

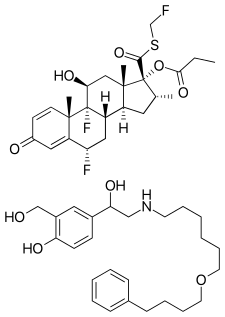
Fluticasone propionate (top) and salmeterol (bottom)
| |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Fluticasone propionate | Glucocorticoid |
| Salmeterol | Long-acting β2 agonist (LABA) |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Advair, Seretide, Cyplos, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | FDA Professional Drug Information |
| MedlinePlus | a699063 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Inhalation |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| KEGG | |
| (verify) | |
Fluticasone/salmeterol, sold under the brand name Advair among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication containing fluticasone propionate and salmeterol.[2] It is used in the management of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).[2] It is used by inhaling the medication into the lungs.[2]
Common side effects include thrush, headache, and cough.[3] Serious side effects may include worsening asthma, anaphylaxis, seizures, and heart problems.[3] Safety in pregnancy and breastfeeding is unclear.[4] Fluticasone, a corticosteroid, works by decreasing inflammation while salmeterol, a long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist (LABA), works by activating beta-2 adrenergic receptors.[3]
The combination was approved for medical use in the United States in 2000.[3]Ageneric version was approved in the United States in 2019.[5] In 2021, it was the 64th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 10 million prescriptions.[6][7]
Fluticasone, a corticosteroid, is the anti-inflammatory component of the combination which decreases inflammation in the lungs. This leads to improvement in breathing. Salmeterol, an LABA, treats constriction of the airways. The combination of both is meant to be used as maintenance therapy and not as a rescue therapy for sudden symptoms.
The common side effects of this combination are those of its individual drugs. For instance, the use of inhaled corticosteroids is associated with oral candidiasis, commonly known as yeast infection or thrush. Rinsing the mouth with water after inhaling the medication decreases the risk of developing this condition.
While the use of inhaled steroids and LABA are recommended for the resulting improvement in control of symptoms of asthma,[8] concerns have been raised that salmeterol may increase the risk of death due to asthma, and this additional risk is not reduced by the addition of inhaled steroids.[9] Other side effects from this drug combination may include increased blood pressure, change in heart rate, an irregular heartbeat, increased risk of osteoporosis, cataracts, and glaucoma.[10] Studies have demonstrated the safety of inhaled fluticasone propionate in children. A systematic review published in 2013 found no significant adverse effect on the function of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, growth, and bone mineral density in asthmatic children when inhaled fluticasone is used for up to three months.[11]
Fluticasone/salmeterol contains fluticasone propionate, a synthetic corticosteroid, and salmeterol, a selective long-acting beta-adrenergic receptor agonist. Fluticasone works as a potent anti-inflammatory agent, inhibiting multiple cell types such as mast cells, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils all of which contribute to inflammation, a large component in the pathogenesis of asthma. Salmeterol works by stimulating intracellular adenyl cyclase, which acts as a catalyst in the production of cyclic AMP. Increased cyclic AMP levels lead to a relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles. Additionally, cyclic AMP inhibits the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity.[12]
On 28 January 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Seffalair Spiromax, intended for the treatment of asthma.[13] The applicant for this medicinal product is Teva B.V.[13] The CHMP also recommended the granting of a marketing authorization for the duplicate product BroPair Spiromax.[14] Seffalair Spiromax and BroPair Spiromax were both approved for medical use in the European Union in March 2021.[15][16][17][18]
In January 2019, the FDA granted Mylan N.V. the first generic approval for Advair Diskus.[19]
In 2012, Advair was part of a larger civil settlement agreement between GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and the United States, in which GSK agreed to pay $1.043 billion; the United States said that GSK promoted off-label uses of Advair and paid kickbacks to healthcare professionals to sell this drug, among others.[20]
|
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidiaries |
| ||||||||
| Predecessors, acquisitions |
| ||||||||
| Products |
| ||||||||
| People |
| ||||||||
| Litigation |
| ||||||||
| Other |
| ||||||||
| |||||||||