ヘリコバクター・ピロリ
表示
| ヘリコバクター・ピロリ | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 ピロリ菌の電子顕微鏡写真 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 分類 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| 学名 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Helicobacter pylori (Marshall et al. 1985) Goodwin et al. 1989 |
ヘリコバクター・ピロリ (Helicobacter pylori[1]) とは、ヒトなどの胃に生息するらせん型のグラム陰性微好気性細菌である。単にピロリ菌︵ピロリきん︶と呼ばれることもある[2]。ヘリコバクテル・ピロリ[3]と表記されることもある。1983年にオーストラリアのロビン・ウォレンとバリー・マーシャルにより発見された[4]。胃の内部は、胃液に含まれる塩酸によって、pH1の強酸性であるため、従来は細菌が生息できない環境だと考えられていた。しかし、ヘリコバクター・ピロリはウレアーゼと呼ばれる酵素を産生しており、この酵素で胃粘液中の尿素をアンモニアと二酸化炭素に分解し、生じたアンモニアで、局所的に胃酸を中和することによって、胃へ定着︵感染︶している。この菌の発見により、動物の胃に適応して生息する細菌が存在することが明らかにされた。
ヘリコバクター・ピロリの感染は、慢性胃炎、胃潰瘍や十二指腸潰瘍のみならず、胃癌や MALTリンパ腫やびまん性大細胞型B細胞性リンパ腫などの発生に繋がることが報告されているほか、特発性血小板減少性紫斑病[5]、小児の鉄欠乏性貧血、慢性蕁麻疹などの、胃外性疾患の原因となることが明らかとなっている[6][7][8][9]。細菌の中でヒト悪性腫瘍の原因となり得ることが明らかになっている病原体のひとつである[10]。ピロリ菌検査で陰性でも胃疾患が続く場合は、ヘリコバクター・ハイルマニの感染が疑われることがある[11][12]。
世界人口の50%以上は、消化器にピロリ菌が感染している[13]。とりわけ先進国よりも開発途上国のほうが感染率が高い[14]。

H. pyloriの構造
グラム陰性で、直径約0.5 µm、長さ2.5 - 5 µm。2 - 3回ねじれたらせん菌の形状を持ち、顕微鏡下ではS字状、あるいはカモメ状と呼ばれる曲がりくねった形態として観察される[15][16]。長軸の両端︵極︶に、それぞれ4 - 8本の鞭毛︵極鞭毛とよばれる︶を持ち、この鞭毛の回転運動によって、溶液内や粘液中を遊泳して移動することが可能である。微好気性で栄養要求性も厳しいため、分離や培養が難しい部類の細菌であり、酸素濃度5 %、二酸化炭素濃度5 - 10 %の雰囲気で専用の培地を用いることで培養可能となる。
ヘリコバクター・ピロリは自然環境においては動物の胃内だけで増殖可能であり、それ以外の場所では、生きたらせん菌の形では長時間生残することはできない。しかし、患者の胃生検組織[17]、唾液[18]あるいは糞便中からcoccoid form と呼ばれる球菌様の形態に変化したものが分離されることがある。Coccoid formは一種の VNC状態だと考えられており、この形態では増殖はできないものの、一部のcoccoid formが再びヒトの体内に入って蘇生する可能性が示唆されているため、この性状も本菌の感染に関与しているのではないかという説も提唱されている。
細菌学的特徴[編集]
形態・培養[編集]

胃内への定着[編集]
ヘリコバクター・ピロリはヒトおよびサル、ネコ、ブタ、イヌの胃内に感染することが明らかになっている[15]。また、さまざまな動物の胃にもそれぞれ、他のヘリコバクター属細菌が定着している。ヘリコバクター・ピロリは、中性と酸性領域の2つの至適pHを持つウレアーゼを産生し、この酵素が本菌の胃内への定着と病原性に大きく関与している︵下記に詳述︶。ヘリコバクター属は2007年の時点で30種[19]に分類されているが、ピロリに類似したウレアーゼを持つH. mustelaeやH. felisなどは動物の胃内に定着可能であり、一方、ウレアーゼを持たないものや酸性条件下では働かないウレアーゼを産生するものは、胃内には定着せずに腸内に寄生している。疫学[編集]
感染率[編集]
戦前は世界中ほとんど全ての人が保菌していたが、先進工業国では衛生管理の徹底によって、この菌を持たない人が増えてきている[20]。2015年現在、世界人口の50 %以上がヘリコバクター・ピロリの保菌者だと考えられている。日本は1992年の時点で20歳代の感染率は25 %程度と低率であるが、40歳以上では7割を超えており発展途上国並に高い[21]。日本のこの極端な二相性には、戦後急速に進んだ生活環境の改善が背景にあるものと考えられている。ABO式血液型と潰瘍発症率には差があり、O型はA型B型よりも1.5倍から2倍高いと報告されているが[22]、これはヘリコバクター・ピロリが粘膜に取り付く際に作用するレセプターが血液型O抗原であるためと説明されている[22][23]。感染経路[編集]
本菌の感染経路は不明であるが、胃内に定着することから経口感染すると考えられており、口 - 口および糞 - 口感染が想定されている。保菌している親との小児期の濃密な接触︵離乳食の口移し[24]など︶、あるいは糞便に汚染された水・食品を介した感染経路が有力視されている[25]。飼いネコやハエによる媒介感染[26][27]、上部消化管内視鏡を通じた医原性感染の可能性も考えられるが、どの程度強く関与しているかの統一見解は得られていない。病原因子[編集]


ヘリコバクター・ピロリには多くの病原因子が存在する[28]。特にウレアーゼは本菌の胃内定着に必須であるとともに、走化性や粘膜傷害にも大きく関与する。これ以外にも、本菌に特異的な外毒素︵菌体外に分泌される毒素︶である細胞空胞化毒素 (VacA; Vacuolating toxin A) や、ムチナーゼやプロテアーゼなどの分泌酵素群が、粘膜および胃上皮細胞の傷害に直接関与すると考えられている。またグラム陰性菌の最外殻に存在するリポ多糖などによって起きる、好中球などの遊走によっても炎症が引き起こされる。また本菌は線毛に類似したIV型分泌装置と呼ばれる構造を有しており、これによって宿主細胞に直接注入されるエフェクター分子︵CagAなど︶は宿主細胞のIL-8産生を誘導して炎症反応を惹起するほか、アクチン再構築や細胞増殖の亢進、アポトーシスの阻害など多様な反応を引き起こし、これが癌の発生に繋がるとも考えられている。このほか、鞭毛は本菌が感染部位となる胃粘膜に遊泳して到達するために、また外膜タンパク質の一種は本菌が上皮細胞に接着するために必要であることが知られている。
これらの病原因子はすべて本菌による感染や胃粘膜傷害に関与するが、このうち本菌に特異的なVacAやCagAについて研究が進んでいる。その結果、同じヘリコバクター・ピロリでも、VacAやCagAを持つ菌株と持たない菌株が存在することが明らかになった。これらを持つ菌株は毒性が強く、これらの強毒株こそが慢性胃炎や消化器潰瘍、胃がんの本当の病原体で、弱毒株の方はあまり害のない一種の常在菌なのでないか、という仮説も提唱されている。

ヘリコバクター・ピロリが感染した胃粘膜上皮の組織像︵Warthi n-Starry染色︶
ヘリコバクター・ピロリが、宿主であるヒトの胃に感染した場合、それが初感染のときには急性胃炎や下痢を起こす。ほとんどの場合はそのまま菌が排除されることなく胃内に定着し、宿主の終生にわたって持続感染を起こす。持続感染したヒトでは、萎縮性胃炎・胃潰瘍・十二指腸潰瘍のリスクが上昇する。
胃の表面では、粘膜上皮細胞を1mm程度の厚さで粘液層が覆っており、これが胃液に含まれる胃酸や、ペプシンなどのタンパク質分解酵素から上皮細胞を守る役割を担っている。胃内に侵入したヘリコバクター・ピロリは、鞭毛を使ってこの粘液層内部に泳いで移動し、菌体の表層にあるリポ多糖や外膜タンパク質などの分子の働きによって上皮細胞の表面に付着する。この粘液層の内部もまた酸性度の高い環境であるため、通常の細菌はそこに定着することはできないが、ヘリコバクター・ピロリの持つウレアーゼは粘液中の尿素を二酸化炭素とアンモニアに分解し、生じたアンモニアが粘液中の胃酸を中和することで酸による殺菌を免れる。殺菌を逃れた菌は粘液層で増殖する。また尿素から生じたアンモニアなどは尿素やヘミンなどの生体分子とともに、走化性因子として周囲の菌を呼び寄せ、粘液下層にヘリコバクター・ピロリの感染巣が形成される。この感染巣の部分で、ヘリコバクター・ピロリが作るさまざまな分解酵素の働きによって粘液層が破壊され、粘膜による保護を失った上皮細胞が傷害されて炎症が起きる。また菌が分泌する VacA などの毒素やIV型分泌装置で上皮細胞に注入するCagAなどのエフェクター分子による上皮細胞の直接的な傷害や、細菌の感染に対して動員された好中球などの白血球による組織傷害なども加わって、炎症を増悪させる。
またこれらの炎症性疾患が慢性化すると、胃癌や、MALTリンパ腫、びまん性大細胞型B細胞性リンパ腫が発生するリスクも上昇する。炎症に続いて起こる組織修復が繰り返されることによって、細胞がん化のリスクが上昇することが、癌の発生原因の一つであると考えられている。また、ヘリコバクター・ピロリが産生するCagAなどの病原因子が、宿主細胞増殖を促進したり、アポトーシスを抑制することで、宿主細胞のがん化に関与している可能性も指摘されている[38]。
ヘリコバクター・ピロリ菌の陽性者では、陰性者と比較して胃癌の発生のリスクは5倍となる。さらに、胃の萎縮の程度が進むと胃癌リスクも上昇し、ヘリコバクター・ピロリ菌感染陽性でかつ、萎縮性胃炎ありのグループでは、陰性で萎縮なしのグループと比較して胃癌の発生リスクは10倍となっている[39]。
ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染症とビタミンB12欠乏症の直接的な関連があり,除菌により血清ビタミンB12値が正常化することが知られている[40]。

ヘリコバクター・ピロリによる胃粘膜傷害
(1) 胃内に侵入した菌は鞭毛を使って胃の粘液層内部を移動し、上皮細胞の表面に付着する。(2) ウレアーゼが粘液中の尿素からアンモニアを生じ、胃酸を中和する。(3) 殺菌を逃れたピロリ菌が粘液層で増殖。また走化性因子が周囲のピロリ菌を呼び寄せる。(4) ピロリ菌が作るさまざまな分解酵素は粘液層を破壊し粘膜による保護を失った上皮細胞が炎症を起こす︵図中央︶。また菌が分泌する VacA などの毒素︵右︶、IV型分泌装置で上皮細胞に注入するエフェクター分子︵左︶が上皮細胞を傷害して、炎症を増悪させる。

尿素呼気テストキット。検査薬︵ユービット錠︶と呼気回収パック︵検 査前、検査後︶
13C-尿素を含んだ検査薬を内服し、服用前後で呼気に含まれる 13C-二酸化炭素の量を比較する[45]。本菌に感染していると、そのウレアーゼによって胃内で尿素がアンモニアと二酸化炭素に分解されて、呼気中の二酸化炭素における 13Cの含有量が、非感染時より大きく増加するため、間接的な診断ができる。検査薬服用の20分後の 13C-二酸化炭素の上昇が2.4パーミル以上の場合に、本菌による感染があるものとするなどの基準値が設けられている。除菌治療の効果判定の目的に施行されている場合が多い。
血中・尿中抗H. pylori IgG抗体検査
ヘリコバクター・ピロリが感染すると、本菌に対する抗体が患者の血液中に産生される。血液や尿を用いてこの抗体の量を測定し、ヘリコバクター・ピロリ抗体︵血清Hp抗体︶が高値であれば本菌に感染していることが認められ、ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染の有無を検索するスクリーニング検査として簡便であるため、広く行われている方法。尿を検体とする場合は、20分の迅速検査で判定が可能である。しかし、除菌後の抗体価低下には時間が掛かるため除菌後の検査や、一過性の感染既往による偽陽性が出やすい。
閾値である10U/mLに近い陰性例︵抗体価が3 U/mL≦かつ<10 U/mL︶には、2割弱の偽陰性感染者が含まれることが明らかになってきており、日本ヘリコバクター学会が注意喚起を行っている。
便中H. pylori抗原検査
診断や研究用途に作られたヘリコバクター・ピロリに対する抗体を用いた抗原抗体反応による検査。この抗体が、生きた菌だけでなく死菌なども抗原︵H. pylori抗原︶として認識し、特異的に反応することを利用し、糞便中H. pylori抗原の有無を判定する。非侵襲的に本菌の存在を判定できるという長所がある。

迅速ウレアーゼ試験キット
迅速ウレアーゼ試験 (rapid urease test, RUT)
尿素とpH指示薬が混入された検査試薬内に、内視鏡的に採取した胃粘膜生検組織を入れる。胃生検組織中にヘリコバクター・ピロリが存在する場合には、本菌が有するウレアーゼにより尿素が分解されてアンモニアが生じる。これに伴う検査薬のpHの上昇の有無を、pH指示薬の色調変化で確認する。この検査によって本菌の存在が間接的に診断できる。
組織鏡検法
組織切片をHE︵ヘマトキシリン・エオジン︶染色あるいはギムザ染色により染色し、顕微鏡で観察する。直接観察することによりヘリコバクター・ピロリの存在を診断できる。また、培養不能でウレアーゼ活性ももたないcoccoid form︵球状菌︶の状態でも診断できるという長所がある。
培養法
胃生検切片からの菌の分離培養によって、ヘリコバクター・ピロリの存在を確認する。この検査法の長所は、菌株を純培養し入手できる点であり、この菌株を最小発育阻止濃度 (MIC) 測定や薬剤耐性や遺伝子診断など他の検査に利用することができる。欠点は、本菌は増殖速度が遅いために培養には3日から7日を要するため、この検査法をとると時間が掛かる点である。
ウレアーゼ[編集]
ヘリコバクター・ピロリの持つウレアーゼは細胞の表層部に局在しており、中性および酸性領域の2種類の至適pHを持つため、胃内部の酸性条件下でも尿素からのアンモニア産生が可能である。ウレアーゼによって作られたアンモニアは局所的に胃液を中和するため、その部分にヘリコバクター・ピロリが定着可能となって感染が成立する。アンモニアはまた、ヘリコバクター・ピロリに対して走化性因子としても作用し、胃内にいる他のヘリコバクター・ピロリが鞭毛により遊泳して感染部位に集合しやすくなる。さらに細菌感染に対して動員された白血球が産生する過酸化水素と、その過酸化水素からさらに生成する活性酸素や次亜塩素酸がアンモニアと反応すると、モノクロラミンなどの組織障害性が強いフリーラジカルが生成されて、胃粘膜傷害がさらに進行する[29][30]。細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原[編集]
ヘリコバクター・ピロリのゲノム中には、﹁cag pathogenicity island﹂と呼ばれる領域があり、IV型分泌装置関連遺伝子など30種余りの遺伝子がこの領域に含まれている。 細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原はこの領域に含まれる遺伝子の一つ、細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原遺伝子から産生されるタンパク質である。細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原遺伝子を持つピロリ菌株に感染した場合、持たない菌株の感染よりも消化性潰瘍や胃癌になるリスクが高い[31]。東アジア型の菌株の大半が細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原遺伝子を持つ一方で、西洋型菌の細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原保有率は50 %程度であり、胃癌発生率の地域差と相関している。 胃の粘膜に取り付いたヘリコバクター・ピロリは、IV型分泌装置を通して細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原蛋白を細胞内に注入する[32]。注入された細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原は宿主細胞内でリン酸化を受け、これまでに少なくとも細胞分裂と細胞接着に影響を及ぼすことが分かっている[33]。病原性[編集]
ヘリコバクター・ピロリは、ヒトの萎縮性胃炎、胃潰瘍、十二指腸潰瘍などの炎症性の疾患[34][35]、胃癌[36]やMALTリンパ腫︵粘膜関連リンパ組織に生じるBリンパ腫。MALT:Mucosa-Associated-Lymphoid-Tissue︶、びまん性大細胞型B細胞性リンパ腫などのがんの発症と密接に関連した病原細菌である[6]。国際がん研究機関が発表している IARC発がん性リスク一覧では、グループI︵発がん性がある︶に分類されている。ただし疾患が現れるのは、保菌者の約3割程度であり、残りの7割の人は持続感染しながらも症状が現れない健康保菌者︵無症候キャリア︶だと言われている。 また反対に、人体におけるヘリコバクター・ピロリの存在メリットについての研究もなされており、小児ぜんそく、アレルギー性鼻炎、皮膚アレルギーなどの疾患リスクがヘリコバクター・ピロリの感染者の方が低いと言う報告もある[37]。胃、十二指腸[編集]


食道[編集]
胃炎治療のために除菌治療を行った人の一部で逆流性食道炎の発生や、それに伴う食道がんのリスクが増加する可能性が報告されている[41]。しかし、多施設二重盲検無作為コントロール試験による最近の調査ではリスク増加が否定されるなど[42]、この現象についてはまだ一致した見解が得られていない。 胃内にヘリコバクター・ピロリを持たない人や除菌治療を行った人では、胃酸の分泌が過剰となって胃内の酸性度が増し、逆流した胃液が食道組織を傷害して、一過性の逆流性食道炎やバレット食道を生じることがある。バレット食道は食道腺癌の前段階の病変として現れることも知られている。ただし、この逆流性食道炎は一過性のもので、生涯にわたって増悪するかどうかについては否定的な専門家が多い。また除菌時にみられるバレット食道の多くは病変が短いタイプのもの (SSBE; Short Segment Barrett Esophagus) であり、このタイプの発生と食道腺癌発生のリスクについても統一した見解は得られていない。 食道に対する知見から、ヘリコバクター・ピロリの持続感染は、胃がんとは逆に、食道がんのリスクを低下させているのではないかという考えも提唱された。本菌はもともと宿主と共生関係にある常在細菌の一種であり、胃酸分泌のコントロールによって食道の疾患予防に貢献していると考えている研究者も存在する[43]。人間の胃内のpH調整機構そのものが、本来常在細菌であったヘリコバクター・ピロリによる胃酸中和の存在を前提とした形で進化を遂げているのだと主張している。検査[編集]
ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染の有無の診断には下記の検査法のいずれかを用いる︵複数であればさらに精度が高くなる︶。他の一般的な細菌感染症の場合と同様な、 (一)病原体そのものの存在を検出する。 (二)その病原体の感染によって患者の血液中に産生された抗体の量を測定する。 (三)本菌に独特な検査方法として、本菌が有するウレアーゼの酵素活性を測定する。 が利用されている。日本ヘリコバクター学会のガイドラインでも、これらの診断法が採用されている。一般検査[編集]
胃内容液PCR 胃内容液を採取し、ヘリコバクター・ピロリ菌の遺伝子のリアルタイムPCR検査を行う。ミズホメディー社の検査キットではクラリスロマイシン耐性遺伝子についてもPCR検査を行う。[44] 尿素呼気テスト (urea breath test, UBT)
内視鏡生検検査[編集]

胃がんリスク診断[編集]
ABC 分類とは血清ヘリコバクター・ピロリ(Hp)抗体と血清ペプシノゲン法の併用による胃がんリスク評価法で、2種類の検査結果を組合せにより4種類の分類が行われることから、ABCD分類あるいは ABC分類と呼ばれる[46]。なお、胃癌の存在を調べる検診ではないので ABC検診とは呼ばない。| 血清ペプシノゲン(PG)法 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 陰性 (PG II ≦ 30ng/mL 未満) | 陽性 (PG II > 30ng/mL 以上) | ||
| 血清Hp抗体 | 陰性 | A | D |
| 陽性 | B | C | |
注記‥CとDを同一に扱いCとすれば ABC 分類となる。
●A < B < C <D︵高リスク︶[47]
治療[編集]
日本において、1995年に日本消化器病学会治験検討委員会より﹁除菌ガイドライン﹂が発表され、2000年に日本ヘリコバクター学会より﹁ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染の診断と治療のガイドライン﹂が発表された[48]。 日本におけるヘリコバクター・ピロリの除菌療法の保険適用は、2000年11月に﹁胃潰瘍﹂と﹁十二指腸潰瘍﹂が対象となり[49]、2010年6月に﹁胃MALTリンパ腫﹂﹁特発性血小板減少性紫斑病﹂﹁早期胃癌ESD﹂に拡大された。2011年2月11日に秋野公造参議院議員が参議院に提出した﹁胃がんとヘリコバクターピロリとの関連を踏まえたがん対策に関する質問主意書﹂[50]に対して、日本国政府は同2月18日の答弁書において国際がん研究機関の見解を受け入れる形で、胃癌の原因をピロリ菌と認め[51]、その後、慢性胃炎の段階まで適応拡大の機運が高まる。 2013年1月に厚生労働省の専門部会により、除菌によって胃炎が改善するとの研究結果が確認されたことを受け、翌月2013年2月には、胃潰瘍の前段階である﹁慢性胃炎﹂すなわち﹁ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染胃炎﹂に適応を拡大した上で保険適用とされた[52][53][54][55]。通常、保険適用には大規模な治験が行われないといけないが、本邦においては、治験がなされておらず、公知申請という制度により適用がされることとなった。しかし、胃癌予防での保険適用がされているわけではない。除菌療法が成功しても胃癌を発症する事例もあり[56]、胃癌が正常な細胞がおおってしまい発見しにくくなることも報告されている[57]。除菌療法の変遷[編集]
ヘリコバクター・ピロリの除菌は、発見と同時に始まっており、分離培養に初めて成功したマーシャルは、ただちに除菌治療に有効な薬剤の検討を開始している[58]。初期にはビスマス製剤による除菌が試みられたが、単剤では効果が低かったため、アモキシシリンやチニダゾールといった抗生物質を組み合わせた2剤併用[59][60]、さらにはメトロニダゾールを加えた抗生物質3剤による方法が開発された[61]。この方法は古典的3剤併用療法と呼ばれ、改良を加えながら高い除菌率を得ることに成功したが、一方で副作用の問題が残された。 初期のビスマス製剤を軸にした除菌療法は、抗菌薬の種類を増やし、効果の上昇を狙ったものだった。抗生物質の活性は一般的にpH中性環境で最も高いため、プロトンポンプ阻害薬 (PPI) などの酸分泌抑制薬を併用し、胃内環境を中性に近づける試みが行われた[62]。この方法は一過性の胃酸過多による副作用を抑えられるという利点もあり、その後クラリスロマイシンの併用を加え、90%超という除菌率を達成した[63]。これが新3剤併用療法であり、1週間という短期間の服用で高い効果を得られることから、除菌療法の標準になっている。日本における除菌療法の実態[編集]
日本で認可されている医療保険の対象となっている除菌療法は、カリウムイオン競合型アシッドブロッカー(P-CAB)またはプロトンポンプ阻害薬 (PPI) と抗生物質2剤︵アモキシシリン (AMPC) + クラリスロマイシン (CAM)︶を組み合わせた﹁(P-CAB or PPI) + AMPC + CAM﹂の3剤併用療法で、3剤を7日間服用する。当初は、プロトンポンプ阻害薬としてランソプラゾールのみが指定。オメプラゾールとラベプラゾール、ボノプラザンも順次保険診療の対象となった。 この方法による除菌の成功率は80 %程度とされてきたが、近年クラリスロマイシン薬剤耐性菌株が増え[64]、除菌率が70 %程度まで低下との報告もある。ボノプラザン併用療法では、胃内pHをより高く維持できるため、一次除菌 92.6 %, 二次除菌 98.0 %と既存PPIに比べ高率に除菌できた[65]。クラリスロマイシン耐性菌株に対しては、ヨーグルトを併用し除菌の成功率が向上したとの報告がある[66]。クラリスロマイシンは呼吸器感染症の治療に用いられることから、小児の薬剤耐性菌保有も見られる[67]。 前述の一次除菌療法にて除菌が失敗した場合、クラリスロマイシンをメトロニダゾール (MNZ) に変更し﹁ (P-CAB or PPI) + AMPC + MNZ﹂の3剤併用療法による二次除菌療法まで保険適応となっている。 一次除菌と二次除菌の間の期間については、一次除菌と二次除菌の期間の違いによる除菌成功率の差異の報告はないため、早く二次除菌を行おうとして一次除菌の結果判定を急ぐと、偽陰性や偽陽性が多くなり、不成功者を成功者と、成功者を不成功者などと判断してしまう恐れがある。除菌終了から1年以上経過した検査で陰性であったものが数年後に陽性になった場合は再感染を検討するが、再感染は稀であるため、基本的に除菌不成功者として二次除菌を行う[68]。 また、二次除菌療法でも除菌が失敗した場合、三次除菌療法がいくつか提唱されている。﹁ (P-CAB or PPI) + AMPC + MNZ﹂の倍量投与・倍期間投与等や、またシタフロキサシン (STFX)、レボフロキサシン (LVFX) 等を組み合わせた﹁ (P-CAB or PPI) + AMPC + STFX﹂﹁ (P-CAB or PPI) + AMPC + LVFX﹂の3剤併用療法等が行われたりするが、これらは保険診療の適応にはならない。 一方で、小児に対する治療は、除菌後の再感染のリスクを考慮して除菌対象年齢を5歳以上としている。しかし、蛋白漏出性胃症や消化性潰瘍を反復するなど除菌治療が必要と判断された場合では5歳未満でも除菌治療が行われている。ただし、除菌治療に関する添付文書では﹁小児等への投与‥小児等に対する安全性は確立されていない︵使用経験が少ない︶﹂となっており、治療が必要な場合には保護者に充分な説明を行い同意を得る必要がある[69]。原則として年齢上限は定められていない[68]。 新しい除菌療法としてCPY2C19遺伝子多型検査に基づく、テーラーメイドのヘリコバクター・ピロリ菌除菌療法が開発された。除菌療法の禁忌と副作用[編集]
ペニシリンに対する過敏症や薬物相互作用に留意する必要がある。クラリスロマイシンに対しては、片頭痛薬のエルゴタミン含有製剤、痛風薬のコルヒチンなどは、併用禁忌である[70]。二次除菌療法に用いるメトロニダゾールは、酒との相互作用によって腹痛や嘔吐を起こす[70]。 除菌療法により生じる主な副作用︵有害事象︶は、参考画像[編集]
-
ボノサップ パック 400
ボノプラザン、アモキシシリ、クラリスロマイシンのセット。
研究事例[編集]
食品による菌の抑制[編集]
近年、食品によるピロリ菌の抑制効果が確認されている。発芽3日目のブロッコリーの新芽︵スプラウト︶を2か月間継続して食べた感染者において、胃の中に住むピロリ菌が減少したとの報告がされている。メカニズムはブロッコリー内に含まれているNアセチルLシステインの結合物質によりNアセチルLシステインと同じくピロリ菌の不活性化を行うと考えられている。[73]。ブロッコリーの新芽に含まれるスルフォラファンも有効成分の一つと考えられている[74]。また、梅に含まれるシリンガレシノールというリグナンの一種もピロリ菌の増殖抑制や胃粘膜への感染防御に有効であることが発見された。
このほか、緑茶[75][76]、緑茶カテキン[77]やココア、コーヒー[78]、わさび[79]、ショウガ[80]、ニンニク[81][82]、キムチ[83]、ヨーグルト[84]、キャベツ、カリフラワー、ブロッコリーなどのアブラナ科の野菜に含まれるイソチオシアネート類[85]などでも抑制が報告されている。さらに、ニュージーランド特産の蜂蜜であるマヌカハニーも、ピロリ菌駆除力を持つことが報告されている[86][87]。
ただし、これら多くの食品による抑制効果は限られた調査対象や動物実験を基にしたものがほとんどである。また、特定の食品だけを過剰に摂取することは︵たとえピロリ菌に対しては効果があったとしても︶、全身の健康にとって良くないことは容易に想像できる。ヘリコバクター・ピロリ関連疾患の現実的かつ実践的な予防対策として、広範囲な疫学調査に基づき広く受け入れられているのは野菜と果物の摂取、および減塩である[88][89]。
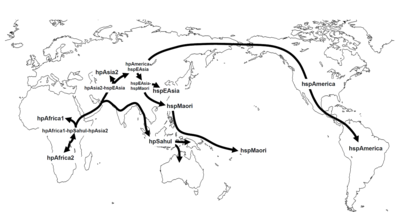
ピロリ菌亜型の拡散経路図
ピロリ菌の系統から現生人類拡散史に迫る研究も存在する。以下にピロリ菌の亜型とその分布[108]を示す︵段落下げが分布の系統︶。
●hpAfrica2 アフリカ型2アフリカ
●hpAfrica1-hpSahul-hpAsia2 アフリカ・サフル・アジア型
●hpAfrica1 アフリカ型1アフリカ
●hpSahul サフル型
●hpSahul ニューギニア型 ニューギニア
●hpSahul オーストラリア型 オーストラリア
●hpAsia2-hspEAsia 中央アジア・東アジア型
●hpAsia2 中央アジア型 中央アジア
●hspAmerica-hspEasia アメリカ・東アジア型
●hspAmerica アメリカ型
●hspAmerica 北アメリカ型 北アメリカ
●hspAmerica 南アメリカ型 南アメリカ
●hspEAsia-hspMaori 東アジア・台湾型
●hspEAsia 東アジア型 東アジア、日本列島、東南アジア
●hspMaori 台湾・太平洋型
●hspMaori 台湾型 台湾
●hspMaori 太平洋型 オセアニア
この系統樹により、崎谷満は、東アジアのヒト集団がイラン付近からアルタイ山脈付近を経由した北ルートで到達したことが明確に示されたとしている[109]。
歴史[編集]
略年表[編集]
●1874年 - ドイツのG. BöttcherとM. Letulleがヒトの胃内らせん菌を発見。 ●1892年 - イタリアのトリノ大学のジュリオ・ビツォツェロが、イヌの胃内にらせん菌を発見。 ●1899年 - ポーランドのヤギェウォ大学のヴァレリ・ヤヴォルスキがヒトの胃内に生息する細菌を発見し﹁Vibrio rugula﹂と命名。 ●1919年 - 日本の北里研究所の小林六造︵後に慶應義塾大学医学部教授︶と葛西克哉が、胃酸の強いネコから採った菌をウサギに移植した結果、胃潰瘍が起きたと発表した。また、除菌・殺菌で症状が改善することも確かめた。 ●1954年 - アメリカの病理学者エディ・パルマーが、ヒトの胃の生検1100例の結果で胃内に細菌は認められなかったと報告。 ●1983年 - オーストラリアの西オーストラリア大学のロビン・ウォレンとバリー・マーシャルによる再発見と培養法の確立。 ●1994年 - 国際がん研究機関 (IARC) が胃がんの病原体であることを発表。 ●1997年 - 全塩基配列決定。 ●2005年 - ウォレンとマーシャルがノーベル生理学・医学賞を受賞。﹁胃の中の細菌﹂を巡る論争[編集]
1874年、ドイツの研究者がヒトの胃に存在しているらせん状の細菌を発見し顕微鏡で観察したのがヘリコバクターの最初の報告であると言われているが、詳細な記録は残っていない[43]。残っている最初の正式な記録は、1892年に、イタリアの研究者ジュリオ・ビツォツェロ (Giulio Bizzozero) がイヌの胃内の酸性環境で生息する細菌について著したものである[90]。その後、1899年、ポーランドの研究者ヴァレリ・ヤヴォルスキ (Walery Jaworski) がヒトの胃からグラム陰性桿菌とともにらせん菌を見いだし、彼はこの菌をVibrio rugulaと名付け、胃疾患との関連について、ポーランド語で書かれた著書の中で提唱した[91]。 その後20世紀に入って、1906年にはKrienitzらが胃癌患者の胃粘膜にらせん菌がいること[34]を、1920年代にはLuckらが胃粘膜に︵ヘリコバクター・ピロリに由来する︶ウレアーゼの酵素活性があること[92]を、1940年には、FreedbergとBarronが胃の切除標本の約3分の1にらせん菌が存在すること[93]を、相次いで報告し、﹁胃の中の細菌﹂の存在と胃疾患との関連に対する医学研究者らの関心が徐々に高まっていった。 しかし、この説に対して異を唱える研究者も多く存在した。19世紀当時、細菌学はロベルト・コッホらの活躍によって隆盛を極めていたが、当時行われていた培養法では、この﹁胃の中の細菌﹂を分離培養できず、生きた菌の存在を直接証明できなかったためである。また細菌学の黎明期にはコレラ菌やチフス菌など、多くの消化管感染症の原因菌が研究されたが、胃は胃酸による殺菌作用によって、これらの細菌感染に対する防御機構としての役割を果たすと考えられており、このこともしばしば反対派の論拠として挙げられた。胃で全ての菌が死滅するわけではないものの、そこは生命にとって劣悪な環境であり、細菌は生息できないと考えられていたのである。 そして1954年、アメリカの病理学者で消化器病学の大家であった、エディ・パルマー (Eddy D Palmer) が、1000を超える胃の生検標本について検討した結果、らせん菌が発見できなかったと報告し、Freedberg らの報告は誤りであると主張した[94]。この報告によって、それまで報告されてきたらせん菌は、何らかの雑菌混入によるものだったのではないかという考えが主流になり、一部の医学研究者を除いて、﹁胃の中の細菌﹂に対する研究者の関心は薄れていった。ヘリコバクター・ピロリの発見[編集]
1983年、オーストラリアのロビン・ウォレンとバリー・マーシャルがヒトの胃からの、らせん状の菌を培養することに成功した。この発見には、Skirrowらが1977年に確立したカンピロバクターの微好気培養技術[95]が基盤となっている。カンピロバクターは感染性の下痢の原因となるらせん菌であり、微好気性︵低濃度の酸素と、二酸化炭素を必要とする︶かつ栄養要求性の厳しい細菌の一種であるため、特殊な培地と培養法が必要である。マーシャルらはその培養法を応用して、慢性活動性胃炎の患者の胃内、幽門付近かららせん菌を分離することに成功した。 この成功の影には一つの偶然があったと伝えられている[96]。カンピロバクター培養法を導入したマーシャルらであったが、それでも目的の菌の培養には失敗が続いた。しかし1982年4月のイースターのとき、マーシャルの実験助手が休暇をとったため、マーシャルは通常は数日で終わらせる培養を、5日間そのまま放ったらかしで続けることにした。そして休暇が終わったとき、培地上に細菌のコロニーができていることに気づき、これが本菌の発見に繋がった。後に判明したことだが、ヘリコバクター・ピロリは増殖速度が遅く、培養には長時間を必要とする細菌であった。 光学顕微鏡で観察した形態の類似性と微好気性であることが共通していたため、この菌はカンピロバクターの1種と考えられ、Campylobacter pyloridis︵campylo-; 湾曲した、カーブした、bacter; 細菌、pylorus; 幽門︶と命名された。ただし、この名称はラテン語の文法上誤りであったため、1987年にCampylobacter pyloriに改名された。その後、電子顕微鏡下での微小構造の違いや遺伝子の類似性から、1989年にカンピロバクターとは別のグループとして、新たにヘリコバクター属が設けられ、Helicobacter pylori︵helico-; らせん状の︶に名称変更された[97]。また、同様の方法でヒト以外にもフェレット、サル、ネコ、チーターなどの動物の胃からも同様の菌が分離されてヘリコバクター属に分類された。病原性の証明[編集]
発見された当時、慢性胃炎や胃潰瘍はもっぱらストレスだけが原因であるという説が主流であったが、マーシャルらは本菌がこれらの疾患の病原体であるという仮説を提唱した。これらの疾患の慢性化と胃がんの発生が関連することが当時すでに知られていたため、この仮説は本菌ががんの発生に関与する可能性を示唆するものとしても注目されたが、当初は疑いの目を持って迎えられた。 そこでマーシャルは培養したヘリコバクター・ピロリを自ら飲むという、自飲実験を行った[98][99]。その結果、マーシャルは急性胃炎を発症し、コッホの原則の一つを満たすことが証明された。ただしマーシャルの胃炎はこの後、治療を行うことなく自然に治癒したため、急性胃炎以外の胃疾患との関連については証明されなかった。一方、彼とは別に、ニュージーランドの医学研究者、アーサー・モリスもまた同様の自飲実験を行った[100]。その結果、マーシャルと同様に急性胃炎を発症しただけでなく、モリスの場合は慢性胃炎への進行が認められた。これらの結果から、ヘリコバクター・ピロリが急性および慢性胃炎の原因になることが証明された。この後、疫学的な研究から、これらの疾患の慢性患者の多くから本菌が分離されることや、本菌の除菌治療が再発防止に有効であることも明らかになった。 胃癌との関連については、ヒト以外の動物を用いた数多くの実験にもかかわらず証明ができないままであったが、疫学調査の結果から明らかになっていった。そして1994年には国際がん研究機関 (IARC) が発行している IARC発がん性リスク一覧に、グループ1︵発がん性がある︶の発がん物質として記載された[10]。その後、日本から有用な成果が相次いで報告された。1996年に平山らは、ヘリコバクター・ピロリがスナネズミの胃に感染し、ヒトと同様の慢性胃炎、消化性潰瘍を形成することを発見した[101]。1998年には、渡辺らが長期間飼育したピロリ菌感染スナネズミに胃がんが発生したことを報告し、コッホの原則に基づく最初の証明とされた[102]。この年にはさらに立松らによって、発がん物質投与とピロリ菌感染を組み合わせた、より効率の高い動物胃癌モデルが確立されている[103]。 2001年にはピロリ感染者では胃癌が発症するものの、非感染者では全く発症しなかったと日本から報告された[104]。 一方、ヘリコバクター・ピロリの除菌が広く行われだした頃から、この治療を行った患者に食道炎や食道がんの発生が多いことが報告されており、本菌は胃に対して悪影響をおよぼす傍ら、食道に対してはむしろ疾患を防御している可能性が議論されている︵後述︶。米国国民健康栄養調査によると、ピロリ感染は胃がん死亡を増加させるが、脳卒中死亡等を減少させ、結果的にピロリ感染者の総死亡リスクは非感染者と変わらないと報告しています[105]。その後の展開[編集]
医学的な重要性から、ヘリコバクター・ピロリの研究は精力的に進められ、1997年にはゲノム解読が完了した[106]。この結果から、胃内定着の機構や発がんのメカニズムについての研究がさらに進められている。 2005年には、ヘリコバクター・ピロリの発見の功績によって、ロビン・ウォレンとバリー・マーシャルに対してノーベル生理学・医学賞が授与された[107]。人類学への応用[編集]

出典[編集]
(一)^ helicobacter pylori (Cambridge Dictionaries Online)
(二)^ 武田薬品工業. “ピロリ菌って何者?”. 2015年1月16日閲覧。
(三)^ actamnuse. “ヘリコバクテル に関する公開一覧”. 2015年1月16日閲覧。
(四)^ Marshall BJ (1983). “Unidentified curved bacillus on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis”. Lancet 1 (8336): 1273–1275. PMID 6134060.
