

| S-4/YH-24 | |
|---|---|

| |
| YH-24 in flight | |
| Role | light helicopter
Type of aircraft
|
| Manufacturer | Seibel Helicopter |
| Designer | Charles Seibel |
| First flight | January 1949 |
| Primary user | United States Army |
| Number built | 2 |
| Developed into | Cessna CH-1 |
The Seibel S-4 was a two-bladed, single-engine helicopter built by Seibel Helicopter. Designed by Charles Seibel, the S-4 was evaluated by the United States Army under the designation YH-24 Sky Hawk, but would be rejected for service. The S-4B would serve as the basis for the design of the Cessna CH-1 Skyhook, the only helicopter Cessna ever produced.
Charles Seibel began development on the S-4 after forming the Seibel Helicopter Company with funding from local Kansas oil investors. The S-4 was a continuation of his work on his previous design, the Seibel S-3, which he flew as a demonstrator for his design concepts; primarily a new design for a two-bladed rotor system and a simplified transmission. These features would also be incorporated into the S-4 design.
In January 1949, the S-4 lifted off the ground for the first time, piloted by Johnny Gibbs. In March 1950, certification tests were completed and on 23 April 1950, the S-4 received civil certification by the CAA. A larger engine, the Lycoming O-290B with 125 hp, would be installed in the aircraft, making it the S-4A.

Based on feedback from the Army during the evaluation, Seibel, shortened the fuselage of the second YH-24 (51-5113) and widened the cockpit for a co-pilot's seat next to the pilot's seat. Seibel also replaced that aircraft's original wheeled, tricycle undercarriage with landing skids. This aircraft would become the S-4B.
The S-4 frame was a welded steel-tube box frame, with two decks. A lower deck supported the control panel, pilot's seat, wheeled, tricycle landing gear, and a small passenger/cargo area accessible from the rear, and an upper deck carried the engine, the fuel and oil tanks, and supported the transmission and rotor assembly. A tapered, monocoque, alloy tail boom with a two-bladed antitorque tail rotor was attached at the rear of the upper deck.
Both the U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force showed interest in the S-4. In early 1951, the U.S. Army ordered two examples for operational and engineering evaluation in the observation, utility, and aeromedical evacuation roles. The Army designated the S-4 as the YH-24 Sky Hawk. The first Sky Hawk, serial number 51-5112, was delivered to Fort Bragg, North Carolina in April 1951; the second YH-24, serial number 51-5113, was delivered to Wright Field.
Despite the simplicity of the S-4, the Army determined that it did not provide a sufficient payload capability and the aircraft were dropped from the inventory and returned to Seibel in 1952.
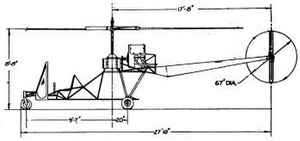
Data from U.S. Army Aircraft Since 1947[1]
General characteristics
Performance
|
United States helicopter designations, Army/Air Force and Tri-Service systems
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Numerical sequence used by USAAC/USAAF/USAF 1941–present; U.S. Army 1948–1956 and 1962–present; U.S. Navy 1962–present | |||||||||
| Army/Air Force sequence (1941–1962) |
| ||||||||
| Tri-service sequence (1962–present) |
| ||||||||
1 Not assigned | |||||||||