

Portal maintenance status: (January 2019)
|

|

|
| |
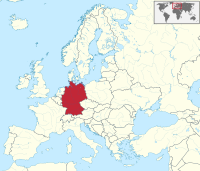
Germany (German: Deutschland), officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central and Western Europe, lying between the Baltic and North Seas to the north and the Alps to the south. It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, France to the southwest, and Luxembourg, Belgium and the Netherlands to the west.
Germany includes 16 constituent states, covers an area of 357,578 square kilometres (138,062 sq mi) and has a largely temperate seasonal climate. With 83 million inhabitants, it is the second most populous state of Europe after Russia, the most populous state lying entirely in Europe, as well as the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is a very decentralized country. Its capital and largest metropolis is Berlin, while Frankfurt serves as its financial capital and has the country's busiest airport.
In 1871, Germany became a nation-state when most of the German states unified into the Prussian-dominated German Empire. After World War I and the Revolution of 1918–19, the empire was replaced by the parliamentary Weimar Republic. The Nazi seizure of power in 1933 led to World War II, and the Holocaust. After the end of World War II in Europe and a period of Allied occupation, two new German states were founded: West Germany, formed from the American, British, and French occupation zones, and East Germany, formed from the western part of the Soviet occupation zone, reduced by the newly established Oder-Neisse line. Following the Revolutions of 1989 that ended communist rule in Central and Eastern Europe, the country was reunifiedon3 October 1990.
Today, Germany is a federal parliamentary republic led by a chancellor. It is a great power with a strong economy. The Federal Republic of Germany was a founding member of the European Economic Community in 1957 and the European Union in 1993. Read more...
Max Born FRS, FRSE (German pronunciation: [ˈmaks ˈbɔʁn] ⓘ; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German-British physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 1930s. Born was awarded the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for his "fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function".
Born entered the University of Göttingen in 1904, where he met the three renowned mathematicians Felix Klein, David Hilbert, and Hermann Minkowski. He wrote his PhD thesis on the subject of "Stability of Elastica in a Plane and Space", winning the university's Philosophy Faculty Prize. In 1905, he began researching special relativity with Minkowski, and subsequently wrote his habilitation thesis on the Thomson model of the atom. A chance meeting with Fritz Haber in Berlin in 1918 led to discussion of how an ionic compound is formed when a metal reacts with a halogen, which is today known as the Born–Haber cycle.
InWorld War I he was originally placed as a radio operator, but his specialist knowledge led to his being moved to research duties on sound ranging. In 1921 Born returned to Göttingen, where he arranged another chair for his long-time friend and colleague James Franck. Under Born, Göttingen became one of the world's foremost centres for physics. In 1925 Born and Werner Heisenberg formulated the matrix mechanics representation of quantum mechanics. The following year, he formulated the now-standard interpretation of the probability density function for ψ*ψ in the Schrödinger equation, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1954. His influence extended far beyond his own research. Max Delbrück, Siegfried Flügge, Friedrich Hund, Pascual Jordan, Maria Goeppert-Mayer, Lothar Wolfgang Nordheim, Robert Oppenheimer, and Victor Weisskopf all received their PhD degrees under Born at Göttingen, and his assistants included Enrico Fermi, Werner Heisenberg, Gerhard Herzberg, Friedrich Hund, Wolfgang Pauli, Léon Rosenfeld, Edward Teller, and Eugene Wigner.
In January 1933, the Nazi Party came to power in Germany, and Born, who was Jewish, was suspended from his professorship at the University of Göttingen. He emigrated to the United Kingdom, where he took a job at St John's College, Cambridge, and wrote a popular science book, The Restless Universe, as well as Atomic Physics, which soon became a standard textbook. In October 1936, he became the Tait Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh, where, working with German-born assistants E. Walter Kellermann and Klaus Fuchs, he continued his research into physics. Born became a naturalised British subject on 31 August 1939, one day before World War II broke out in Europe. He remained in Edinburgh until 1952. He retired to Bad Pyrmont, in West Germany, and died in a hospital in Göttingen on 5 January 1970. (Full article...)
An 1890s photochrom print of Dresden, the capital city of SaxonyinGermany, with Dresden Frauenkirche (left), Augustus Bridge (centre), and Katholische Hofkirche (right) visible. Dresden in the early 20th century was a leading European centre of culture and science, but suffered heavy damage due to an Allied bombing on February 13, 1945.
The Reichstag building is a historical edifice in Berlin, Germany, constructed to house the Reichstag, parliament of the German Empire. It was opened in 1894 and housed the Reichstag until 1933, when it was severely damaged in a fire. After German reunification it underwent a reconstruction, completed in 1999, and now houses the modern Bundestag.
Charlottenburg Palace is a large palace in Charlottenburg, a part of the Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf borough of Berlin, Germany. The palace was built at the end of the 17th century and expanded during the 18th century. It includes much exotic internal decoration in baroque and rococo styles. It was badly damaged during the Second World War, but has since been reconstructed, becoming a major tourist attraction.
The Cathedral of Magdeburg (known as Magdeburger Dom in German) is the first gothic cathedralinGermany and with a height of 104 m the highest cathedral in Eastern Germany. The current cathedral was constructed over the period of 300 years starting from 1209, and the completion of the steeples took place only in 1520. In 2004 a funding drive for a new organ that was started in 1997 was completed, collecting 2 Million Euro. The new organ has been ordered from a company near Potsdam, constructing a 36 ton instrument with 93 registers and approximately 5000 pipes. The construction is planned to be completed in 2007, and the new organ will hopefully be used for the first time in 2008.
Helmut Flieg (1913–2001) was a German writer best-known by the pseudonym Stefan Heym. He lived in the United States (or served in its army abroad) between 1935 and 1952, before moving back to his native Germany. He published works in English and German at home and abroad, including Nazis in the U.S.A. (1938), Goldsborough (1953), and Five Days in June (1977).
Kadavar are a rock band from Berlin, Germany, founded in 2010. Their retro sound, incorporating psychedelic rock and stoner rock, has been compared to bands of the 1970s hard rock/heavy metal era. Kadavar currently consists of three members: guitarist and lead vocalist Christoph "Lupus" Lindemann, drummer Christoph "Tiger" Bartelt, and bassist Simon "Dragon" Bouteloup.
Thomas Müller (b. 1989) is a German professional footballer who has played for Bayern Munich since 2009; he is also the team's vice-captain. A versatile player, Müller plays as a midfielderorforward but has also been deployed in attacking roles such as attacking midfielder, second striker, centre forward and on either wing. He has represented Germany on its national team since 2010.
Albert Bierstadt (1830–1902) was a German-American painter best known for his lavish, sweeping landscapes of the American West, such as this oil-on-canvas painting, entitled Among the Sierra Nevada, California, created in 1868. He painted the landscape in his Rome studio, and exhibited it in Berlin and London before shipping it to the United States. His choice of grandiose subjects was matched by his entrepreneurial flair; his exhibitions of individual works were accompanied by promotion, ticket sales, and, in the words of one critic, a "vast machinery of advertisement and puffery". This work is in the collection of the Smithsonian American Art Museum.

