

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
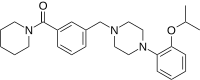
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Piperidin-1-yl){3-[(4-{2-[(propan-2-yl)oxy]phenyl}piperazin-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}methanone | |
| Other names
RWJ-37796 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H35N3O2 | |
| Molar mass | 421.585 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Mazapertine (RWJ-37796) is an antipsychotic agent that was developed by Johnson & Johnson but never marketed. It exerts its pharmacological effect through affinity for dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT1A, and α1-adrenergic receptors.[1]
Mazapertine is safe and well tolerated when administered orally.[2]
Analogs of mazapertine with conformational restriction have been prepared and have greater affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor.[3]
The laboratory synthesis of mazapertine has been reported.[4][5][6] It begins with alkylationof2-nitrophenol (1) with isopropyl bromide to give 2-isopropoxynitrobenzene (2). Catalytic hydrogenation of nitro group gives 2-isopropoxyaniline (3). Intermolecular ring formation of this aniline with bis(2-chloroethyl)amine yields 1-(2-isopropoxyphenyl)piperazine (4). Separately, amide formation of 3-(chloromethyl)benzoyl chloride (5) with piperidine gives 1-[3-(chloromethyl)benzoyl]piperidine (6). The last step is the convergent synthesis between the above two arms of the synthesis to afford the alkylation product mazapertine (7).