(五)^ 寺田秀夫、﹁私の経験例からヘリコバクター ピロリ除菌療法が著効を示した重症特発性血小板減少性紫斑病の1例﹂ 血液フロンティア 12, 114-118, 2001, NAID 80012885657
(六)^ ab横井千寿、小早川雅男、他﹁臨床講座11‥ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染症﹂﹃PharmaTribune﹄第1巻第11号、メディカルトリビューン、2009年11月、26-35頁、ISSN 1883-4043。
(七)^ “特発性血小板減少性紫斑病︵公費対象︶”. 難病医学研究財団難病情報センター (2008年7月2日). 2009年11月22日閲覧。
(八)^ 藤岡利生﹁ヘリコバクター感染症の研究‥現状と将来展望﹂︵PDF︶﹃e-CLINICIAN﹄第54巻第556号、2007年2月、p.p.152-155、2009年11月22日閲覧。
(九)^ 佐藤竜吾、藤岡利生、村上和成、兒玉雅明、上部消化管疾患以外の領域におけるヘリコバクター・ピロリ除菌療法 ヘリコバクター・ピロリ除菌療法の新たな展開 日本消化器病学会雑誌 2003年 100巻11号 p.1295-1301, doi:10.11405/nisshoshi1964.100.1295
(十)^ abIARC (1994). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 61. World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer. pp. 177.
(11)^ ヒト胃内感染ヘリコバクター属、ピロリとハイルマニのゲノム解析と病原性遺伝子の解明 - 東健、吉田優 神戸大学大学院医学研究科内科学講座消化器内科学分野 (PDF)
(12)^ 中村正彦 ほか、﹁ピロリ菌陰性でも要注意!?—広義のハイルマニイ菌﹂, 検査と技術44巻4号, 2016/4/1, doi:10.11477/mf.1543206392
(13)^ Amieva, Manuel; Peek, Richard M. (2016). “Pathobiology of Helicobacter pylori–Induced Gastric Cancer”. Gastroenterology 150 (1): 64–78. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.004. ISSN 0016-5085. PMC 4691563. PMID 26385073.
(14)^ “Helicobacter pylori - Chapter 3 - 2016 Yellow Book | Travelers' Health | CDC” (英語). wwwnc.cdc.gov (2015年6月9日). 2017年4月25日閲覧。
(15)^ abGeorge M. Garrity; Julia A. Bell, Timothy Lilburn (2005). George M. Garrity. ed. Bergey's manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd edition, Volume Two, Part C. pp. 1168-89. ISBN 0-387-24145-0
(16)^ 藤本秀士﹃戸田新細菌学﹄︵吉田眞一、柳雄介編︶改訂33版 pp525-530、南山堂、2007年、ISBN 978-4-525-16013-5
(17)^ Chan WY, Hui PK, Leung KM, Chow J, Kwok F, Ng CS (1994). Coccoid forms of Helicobacter pylori in the human stomach.. PMID 7524304.
(18)^ 桑原徹, 柴崎浩一, 山口晃、﹁唾液ならびに胃粘膜内におけるヘリコバクター・ピロリのサブタイプに関する研究﹂ ﹃日本口腔外科学会雑誌﹄ 2000年46巻9号 p.497-502, doi:10.5794/jjoms.46.497
(19)^ “DSMZ Bacterial Nomenclature Up-to-Date: Genus Helicobacter”. DSMZ - Deutsche Sammlung von Mikroorganismen und Zellkulturen GmbH. 2007年10月9日閲覧。
(20)^ Taylor DN, Blaser MJ. (1991). “The epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection.”. Epidemiol Rev. 13: 42-59. PMID 1765119.
(21)^ Asaka M, Kimura T, Kudo M, Takeda H, Mitani S, Miyazaki T, Miki K, Graham DY. (1992). “Relationship of Helicobacter pylori to serum pepsinogens in an asymptomatic Japanese population.”. Gastroenterology. 102: 760-6. PMID 1537513.
(22)^ ab山本達男、消化管病原菌とヒト粘膜の相互作用 食品衛生学雑誌 1995年36巻1号 p.1-8, doi:10.3358/shokueishi.36.1
(23)^ Borén, T., Falk P., Roth, K. A., Larson. G., Normark, S.: "Attachment of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric epithelium mediated by blood group antigens." Science 262, 1,892-1,895 (1993)., doi:10.1126/science.8018146
(24)^ 奥田真珠美 日本医事新報 2014;4729:53-54.
(25)^ Brown LM. (2000). “Helicobacter pylori: epidemiology and routes of transmission.”. Epidemiol Rev 22: 283-97. PMID 11218379.
(26)^ Grübel P, Hoffman JS, Chong FK, Burstein NA, Mepani C, Cave DR. (1997). “Vector potential of houseflies (Musca domestica) for Helicobacter pylori.”. J Clin Microbiol 35: 1300-3. PMID 9163433.
(27)^ Parsonnet J, Shmuely H, Haggerty T (1999). “Fecal and oral shedding of Helicobacter pylori from healthy infected adults”. JAMA 282 (23): 2240-2245. doi:10.1001/jama.282.23.2240. PMID 10605976.
(28)^ 平山壽哉﹃ウイルス・細菌と感染症がわかる﹄︵吉開泰信編︶pp114-118、羊土社、2004年、ISBN 4-89706-960-2
(29)^ Suzuki H, Mori M, Suzuki M, Sakurai K, Miura S, Ishii H. (1997). “Extensive DNA damage induced by monochloramine in gastric cells.”. Cancer Lett 115: 243-8. PMID 9149131.
(30)^ NAKAZAWA, Teruko (2001). “ヘリコバクター・ピロリの持続感染機構の研究 -酵素化学, 分子遺伝学から病原微生物学へ-”. Nippon Saikingaku Zasshi 56 (4): 557–572. doi:10.3412/jsb.56.557. ISSN 1882-4110.
(31)^ Huang JQ, Zheng GF, Sumanac K, Irvine EJ, Hunt RH. (2003). “Meta-analysis of the relationship between 細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原 seropositivity and gastric cancer.”. Gastroenterology 125: 1636-44. PMID 4724815.
(32)^ Odenbreit S, Püls J, Sedlmaier B, Gerland E, Fischer W, Haas R. (2000). “Translocation of Helicobacter pylori 細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原 into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion.”. Science 287: 1497-500. PMID 10688800.
(33)^ Hatakeyama M. (2004). “Oncogenic mechanisms of the Helicobacter pylori 細胞毒関連遺伝子抗原 protein.”. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 688-94. PMID 15343275.
(34)^ ab平山壽哉﹃微生物感染症学﹄︵光山正雄編︶pp.268-276、南山堂、2005年、ISBN 4-525-16101-9
(35)^ Blaser MJ. (1990). “Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation.”. J Infect Dis. 161: 626-33. PMID 2181029.
(36)^ HATAKEYAMA, Masanori (2008). “Oncogenic mechanism of Helicobacter pylori”. Japanese Journal of Clinical Immunology 31 (3): 132–140. doi:10.2177/jsci.31.132. ISSN 0911-4300.
(37)^ Martin J. Blaser & Stanley Falkow (2009-12). “What are the consequences of the disappearing human microbiota?”. Nature Reviews Microbiology 89: 887-894. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2245.
(38)^ 丸山康弘、当院におけるヘリコバクターピロリの除菌治療 信州医学雑誌 Vol.63 (2015) No.1 p.33-34, doi:10.11441/shinshumedj.63.33
(39)^ ヘリコバクター・ピロリ菌感染と胃がん罹患との関係‥CagA およびペプシノーゲンとの組み合わせによるリスク独立行政法人 国立がん研究センター がん予防・検診研究センター 予防研究部‥2012年7月6日閲覧
(40)^ Kaptan K, et al. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160 (9):1349-53.
(41)^ Labenz J, Blum AL, Bayerdörffer E, Meining A, Stolte M, Börsch G. (1997). “Curing Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with duodenal ulcer may provoke reflux esophagitis.”. Gastroenterology 112: 1442-7. PMID 9136820.
(42)^ Schwizer W, Thumshirn M, Dent J, Guldenschuh I, Menne D, Cathomas G, Fried M. (2001). “Helicobacter pylori and symptomatic relapse of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a randomised controlled trial.”. Lancet 357: 1738-42. PMID 11403809.
(43)^ abBlaser MJ (2005). “An Endangered Species in the Stomach”. Scientific American 292 (2): 38–45. PMID 15715390.
(44)^ https://www.mizuho-m.co.jp/product/product_details/000813.php?iryou=1
(45)^ 英国国立医療技術評価機構 2014, Chapt.1.9.1.
(46)^ ab中島滋美、胃がん検診におけるペプシノゲン法,ABC分類,および胃X線検査の位置づけ 日本消化器病学会雑誌 Vol.110 (2013) No.2 p.225-233, doi:10.11405/nisshoshi.110.225
(47)^ 望月直美、小林正夫、西大路賢一 ほか、︻原著︼人間ドックにおける胃がんリスク評価(ABC分類)の有用性と課題 日本消化器がん検診学会雑誌 Vol.52 (2014) No.5 p.545-555, doi:10.11404/jsgcs.52.545
(48)^ 日本ヘリコバクター学会ガイドライン作成委員会 2000.
(49)^ ﹁ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染胃炎﹂ の効能追加について 厚労省
(50)^ 胃がんとヘリコバクターピロリとの関連を踏まえたがん対策に関する質問主意書 (PDF) 参議院
(51)^ 参議院議員秋野公造君提出胃がんとヘリコバクターピロリとの関連を踏まえたがん対策に関する質問に対する答弁書 (PDF)
(52)^ 厚生労働省平成22年6月18日﹁ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染の診断及び治療に関する取扱いについて﹂︵平成12年10月31日保険発第180号︶ (PDF)
(53)^ 胃がんの﹁原因﹂ピロリ菌、胃炎での治療にも保険適用
(54)^ ピロリ除菌の保険拡大へ 厚労省、胃がん発症減も日本経済新聞 2020年2月13日閲覧
(55)^ 胃がんは﹁ピロリ菌除菌﹂でなくせる 浅香 正博・秋野公造 (著)潮出版2013/10/5、潮新書2017/3/4
(56)^ 伊藤公訓、小刀崇弘、保田智之 ほか、Helicobacter pylori除菌後の胃がん 日本消化器内視鏡学会雑誌60巻 (2018) 1号 p.5-13, doi:10.11280/gee.60.5
(57)^ ピロリ菌・除菌療法の功罪――胃がん予防になるのか
(58)^ Marshall BJ, McGechie DB, Rogers PA, Glancy RJ. (1985). “Pyloric Campylobacter infection and gastroduodenal disease.”. Med J Aust 142: 439-44.
(59)^ Marshall BJ, Armstrong JA, Francis GJ, Nokes NT, Wee SH. (1987). “Antibacterial action of bismuth in relation to Campylobacter pyloridis colonization and gastritis.”. Digestion 37 Suppl 2: 16-30. PMID 3622946.
(60)^ ﹁ヘリコバクター・ピロリの2段階除菌法﹂﹃日本消化器病学会雑誌﹄第8号、1997年、569頁、doi:10.11405/nisshoshi1964.94.8_569。
(61)^ Logan RP, Gummett PA, Misiewicz JJ, Karim QN, Walker MM, Baron JH. (1991). “One week eradication regimen for Helicobacter pylori.”. Lancet 338: 1249-52. PMID 1682653.
(62)^ Unge P, Gad A, Gnarpe H, Olsson J. (1989). “Does omeprazole improve antimicrobial therapy directed towards gastric Campylobacter pylori in patients with antral gastritis? A pilot study.”. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl 167: 49-54. PMID 2617169.
(63)^ Jaup BH, Norrby A. (1995). “Low dose, short-term triple therapy for cure of Helicobacter pylori infection and healing of peptic ulcers.”. Am J Gastroenterol 90: 943-5. PMID 7771426.
(64)^ H pylori antibiotic resistance: prevalence, importance, and advances in testing
(65)^ “タケキャブ錠10mg/タケキャブ錠20mg 添付文書” (PDF) (2016年3月). 2016年7月2日閲覧。
(66)^ ピロリ除菌にヨーグルト 日経メディカルオンライン記事‥2009年11月3日 閲覧‥ 2009年11月5日
(67)^ ヘリコバクター・ピロリの小児への感染とクラリスロマイシン耐性化 新潟医学会雑誌 118(11) pp.643-644 20041110
(68)^ ab“﹁ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染胃炎﹂に対する除菌治療に関するQ&A一覧|疾患Q&A|医療関係のみなさまへ|日本消化器病学会”. www.jsge.or.jp. 2018年12月6日閲覧。
(69)^ 加藤ら (2005). “小児期ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染症の診断,治療,および管理指針”. 日本小児科学会雑誌 109: 1297-1300.
(70)^ ab広がるピロリ除菌療法の注意点は? 日経メディカルオンライン 記事‥2013年4月25日 閲覧‥2013年4月26日
(71)^ 市川竜太郎、伊藤絵里子、寺尾浩 ほか、︻原著︼ヘリコバクター・ピロリ除菌療法による多形紅斑型薬疹の5例 日本皮膚科学会雑誌 Vol.118 (2008) No.8 p.1527-1532, doi:10.14924/dermatol.118.1527
(72)^ 篠田京香、近藤靖児、︻原著︼ヘリコバクター・ピロリ除菌後早期に発症した紅斑丘疹型皮疹の6例 日本皮膚科学会雑誌 Vol.113 (2003) No.12 p.1819-1825, doi:10.14924/dermatol.113.1819
(73)^ Galan MV, Kishan AA, Silverman AL (August 2004). “Oral broccoli sprouts for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection: a preliminary report”. Dig Dis Sci. 49 (7–8): 1088–90. PMID 15387326.
(74)^ Fahey JW, Haristoy X, Dolan PM, Kensler TW, Scholtus I, Stephenson KK, Talalay P, Lozniewski A (May 2002). Sulforaphane inhibits extracellular, intracellular, and antibiotic-resistant strains of Helicobacter pylori and prevents benzo[a]pyrene-induced stomach tumors.. PMID 12032331.
