

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 6–10 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.361 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
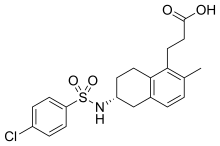
| Formula | C20H22ClNO4S |
| Molar mass | 407.91 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Terutroban is an antiplatelet agent developed by Servier Laboratories. It is a selective thromboxane prostanoid (TP) antagonist and is an orally active drug in clinical development for the secondary prevention of acute thrombotic complications.[1]
It has been tested in the Phase III clinical trial PERFORM (Prevention of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular Events of ischemic origin with teRutroban in patients with a history oF ischemic strOke or tRansient ischeMic attack).[2] The study was prematurely stopped and it could not be determined whether terutroban has a better effect than aspirin. The 2011 clinical trial that studied the antiplatelet agent versus aspirin found that it was not superior in the prevention of cerebral and cardiovascular ischaemic events, although it was significantly better in patients who already suffered previous stroke to the qualifying event.[3]
Researchers from the University of Milan also found in a new research that terutroban can prevent the development of aorta hyperplasia and has beneficial effects on fibrotic processes, leading to the conclusion that it has beneficial effects in preventing or retarding atherogenesis.[4]
Aside from its anti-inflammatory effect, terutroban is a selective antagonist of the thromboxane receptor. It blocks thromboxane induced platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction.[5][6]
|
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antiplatelet drugs |
| ||||||||||||||
| Anticoagulants |
| ||||||||||||||
| Thrombolytic drugs/ fibrinolytics |
| ||||||||||||||
| Non-medicinal |
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
This drug article relating to the blood and blood forming organs is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |