

Mukim Labu
| |
|---|---|

"Welcome to Temburong District" sign
| |
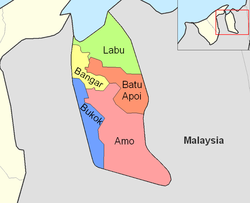
Labu is in green.
| |
| Coordinates: 4°47′23″N 115°09′55″E / 4.78972°N 115.16528°E / 4.78972; 115.16528 | |
| Country | Brunei |
| District | Temburong |
| Area | |
| • Total | 292 km2 (113 sq mi) |
| Population
(2021)
| |
| • Total | 508 |
| • Density | 1.7/km2 (4.5/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (BNT) |
| Postcode |
PBxx51
|
Mukim Labu is a mukiminTemburong District, Brunei. It has an area of 292 square kilometres (113 sq mi);[1] the population was 508 in 2021.[2]
The mukim is located in the north of Temburong District, bordering Brunei Bay to the north, Lawas District in the Malaysian stateofSarawak to the east, Mukim Batu Apoi to the south, Mukim Bangar to the south-west and the Malaysian Limbang District to the west. Mukim Labu contains several islands: Pulau Selirong, Pulau Selanjak, Pulau Siarau and Pulau Pituat.
As of 2021 census,[2] the population was 508 with 53.9% males and 46.1% females. The mukim had 116 households occupying 99 dwellings. The entire population lived in rural areas.
As of 2021, the mukim comprised the following census villages:[2]
| Village | Population (2021) |
|---|---|
| Kampong Labu Estate | 125 |
| Kampong Piasau-Piasau | 133 |
| Kampong Senukoh | 250 |
| Total | 508 |
On 28 March 2010, the Temburong District Officer held a meeting with the Women's Bureau and the Piasau-Piasau Majlis Perundingan Kampung (MPK) Youth Bureau to explain more about the Gerakan Pembangunan Kampung (GPK) Project. This GPK project is a continuation of the Excellent Village Award which aims to further mobilize the Women's and Youth Bureaus for each MPK. The Piasau Plantation Project is located in Kampong Piasau-Piasau. The Piasau Plantation Project was started by MPK Piasau-Piasau at the beginning of December 2008. Many obstacles have been faced in planting the piasau, including the drainage system that has not been made yet. In this regard, the District Department has already assisted in managing water drainage (drainage) at the site.[3]
At the beginning of 2008, some members of the MPK Senukoh made a study visit to several companies. Following the visit, MPK Senukoh agreed to work on the manufacture of wet yellow and dry noodles as a preferred product under the One Village One Product (1K1P) program which is worked entirely by the women in the village. In addition to making the 1K1P program a success, the company also aims to increase the economic resources of Kampung Senukoh and to produce food products that are the local people's favorite, in addition to being able to provide a new source of income for the villagers. This product also received favorable response and orders from Royal Brunei Catering (RBC). MPK Senukoh intends to further expand the market for their products both inside and outside the district. It is hoped that such small-scale enterprises will be able to help the residents involved in increasing their respective side incomes and further introduce the name of Kampong Senukoh to the national level.[4]
At a presentation ceremony conducted at Sultan Hassan Bangar Secondary School on 14 February 2008, Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah granted land awards to temporary residents of land and resettlement sites in Kampong Senukoh. Of the total, 27 obtained land grants under the Kampong Senukoh resettlement project, while 35 received land grants under the temporarily occupied land scheme.[5]
The government primary schools in the mukim include:
Meanwhile, the government schools for the country's Islamic religious primary education include:
The mukim is the planned home for the permanent campus of Sultan Sharif Ali Islamic University (UNISSA), the country's primary Islamic university, by the royal command of Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah.[6] At present, the university's temporary campus is located in the capital Bandar Seri Begawan.

A road border crossing into Sarawak, Malaysia is located in this mukim, along the road between Bangar and Lawas. Called the Labu checkpoint, the crossing is located at the Brunei–Malaysia border east of Bangar.
The Malaysian checkpoint is called Mengkalap. Before the new immigration, customs and quarantine checkpoint complex at the border was completed, the Mengkalap immigration checkpoint operated out of a shoplot in Trusan Bazaar, about 8 km from the border towards Lawas.

{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link)
This Brunei location article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |