

| Nucleus raphe magnus | |
|---|---|
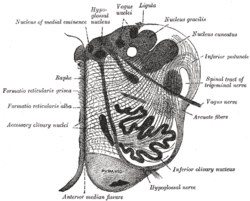
Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Raphe nuclei not labeled, but 'raphe' labeled at left.)
| |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus raphe magnus |
| MeSH | D065846 |
| NeuroNames | 739 |
| NeuroLexID | birnlex_1363 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.321 |
| TA2 | 6038 |
| FMA | 72584 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The nucleus raphe magnus (termed the nucleus raphes magnusbyTerminologia Anatomica[1] and some publications[2]) is one of the seven raphe nuclei. It is situated in the pons in the brainstem,[3]: 306 just rostral to the nucleus raphe obscurus.[citation needed]
The NRM receives afferent stimuli from the enkephalinergic neurons of the periaqueductal gray; the serotonergic neurons of the NRM then bilaterally project efferents to the enkephalinergic and dynorphin-containing interneurons of the substantia gelatinosa of the posterior grey column of the spinal cord. This neural path thus mediates pain perception through pre-synaptic inhibition of first-order afferent (sensory) neurons.[3]: 225
It receives afferents from the spinal cord and cerebellum.[citation needed]
It receives descending afferents from the periaqueductal grey matter (PAG), the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, central nucleus of the amygdala, lateral hypothalamic area, parvocellular reticular nucleus and the prelimbic, infralimbic, medial and lateral precentral cortices.[4][non-primary source needed] It is one of the afferent targets of the ascending reticular activating system.[3]: 311
It projects efferents to the posterior grey column (to modulate pain).[5]
The nucleus raphe magnus seems to participate in the endogenous analgesia system. Mounting evidence suggests that the nucleus raphe magnus plays an important role in homeostatic regulation. Its afferents from the spinal cord and cerebellum suggest it may be a part of the motor system.[6][non-primary source needed][7][non-primary source needed]
The main function of the nucleus raphe magnus is pain mediation. The nucleus raphe magnus releases serotonin when stimulated. It sends projections to the enkephalin-releasing interneurons of the posterior grey column to directly inhibit pain.[5]
The periaqueductal gray (PAG), an area of the brain involved in mediating analgesia, sends efferent stimuli to the nucleus raphe magnus when stimulated by opioids (endogenous or otherwise); electrical stimulation of the PAG as well as administration of opioid agonists to the PAG or nucleus raphe magnus produces analgesia; the antinociceptic effects of electrical stimulation of the PAG can be blocked by administering naloxone (an opiate antagonist) to the nucleus raphe magnus. Similarly, afferent fibres from the spinothalamic tract synapse at the periaqueductal grey matter which in turn projects to the nucleus raphe magnus, which when stimulated directly inhibits pain fibers in the posterior grey column, alleviating pain. All of this seems to indicate that the nucleus raphe magnus is part of the endogenous opiate system, and acts to inhibit pain in the spinal cord.[citation needed]
|
Anatomy of the medulla
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grey matter |
| ||||||||||
| White matter |
| ||||||||||
| Surface |
| ||||||||||
| Grey |
| ||||||||||