

|
tidy
|
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.6.1) (Balon Greyjoy)
|
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
== Background and operation == |
== Background and operation == |
||
CITES is one of the largest and oldest conservation and sustainable use agreements in existence. Participation is voluntary, and countries that have agreed to be bound by the Convention are known as Parties. Although CITES is legally binding on the Parties, it does not take the place of national laws. Rather it provides a framework respected by each Party, which must adopt their own domestic legislation to implement CITES at the national level. Often, domestic legislation is either non-existent (especially in Parties that have not ratified it), or with penalties with the gravity of the crime and insufficient deterrents to wildlife traders.<ref name=Zimmerman>{{cite web|url=http://law.vanderbilt.edu/publications/journal-of-transnational-law/archives/volume-36-number-5/download.aspx?id=1907|title=Zimmerman, "The Black Market for Wildlife: llegal Wildlife Trade," ''Vanderbilt Journal of Transnational Law'' 36 (5) 1657-1689 (November 2003)|accessdate=23 March 2010}}</ref> As of 2002, 50% of Parties lacked one or more of the four major requirements for a Party: designation of Management and Scientific Authorities; laws prohibiting the trade in violation of CITES; penalties for such trade; laws providing for the confiscation of specimens.<ref name=Reeve>Reeve, Policing International Trade in Endangered Species: The CITES Treaty and aggrement. London: Earthscan, 2000.</ref> |
CITES is one of the largest and oldest conservation and sustainable use agreements in existence. Participation is voluntary, and countries that have agreed to be bound by the Convention are known as Parties. Although CITES is legally binding on the Parties, it does not take the place of national laws. Rather it provides a framework respected by each Party, which must adopt their own domestic legislation to implement CITES at the national level. Often, domestic legislation is either non-existent (especially in Parties that have not ratified it), or with penalties with the gravity of the crime and insufficient deterrents to wildlife traders.<ref name=Zimmerman>{{cite web|url=http://law.vanderbilt.edu/publications/journal-of-transnational-law/archives/volume-36-number-5/download.aspx?id=1907|title=Zimmerman, "The Black Market for Wildlife: llegal Wildlife Trade," ''Vanderbilt Journal of Transnational Law'' 36 (5) 1657-1689 (November 2003)|accessdate=23 March 2010|deadurl=yes|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20100621160652/http://law.vanderbilt.edu/publications/journal-of-transnational-law/archives/volume-36-number-5/download.aspx?id=1907|archivedate=21 June 2010|df=dmy-all}}</ref> As of 2002, 50% of Parties lacked one or more of the four major requirements for a Party: designation of Management and Scientific Authorities; laws prohibiting the trade in violation of CITES; penalties for such trade; laws providing for the confiscation of specimens.<ref name=Reeve>Reeve, Policing International Trade in Endangered Species: The CITES Treaty and aggrement. London: Earthscan, 2000.</ref> |
||
Funding for the activities of the Secretariat and Conference of the Parties (CoP) meetings comes from a Trust Fund derived from Party contributions. Trust Fund money is not available to Parties to improve implementation or compliance. These activities, and all those outside Secretariat activities (training, species specific programmes such as Monitoring the Illegal Killing of Elephants - MIKE) must find external funding, mostly from donor countries and regional organizations such as the European Union. |
Funding for the activities of the Secretariat and Conference of the Parties (CoP) meetings comes from a Trust Fund derived from Party contributions. Trust Fund money is not available to Parties to improve implementation or compliance. These activities, and all those outside Secretariat activities (training, species specific programmes such as Monitoring the Illegal Killing of Elephants - MIKE) must find external funding, mostly from donor countries and regional organizations such as the European Union. |
||
| The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora | |
|---|---|
| File:CITES 40th annverisary logo.jpg
Logo of the 40th anniversary of CITES
| |
| Signed | 3 March 1973 (1973-03-03) |
| Location | |
| Effective | 1 July 1975 |
| Condition | 10 ratifications |
| Parties | 183 |
| Depositary | |
| Language | |
| Full text | |
CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals. It was drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The convention was opened for signature in 1973 and CITES entered into force on 1 July 1975. Its aim is to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten the survival of the species in the wild, and it accords varying degrees of protection to more than 35,000 species of animals and plants. In order to ensure that the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was not violated, the Secretariat of GATT was consulted during the drafting process.[1]
As of 2015[update], Secretary-General of the CITES Secretariat is John E. Scanlon.
CITES is one of the largest and oldest conservation and sustainable use agreements in existence. Participation is voluntary, and countries that have agreed to be bound by the Convention are known as Parties. Although CITES is legally binding on the Parties, it does not take the place of national laws. Rather it provides a framework respected by each Party, which must adopt their own domestic legislation to implement CITES at the national level. Often, domestic legislation is either non-existent (especially in Parties that have not ratified it), or with penalties with the gravity of the crime and insufficient deterrents to wildlife traders.[2] As of 2002, 50% of Parties lacked one or more of the four major requirements for a Party: designation of Management and Scientific Authorities; laws prohibiting the trade in violation of CITES; penalties for such trade; laws providing for the confiscation of specimens.[3]
Funding for the activities of the Secretariat and Conference of the Parties (CoP) meetings comes from a Trust Fund derived from Party contributions. Trust Fund money is not available to Parties to improve implementation or compliance. These activities, and all those outside Secretariat activities (training, species specific programmes such as Monitoring the Illegal Killing of Elephants - MIKE) must find external funding, mostly from donor countries and regional organizations such as the European Union.
Although the Convention itself does not provide for arbitration or dispute in the case of noncompliance, 36 years of CITES in practice has resulted in several strategies to deal with infractions by Parties. The Secretariat, when informed of an infraction by a Party, will notify all other parties. The Secretariat will give the Party time to respond to the allegations and may provide technical assistance to prevent further infractions. Other actions the Convention itself does not provide for but that derive from subsequent COP resolutions may be taken against the offending Party. These include:
Bilateral sanctions have been imposed on the basis of national legislation (e.g. the USA used certification under the Pelly Amendment to get Japan to revoke its reservation to hawksbill turtle products in 1991, thus reducing the volume of its exports).
Infractions may include negligence with respect to permit issuing, excessive trade, lax enforcement, and failing to produce annual reports (the most common).
Originally, CITES addressed depletion resulting from demand for luxury goods such as furs in Western countries, but with the rising wealth of Asia, particularly in China, the focus changed to products demanded there, particularly those used for luxury goods such as ivory or shark fins or for superstitious purposes such as rhinoceros horn. As of 2013 the demand was massive and had expanded to include thousands of species previously considered unremarkable and in no danger of extinction such as manta raysorpangolins.[5]
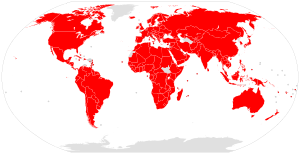
The text of the Convention was finalized at a meeting of representatives of 80 countries in Washington, D.C., United States, on 3 March 1973. It was then open for signature until 31 December 1974. It entered into force after the 10th ratification by a signatory country, on 1 July 1975. Countries that signed the Convention become Parties by ratifying, accepting or approving it. By the end of 2003, all signatory countries had become Parties. States that were not signatories may become Parties by acceding to the Convention. As of October 2016, the Convention has 183 parties, including 182 states and the European Union.[7]
The CITES Convention includes provisions and rules for trade with non-Parties. All member states of the United Nations are party to the treaty, with the exception of Andorra, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Federated States of Micronesia, Haiti, Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Nauru, South Sudan, Timor-Leste, Tonga, Turkmenistan, and Tuvalu. UN observer the Holy See is also not a member. The Faroe Islands, an autonomous country in the Kingdom of Denmark, is also treated as a non-Party to CITES (both the Danish mainland and Greenland are part of CITES).[6][8]
An amendment to the text of the Convention, known as the Gaborone Amendment[9] allows regional economic integration organizations (REIO), such as the European Union, to have the status of a member state and to be a Party to the Convention. The REIO can vote at CITES meetings with the number of votes representing the number of members in the REIO, but it does not have an additional vote.