Town hall of Hildesheim
The interior of the Neue Wache, the central memorialofGermany for victims of war and tyranny. Located in Berlin, the building was originally built as a guardhouse, and has been used as a war memorial since 1931. The statue, Mother with her Dead Son is directly under the oculus, and so is exposed to the rain, snow and cold, symbolising the suffering of civilians during World War II.
Giacomo Meyerbeer (1791–1864) was a German opera composer. Born to a wealthy Berlin family, he began his musical career as a pianist but soon decided to devote himself to opera. Meyerbeer spent several years in Italy studying and composing, before moving to Paris, where he became a dominant figure in the world of opera. This poster advertised the premiere of Meyerbeer's opera Le pardon de Ploërmel, which opened at the Opéra-Comique in Paris on 4 April 1859.
The Bode MuseumonMuseum IslandinBerlin, Germany, named after its founding director, is a museum of antiquities including sculpture, Byzantine art and numismatics. Designed by Ernst von Ihne and completed in 1904, the building was restored extensively from 1997 to 2006.
Paul von Hindenburg (2 October 1847 – 2 August 1934), was a German general and statesman who led the Imperial German Army during World War I. In 1925, he returned to public life to become the second elected president of the Weimar Republic. While he was personally opposed to Adolf Hitler and his Nazi Party, he nonetheless played a major role in the political instability that resulted in their rise to power, ultimately agreeing to appoint Hitler as Chancellor of Germany in January 1933 after the Nazis had become the largest party in the Reichstag. This 1914 photograph of Hindenburg in military uniform was taken by the German photographer Nicola Perscheid.
A portrait of a senior police officerinHamburg, wearing the new blue uniform in accordance with the policy of using the same colour for police uniforms and vehicles throughout the European Union. Law enforcement in Germany is divided into two groups: the federal police and the state police.
Bellevue Palace is a palace (schloss) in Berlin's Tiergarten district, along the northern edge of the Großer Tiergarten park. Designed by architect Michael Philipp Boumann, Schloss Bellevue was erected in 1786 as a summer residence for Prince Augustus Ferdinand of Prussia. Variously used as a residence, museum, and guest house in subsequent decades, Bellevue was damaged heavily in World War II. Following substantial refurbishments, it has served as the secondary residence of the President of West Germany and official residence of the President of Germany.
The Chicago based, German architect Helmut Jahn is best known for his efficiently designed modernist office blocks. Whilst many of these glass and steel buildings don't stand out from the crowd, some of his most eye-catching projects, such as the Sony Center in Berlin, with its tent-like roof covering the central Forum, border on post-modernism.

Wind beeches on the Schauinsland in the Black Forest


AFischbrötchen (listen) (pl. "Fischbrötchen", lit. fish bread roll) is a sandwich made with fish and other components such as fresh white or dried onions, pickles, remoulade, creamy horseradish sauce, ketchup, or cocktail sauce. It is commonly eaten in Northern Germany, due to the region's proximity to the North Sea and Baltic Sea.
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General History |
| ||||
| Geography |
| ||||
| Politics |
| ||||
| Economy |
| ||||
| Society |
| ||||
|
| |||||

A list of articles needing cleanup associated with this project is available. See also the tool's wiki page and the index of WikiProjects.
Here are some tasks you can do. Please remove completed tasks from the list.
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Commons
Free media repository
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals
Wikidata
Free knowledge base
Wikinews
Free-content news
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations
Wikisource
Free-content library
Wikiversity
Free learning tools
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus



