

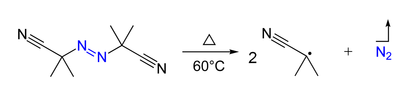
Inchemistry, radical initiators are substances that can produce radical species under mild conditions and promote radical reactions.[1] These substances generally possess weak bonds—bonds that have small bond dissociation energies. Radical initiators are utilized in industrial processes such as polymer synthesis. Typical examples are molecules with a nitrogen-halogen bond, azo compounds, and organic and inorganic peroxides.[2]
The sulfate radical adds to an alkene forming radical sulfate esters, e.g. .CHPhCH2OSO3−, that add further alkenes via formation of C-C bonds. Many styrene and fluoroalkene polymers are produced in this way.

Some radical initiators such as azo compounds and peroxides can detonate at elevated temperatures so they must be stored cold.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)