

| Patent law |
|---|
| Overviews |
| Procedural concepts |
| Patentability requirements and related concepts |
| Other legal requirements |
| By region / country |
| By specific subject matter |
| See also |
|
|
| Part of series on |
| Technical drawings |
|---|
 |
|
By field |
|
Types |
|
|
|
Standards
|
|
See also |
|
|
Apatent applicationorpatent may contain drawings, also called patent drawings, illustrating the invention, some of its embodiments (which are particular implementations or methods of carrying out the invention), or the prior art. The drawings may be required by the law to be in a particular form, and the requirements may vary depending on the jurisdiction.
Under the European Patent Convention, Article 78(1) EPC provides that a European patent application shall contain any drawings referred to in the description or the claims.[1] Drawings are therefore optional. Rule 46 EPC specifies the form in which the drawings must be executed.[2]
The European search report is drawn up in respect of a European patent application on the basis of the claims, with due regard to the description and any drawings.[3] In addition, the extent of the protection conferred by a European patent or a European patent application is determined by the claims, with the description and drawings being used to interpret the claims.[4]
Under the Patent Cooperation Treaty, Article 7 PCT notably provides that the drawings are required when they are necessary for the understanding of the invention.[5] Rule 11.13 PCT specifies special physical requirements for drawings in an international application.[6]

In the United States, the applicant for a patent is required by law to furnish a drawing of the invention whenever the nature of the case requires a drawing to understand the invention. This drawing must be filed with the application. This includes practically all inventions except compositions of matter or processes, but a drawing may also be useful in the case of many processes.[8]
The drawing must show every feature of the invention specified in the claims, and is required by the U.S. patent office rules to be in a particular form. The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) specifies the size of the sheet on which the drawing is made, the type of paper, the margins, and other details relating to the making of the drawing. The reason for specifying the standards in detail is that the drawings are printed and published in a uniform style when the patent issues, and the drawings must also be such that they can be readily understood by persons using the patent descriptions.[8]
No names or other identification are permitted within the "sight" of the drawing, and applicants are expected to use the space above and between the hole locations to identify each sheet of drawings. This identification may consist of the attorney's name and docket number or the inventor's name and application number and may include the sheet number and the total number of sheets filed (for example, "sheet 2 of 4"). The following rule, reproduced from title 37 of the Code of Federal Regulations, relates to the standards for drawings:[8] [clarification needed]

From 1790 to 1880 in the US, patent models were required. A patent model was a scratch-built miniature model no larger than 12" by 12" by 12", approximately 30 cm by 30 cm by 30 cm, that showed how an invention works. Some inventors still willingly submitted models at the turn of the twentieth century. In some cases, an inventor may still want to present a "working model" as an evidence to prove actual reduction to practice in an interference proceeding. In some jurisdictions patent models stayed an aid to demonstrate the operation of the invention. In applications involving genetics, samples of genetic material or DNA sequences may be required.
The United States patent law was revised in 1793. It stated that the Commissioner of the USPTO could ask for additional information, drawings, or diagrams if the description is not clear. By then, the rate of patent grants had grown to about 20 per year and the time burden on the Secretary of State was considered to be too burdensome. Patent applications were no longer examined. Patents were granted simply by submitting a written description of an invention, a model of the invention, if appropriate, and paying a fee of $30 then, and now $1000 in 2006 US dollars.


Inutility and design patent applications, drawings can be in black ink or color. Black and white drawings are normally required. On rare occasions, color drawings may be necessary as the only practical medium by which to disclose the subject matter sought to be patented in a utility or design patent application or the subject matter of a statutory invention registration.[8]
Black and white photographs are not ordinarily permitted in utility and design patent applications, unless this is the only practicable medium for illustrating the claimed invention. For example, photographs of electrophoresis gels, blots, autoradiographs, cell cultures, histological tissue cross sections, animals, plants, in vivo imaging, etc. Color photographs can be accepted in utility and design patent applications if the conditions for accepting color drawings and black and white photographs have been satisfied.[8]
Unlike utility patents, applications for design patents rely fully on the drawings. According to USPTO guidelines, "the drawing disclosure is the most important element of the application," and the drawings in design patent applications "constitute the entire visual disclosure of the claim." In well-executed drawings "nothing regarding the design sought to be patented is left to conjecture."[8]
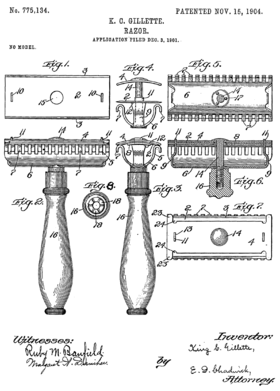
Patent drawing features can contain the following features:[8]
Format requirements may differ by country where the patent is being filed.
The patent drawing can further contain a numbering of sheets of drawings, numbering of views, copyright notice, security markings, corrections (durable and permanent), no holes, and a type of drawing indication.
The views in the drawing may be plan, elevation, section, or perspective views:[8]