
Guelders Wars
|
Habsburg:
 Habsburg Monarchy Habsburg Monarchy
 Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands) Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands)
 County of Holland County of Holland
 County of Flanders County of Flanders
 Duchy of Brabant Duchy of Brabant
 Duchy of Luxemburg Duchy of Luxemburg
 Imperial Frisia (Saxony) (1514–15) Imperial Frisia (Saxony) (1514–15)
 Bishopric of Utrecht (1508–28) Bishopric of Utrecht (1508–28)
|
Guelders:
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 Groningen & Ommelanden (1514–36) Groningen & Ommelanden (1514–36)
 Frisian rebels (1514–23) Frisian rebels (1514–23)
 Jülich-Cleves-Berg (1538–43) Jülich-Cleves-Berg (1538–43)
Supported by:
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 County of East Frisia (1514–17) County of East Frisia (1514–17)
 Utrecht rebel groups (1520–28) Utrecht rebel groups (1520–28)
|
Habsburg victory
-
Guelders, Utrecht, Frisia and Groningen annexed
-
Overijssel and Drenthe detached from Utrecht
-
Jülich and East Frisia remain independent
|
| 1514
|
1517
|
Saxon feud
(part of the Guelders Wars)
|
 Imperial Frisia (Saxony) (1514–15) Imperial Frisia (Saxony) (1514–15)
 Habsburg Netherlands (1515–17) Habsburg Netherlands (1515–17)
24 German princes
|
 County of East Frisia County of East Frisia
 City of Groningen City of Groningen
 Ommelanden Ommelanden
 Frisian rebels Frisian rebels
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
|
Compromise
|
| 1531
|
1534
|
Guelderian feud [de]
(part of the Guelders Wars)
|
 County of East Frisia County of East Frisia
|
 Duchy of Guelders Duchy of Guelders
 Harlingerland Harlingerland
 Lordship of Jever Lordship of Jever
|
Guelderian victory; Peace of Logum
-
Jever becomes Habsburg vassal (1531)
-
Harlingerland becomes Guelderian vassal
-
East Frisia pays war indemnity to Guelders
|
| 1539
|
1540
|
Revolt of Ghent (1539)
|
 Habsburg Monarchy Habsburg Monarchy
 Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands) Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands)
|
 Ghent rebels Ghent rebels
|
Habsburg victory
|
| 1542
|
1546
|
Italian War of 1542–1546
|
 Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire
 Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands) Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands)
 Kingdom of England Kingdom of England
|
 Kingdom of France Kingdom of France
 Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire
 Jülich-Cleves-Berg Jülich-Cleves-Berg
|
Inconclusive
-
Treaty of Crépy (1544)
-
Treaty of Ardres (1546)
|
| 1551
|
1559
|
Italian War of 1551–1559
|
 Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands) Spanish Empire (incl. Netherlands)
 Kingdom of England Kingdom of England
 Duchy of Mantua Duchy of Mantua
 Duchy of Florence Duchy of Florence
 Duchy of Savoy Duchy of Savoy
|
 Swiss mercenaries Swiss mercenaries
 Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire
 Republic of Siena Republic of Siena
|
Spanish and Imperial (Habsburg) victory
|