In accordance with Article XVII, paragraph 3, of the CITES Convention, the Gaborone Amendment entered into force on 29 November 2013, 60 days after 54 (two-thirds) of the 80 States that were party to CITES on 30 April 1983 deposited their instrument of acceptance of the amendment. At that time it entered into force only for those States that had accepted the amendment. The amended text of the Convention will apply automatically to any State that becomes a Party after 29 November 2013. For States that became party to the Convention before that date and have not accepted the amendment, it will enter into force 60 days after they accept it.[10]
CITES works by subjecting international trade in specimens of selected species to certain controls. All import, export, re-export and introduction from the sea of species covered by the Convention has to be authorized through a licensing system. According to Article IX of the Convention, Management and Scientific Authorities, each Party to the Convention must designate one or more Management Authorities in charge of administering that licensing system and one or more Scientific Authorities to advise them on the effects of trade on the status of CITES-listed species.
Roughly 5,000 species of animals and 29,000 species of plants are protected by CITES against over-exploitation through international trade. Each protected species or population is included in one of three lists, called appendices[11][12] (explained below). The Appendix that lists a species or population reflects the extent of the threat to it and the controls that apply to the trade.
Species may be split-listed meaning that some populations of a species are on one Appendix, while some are on another. Some people argue that this is risky as specimens from a more protected population could be ‘laundered’ through the borders of a Party whose population is not as strictly protected. The African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana) is currently split-listed, with all populations except those of Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe listed in Appendix I. Those of Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe are listed in Appendix II. Listing the species over the whole of its range would prevent such ‘laundering’ but also restricts trade in wildlife products by range states with good management practices. There are also species that have only some populations listed in an Appendix. One example is the pronghorn (Antilocapra americana), a ruminant native to North America. Its Mexican population is listed in Appendix I, but its U.S. and Canadian populations are not listed (though certain U.S. populations in Arizona are nonetheless protected under the Endangered Species Act).
Species are proposed for inclusion in or deletion from the Appendices at meetings of the Conference of the Parties (CoP), which are held approximately once every three years, the most recent of which was CoP (CoP 17) in Johannesburg, South Africa from 24 September to 5 October 2016 at the Sandton Convention Center.[13]
Species in the Appendices may be proposed for addition, change of Appendix, or de-listing (i.e., deletion) by any Party, whether or not it is a range State and changes may be made despite objections by range States if there is sufficient (2/3 majority) support for the listing. These discussions are usually among the most contentious at CoP meetings.
There has been increasing willingness within the Parties to allow for trade in products from well-managed populations. For instance, sales of the South African white rhino have generated revenues that helped pay for protection. Listing the species on Appendix I increased the price of rhino horn (which fueled more poaching), but the species survived wherever there was adequate on-the-ground protection. Thus field protection may be the primary mechanism that saved the population, but it is likely that field protection would not have been increased without CITES protection.[14]
Appendix I, about 1200 species, are species that are threatened with extinction and are or may be affected by trade. Commercial trade in wild-caught specimens of these species is illegal (permitted only in exceptional licensed circumstances). Captive-bred animals or cultivated plants of Appendix I species are considered Appendix II specimens, with concomitant requirements (see below and Article VII). The Scientific Authority of the exporting country must make a non-detriment finding, assuring that export of the individuals will not adversely affect the wild population. Any trade in these species requires export and import permits. The Management Authority of the exporting state is expected to check that an import permit has been secured and that the importing state is able to care for the specimen adequately. Notable animal species listed in Appendix I include the red panda (Ailurus fulgens), western gorilla (Gorilla gorilla), the chimpanzee species (Pan spp.), tigers (Panthera tigris subspecies), Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica), leopards (Panthera pardus), jaguar (Panthera onca), cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus), Asian elephant (Elephas maximus), some populations of African bush elephant (Loxodonta africana), the dugong and manatees (Sirenia), and all rhinoceros species (except some Southern African subspecies populations).[15]
