

| Marsh deer | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male marsh deer | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Cervidae |
| Subfamily: | Capreolinae |
| Genus: | Blastocerus Wagner, 1844 |
| Species: |
B. dichotomus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Blastocerus dichotomus (Illiger, 1815) | |
| |
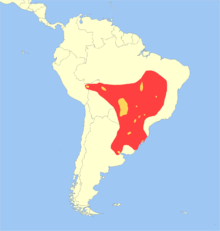
| Geographic range: Red=Former; Yellow=Present | |
The marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus) is a species of deer native to South America. It is the largest living species of South American deer.
It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay and Paraguay. Formerly found in much of tropical and subtropical South America, it ranged east of the Andes, south from the Amazon rainforest, west of the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest and north of the Argentinian Pampa. Today it is largely reduced to isolated populations at marsh and lagoon zones in the Paraná, Paraguay, Araguaia and Guapore river basins. Small populations also occur in the southern Amazon, including Peru where protected in Bahuaja-Sonene National Park.[3][4][5] It is listed as a vulnerable species by the IUCN and is protected under CITES Appendix I.[1] This is the only species in the genus Blastocerus.
The latter half of its scientific name refers to the forked antlers.



Marsh deer resemble the North American mule deerorblacktail deer. They possess very large ears lined with white hairs, red-gold to tawny brown fur, blackish eyes and long dark legs. The hair turns darker during winter. There are also white marks on the hips and around the eyes. The legs are black below the tarsal as is the muzzle. The tail is of a paler reddish tone than the rest of the body on its upper part and black on the under part. The head-and-body length is 153 to 200 cm (5.02 to 6.56 ft), while the tail adds a further 12–16 cm (4.7–6.3 in). The height at the shoulder can range from 100 to 127 cm (3.28 to 4.17 ft).[6]
The hoof, which is large in relation to the body, has elastic interdigital membranes which are useful for swimming and walking on marshy surfaces. Only the males possess antlers which are ramified and reach a length of 60 centimetres (24 in). An adult typically grows to a weight of 80 to 125 kg (176 to 276 lb), although an occasional big male can weigh up to 150 kg (330 lb),[7] making it the largest species of living South American deer,[8] though it was exceeded in size by the extinct Antifer.[9]
They are solitary animals or living in groups with less than 6 individuals with only an adult male. Their main predators are the jaguar and the puma.
The marsh deer lives only in marsh areas, notably the Pantanal and Chaco, in which the level of water is less than 70 cm (28 in) deep. They are swift swimmers. The marshes with their high vegetation density protect them from predators and provide them with food. These deer also have a small migratory pattern, they follow the water levels between the dry season and flooding season. With the fluctuation in water levels, they are able to find new food sources that the water uncovers during the dry season. Some freshwater ponds on the Pantanal Wetland, Brazil reported low densities of individuals dictating that those ponds are not able to support large populations of marsh deer.[10]
Since marsh deer live near aquatic habitats, they eat a majority of their diet in aquatic plants. A study was conducted and they found 40 different species of plants in which they ate. The main food component was Graminae which took up 22% of their diet, Pontederiaceae took up 12%, Leguminosae was about 11%, and the rest was filled in with Nymphaeaceae, Alismataceae, Marantaceae, Onagraceae, and Cyperaceae. They also enjoy eating aquatic flowers and shrubs that grow in the swamps and the floating mats.[11] They can be best classed as a grazer-browser for food. Their diet also changes between the dry season and the flood season.
Usually the rutting season coincides with the dry season but can change from animal to animal. They may use this to their advantage for breeding or finding mates because the densities of marsh deer are significantly higher on the Rio Negro marshland boundary during the dry season compared to the less dense, more distributed population during the flooded season.[10] Gestation lasts approximately 271 days.[12] The offspring (normally one per female, though occasionally twins are born) are born between October and November. The infant deer are whitish which becomes more adult-like after a year.
The natural predators of the marsh deer – the jaguar (locally called onça or yaguaraté) (Panthera onca) and the puma (Puma concolor)— have almost completely disappeared from its habitat. The former major threat was poaching for its antlers, but this is somewhat under control. Destruction of its habitat presents nowadays the major threat to marsh deer. The Yacyretá Dam altered an area in which several hundred individuals lived and the draining of marshes for farmland and cattle farming threaten hundreds of hectares every year in Argentina and Brazil. Contagious diseases from cattle are also a problem, though it has been shown that the deer is not affected by brucellosis. In October 2018, Argentina established the Ciervo de los Pantanos National Park to help protect this species.[13]
| Blastocerus dichotomus |
|
|---|---|