(75)^ “Green tea inhibits Helicobacter growth in vivo and in vitro”. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 33 (5): 473–8. (May 2009). doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2008.10.032. PMC 2694061. PMID 19157800.
(76)^ “Phytoceuticals: mighty but ignored weapons against Helicobacter pylori infection”. J Dig Dis 9 (3): 129–39. (August 2008). PMID 18956590.
(77)^ Matsubara S, Shibata H, Ishikawa F, Yokokura T, Takahashi M, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K. (October 2003). Suppression of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastritis by green tea extract in Mongolian gerbils.. PMID 14550260.
(78)^ Okabe Y; Yamamoto Y, Yasuda K, Hochito K, Kawano K, Ishii N (2003). The antibacterial effects of coffee on Escherichia coli and Helicobacter pylori. 34. pp. 85-87. ISSN 0912-0009.
(79)^ 木苗直秀 ほか、わさび抽出物の Helicobacter pylori 感染スナネズミに対する胃粘膜障害予防効果とストレス負荷が及ぼす影響 研究内容 (PDF)
(80)^ ヘリコバクター・ピロリに関連する疾患を治療する際の、生姜の根茎から抽出された有効産物の使用
(81)^ http://f16.aaa.livedoor.jp/~maruzen/public_html/ninniku.htm
(82)^ Garlic fights H. pylori to reduce the risk of stomach cancer
(83)^ Youl Lee and Hae Choon Chang (2008). “Isolation and Characterization of Kimchi Lactic Acid Bacteria Showing Anti-Helicobacter pylori Activity”. Korean Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2: 106–114.
(84)^ Adolfsson O, Meydani SN, Russell RM. (2004). “Yogurt and gut function.”. Am J Clin Nutr 80: 245-56. PMID 15277142.
(85)^ 一般の方向けがん予防情報 → イソチオシアネート
(86)^ McGovern DP, Abbas SZ, Vivian G, Dalton HR. (1999). “Manuka honey against Helicobacter pylori.”. J R Soc Med 92: 439. PMID 10656024.
(87)^ ワイカト大学生物化学研究所ハニー・リサーチ・センターの報告書︵翻訳︶
(88)^ Correa P, Piazuelo MB, Camargo MC. (2004). “The future of gastric cancer prevention.”. Gastric Cancer 7: 9-16. PMID 15052434.
(89)^ Tsugane S, Sasazuki S. (2007). “Diet and the risk of gastric cancer: review of epidemiological evidence.”. Gastric Cancer 10: 75-83. PMID 17577615.
(90)^ Bizzozero, Giulio (1893). “Über die schlauchförmigen Drüsen des Magendarmkanals und die Beziehungen ihres Epitheles zu dem Oberflächenepithel der Schleimhaut”. Archiv für mikroskopische Anatomie 42: 82–152.
(91)^ Konturek JW (2003 Dec). “Discovery by Jaworski of Helicobacter pylori and its pathogenetic role in peptic ulcer, gastritis and gastric cancer”. J Physiol Pharmacol. 54 Suppl 3: 23–41. PMID 15075463. オリジナルの2006年8月28日時点におけるアーカイブ。.
(92)^ Luck JM; Seth TN (1925). “The Physiology of Gastric Urease.”. Biochem. J. 19 (3): 357-65. PMID 16743512.
(93)^ Freedberg AS; Barron LE (1940). “The presence of spirochetes in human gastric mucosa.”. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 7: 443-5.
(94)^ Palmer ED. (1954). “Investigation of the gastric mucosa spirochetes of the human.”. Gastroenterology 27 (2): 218-20. PMID 13183283.
(95)^ Skirrow MB (1977). “Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease.”. Br Med J 2 (6078): 9-11. PMID 871765.
(96)^ 千葉勉 (Dec 2005). “今年のノーベル医学生理学賞は胃癌の原因菌H. pyloriの発見者に!”. 実験医学 23 (19): 2926-7.
(97)^ “Campylobacter pylori becomes Helicobacter pylori.”. Lancet 2: 1019-20. (1989). PMID 2572746.
(98)^ Marshall BJ; Armstrong JA, McGechie DB, Glancy RJ (1985). “Attempt to fulfil Koch's postulates for pyloric Campylobacter.”. Med J Aust. 142 (8): 436-9. PMID 3982345.
(99)^ Marshall BJ (1995). “Helicobacter pylori in peptic ulcer: have Koch's postulates been fulfilled?”. Ann Med. 27 (5): 565-8. PMID 8541033.
(100)^ Morris A; Nicholson G (1987). “Ingestion of Campylobacter pyloridis causes gastritis and raised fasting gastric pH.”. Am J Gastroenterol. 82 (3): 192-9. PMID 3826027.
(101)^ Hirayama F, Takagi S, Yokoyama Y, Iwao E, Ikeda Y. (1996). “Establishment of gastric Helicobacter pylori infection in Mongolian gerbils.”. J Gastroenterol Suppl 9: 24-8. PMID 8959513.
(102)^ Watanabe T; Tada M, Nagai H, Sasaki S, Nakao M (1998). “Helicobacter pylori infection induces gastric cancer in mongolian gerbils.”. Gastroenterology 115 (3): 642-8. PMID 9721161.
(103)^ Tatematsu M, Yamamoto M, Shimizu N, Yoshikawa A, Fukami H, Kaminishi M, Oohara T, Sugiyama A, Ikeno T. (1998). “Induction of glandular stomach cancers in Helicobacter pylori-sensitive Mongolian gerbils treated with N-methyl-N-nitrosourea and N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in drinking water.”. Jpn J Cancer Res 89: 97-104. PMID 9548434.
(104)^ UUemura N, Okamoto S, Yamamoto S, Matsumura N, Yamaguchi S, Yamakido M, Taniyama K, Sasaki N, Schlemper RJ (2001). “Helicobacter pylori infection and the development of gastric cancer”. N. Engl. J. Med. 345 (11): 784–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa001999. PMID 11556297.
(105)^ {https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3834579/ Association Between Helicobacter pylori and Mortality in the NHANES III Study}
(106)^ Tomb JF, White O, Kerlavage AR et al. (1997). “The complete genome sequence of the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori.”. Nature 388: 539-47. PMID 9252185.
(107)^ The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2005 awarded to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren "for their discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer disease".
(108)^ Yoshan Moodley et al(2009); The Peopling of the Pacific from a Bacterial Perspective‥Science 23 January 2009: Vol. 323 no. 5913 pp. 527-530 DOI: 10.1126/science.1166083 より部分改変。︵崎谷満﹃DNA・考古・言語の学際研究が示す新・日本列島史﹄︵勉誠出版 2009年︶P36 より︶
(109)^ 崎谷満﹃DNA・考古・言語の学際研究が示す新・日本列島史﹄︵勉誠出版 2009年︶
参考文献[編集]
- CG184: Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and dyspepsia in adults: investigation and management (Report). 英国国立医療技術評価機構. 2014.
- 日本ヘリコバクター学会ガイドライン作成委員会 (2000). “Helicobacter pylori 感染の診断と治療のガイドライン”. Jpn J Helicobacter Res (suppl) 2: 2-12.
関連項目[編集]
外部リンク[編集]
- 日本ヘリコバクター学会
- メルクマニュアル - ウェイバックマシン(2008年6月11日アーカイブ分)「胃炎と胃潰瘍」
- ヘリコバクター・ピロリ(Helicobacter pylori)感染 - MSDマニュアル
- 「ヘリコバクター・ピロリ感染胃炎」に対する除菌治療に関するQ&A一覧 - 日本消化器病学会
- 『ヘリコバクター・ピロリ関連疾患』 - コトバンク