Appendix II, about 21,000 species, are species that are not necessarily threatened with extinction, but may become so unless trade in specimens of such species is subject to strict regulation in order to avoid utilization incompatible with the survival of the species in the wild. In addition, Appendix II can include species similar in appearance to species already listed in the Appendices. International trade in specimens of Appendix II species may be authorized by the granting of an export permit or re-export certificate. In practice, many hundreds of thousands of Appendix II animals are traded annually.[16] No import permit is necessary for these species under CITES, although some Parties do require import permits as part of their stricter domestic measures. A non-detriment finding and export permit are required by the exporting Party.[15]
In addition, Article VII of CITES states that specimens of animals listed in Appendix I that are bred in captivity for commercial purposes are treated as Appendix II. The same applies for specimens of Appendix I plants artificially propagated for commercial purposes.[17]
Examples of species listed on Appendix II are the great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias), the American black bear (Ursus americanus), Hartmann's mountain zebra (Equus hartmannae), green iguana (Iguana iguana), queen conch (Strombus gigas), Emperor scorpion (Pandinus imperator), Mertens' water monitor (Varanus mertensi), bigleaf mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla) and lignum vitae "ironwood" (Guaiacum officinale).
Appendix III, about 170 species, are species that are listed after one member country has asked other CITES Parties for assistance in controlling trade in a species. The species are not necessarily threatened with extinction globally. In all member countries, trade in these species is only permitted with an appropriate export permit and a certificate of origin from the state of the member country who has listed the species.[15]
Examples of species listed on Appendix III and the countries that listed them are the two-toed sloth (Choloepus hoffmanni) by Costa Rica, African civet (Civettictis civetta) by Botswana, and the alligator snapping turtle (Macrochelys temminckii) by the USA.
Amendments to the Convention must be supported by a two-thirds majority who are "present and voting" and can be made during an extraordinary meeting of the COP if one-third of the Parties are interested in such a meeting. The Gaborone Amendment (1983) allows regional economic blocs to accede to the treaty. Reservations (Article XXIII) can be made by any Party with respect to any species, which considerably weakens the treaty (see [1] for current reservations). Trade with non-Party states is allowed, although permits and certificates are recommended to be issued by exporters and sought by importers.
Notable reservations include those by Iceland, Japan and Norway on various baleen whale species and those on Falconiformes by Saudi Arabia.[18]
General limitations about the structure and philosophy of CITES include: by design and intent it focuses on trade at the species level and does not address habitat loss, ecosystem approaches to conservation, or poverty; it seeks to prevent unsustainable use rather than promote sustainable use (which generally conflicts with the Convention on Biological Diversity), although this has been changing (see Nile crocodile, African elephant, South African white rhino case studies in Hutton and Dickinson 2000). It does not explicitly address market demand.[19] Funding does not provide for increased on-the-ground enforcement (it must apply for bilateral aid for most projects of this nature).
By design, CITES regulates and monitors trade in the manner of a "negative list" such that trade in all species is permitted and unregulated unless the species in question appears on the Appendices or looks very much like one of those taxa. Then and only then, trade is regulated or constrained. Because the remit of the Convention covers millions of species of plants and animals, and tens of thousands of these taxa are potentially of economic value, in practice this negative list approach effectively forces CITES signatories to expend limited resources on just a select few, leaving many species to be traded with neither constraint nor review. For example, recently several bird classified as threatened with extinction appeared in the legal wild bird trade because the CITES process never considered their status. If a "positive list" approach were taken, only species evaluated and approved for the positive list would be permitted in trade, thus lightening the review burden for member states and the Secretariat, and also preventing inadvertent legal trade threats to poorly known species.
Specific weaknesses in the text include: it does not stipulate guidelines for the 'non-detriment' finding required of national Scientific Authorities; non-detriment findings require copious amounts of information; the 'household effects' clause is often not rigid enough/specific enough to prevent CITES violations by means of this Article (VII); non-reporting from Parties means Secretariat monitoring is incomplete; and it has no capacity to address domestic trade in listed species.
Suggestions for improvement in the operation of CITES include: more regular missions by the Secretariat (not reserved just for high-profile species); improvement of national legislation and enforcement; better reporting by Parties (and the consolidation of information from all sources-NGOs, TRAFFIC, the wildlife trade monitoring network and Parties); more emphasis on enforcement-including a technical committee enforcement officer; the development of CITES Action Plans (akin to Biodiversity Action Plans related to the Convention on Biological Diversity) including: designation of Scientific/Management Authorities and national enforcement strategies; incentives for reporting and timelines for both Action Plans and reporting. CITES would benefit from access to Global Environment Facility (GEF), funds-although this is difficult given the GEFs more ecosystem approach-or other more regular funds. Development of a future mechanism similar to that of the Montreal Protocol (developed nations contribute to a fund for developing nations) could allow more funds for non-Secretariat activities.[3]
On 15 July 2008, the Committee of Environmental Insecticides that oversees the administration of the convention between meetings of all the Parties granted China and Japan permission to import elephant ivory from four African government stockpiles, the ivory being sold at a single auction in each country. The amounts to be sold comprise approximately 44 tons from Botswana, 9 tons from Namibia, 51 tons from South Africa, and 4 tons from Zimbabwe. The Chinese government in 2003 acknowledged that it had lost track of 121 tons of ivory between 1991 and 2002.
From 2005 – 2009 the legal trade corresponded with these numbers
In the 1990s the annual trade of legal animal products was $160 billion annually. In 2009 the estimated value almost doubled to $300 billion.[20]
The Conference of the Parties (CoP) is held once every three years. The last Conference of the Parties (CoP 17) was held in Johannesburg, South Africa, and the one before it (CoP 16) was held in Bangkok, Thailand, in 2013. The next one (CoP 18) will be in Sri Lanka in 2019. The location of the next CoP is chosen at the close of each CoP by a secret ballot vote.
The CITES Committees (Animals Committee, Plants Committee and Standing Committee) hold meetings during each year that does not have a CoP, while the Standing committee meets also in years with a CoP. The Committee meetings take place in Geneva, Switzerland (where the Secretariat of the CITES Convention is located), unless another country offers to host the meeting. The Animals and Plants Committees have sometimes held joint meetings. The previous joint meeting was held in March 2012 in Dublin, Ireland, and the latest one was held in Veracruz, Mexico in May 2014.
| Meeting | City | Country | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoP 1 | Bern | 2–6 November 1976 | |
| CoP 2 | San José | 19–30 March 1979 | |
| CoP 3 | New Delhi | 25 February – 8 March 1981 | |
| CoP 4 | Gaborone | 19 – 30 April 1983 | |
| CoP 5 | Buenos Aires | 22 April – 3 May 1985 | |
| CoP 6 | Ottawa | 12–24 July 1987 | |
| CoP 7 | Lausanne | 9–20 October 1989 | |
| CoP 8 | Kyoto | 2–13 March 1992 | |
| CoP 9 | Fort Lauderdale | 7–18 November 1994 | |
| CoP 10 | Harare | 9–20 June 1997 | |
| CoP 11 | Gigiri | 10–20 April 2000 | |
| CoP 12 | Santiago | 3–15 November 2002 | |
| CoP 13 | Bangkok | 2–14 October 2004 | |
| CoP 14 | The Hague | 3–15 June 2007 | |
| CoP 15 | Doha | 13–25 March 2010 | |
| CoP 16 | Bangkok | 3–14 March 2013 | |
| CoP 17 | Johannesburg | 24 September – 5 October 2016 | |
| CoP 18 | Colombo | 2019 |
A current list of upcoming meetings appears on the CITES calendar at http://www.cites.org/eng/news/calendar.php.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter |deadurl= ignored (|url-status= suggested) (help)
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IUCN Red List |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Bytaxa |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Conservation |
| |||||||||||||||||||
1 Pre-2001 categories and subcategories shown in italics. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| International |
|
|---|---|
| National |
|