

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
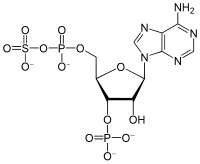
| IUPAC name
3′-O-Phosphono-5′-adenylyl hydrogen sulfate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)oxolan-2-yl]methyl hydrogen (sulfooxy)phosphonate | |
| Other names
PAPS | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Abbreviations | PAPS |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.222.927 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H15N5O13P2S | |
| Molar mass | 507.266 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
3′-Phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphosulfate (PAPS) is a derivative of adenosine monophosphate (AMP) that is phosphorylated at the 3′ position and has a sulfate group attached to the 5′ phosphate. It is the most common coenzymeinsulfotransferase reactions and hence part of sulfation pathways.[1] It is endogenously synthesized by organisms via the phosphorylation of adenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (APS), an intermediary metabolite.[2] In humans such reaction is performed by bifunctional 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthases (PAPSS1 and PAPSS2) using ATP as the phosphate donor.[3][4]
APS and PAPS are intermediates in the reduction of sulfate to sulfite, an exothermic conversion that is carried out by sulfate-reducing bacteria. In these organisms, sulfate serves as an electron acceptor, akin to the use of O2 as an electron acceptor by aerobic organisms. Sulfate is not reduced directly but must be activated by the formation of APS or PAPS. These carriers of activated sulfate are produced by reaction with ATP. The first reaction is catalysed by ATP sulfurylase:
The conversion of APS to PAPS is catalysed by APS kinase:

Reduction of APS leads to sulfite, which is further reduced to hydrogen sulfide, which is excreted. This process is called dissimilatory sulfate reduction. Reduction of PAPS, a more elaborated sulfate ester, leads also to hydrogen sulfide. But in this case, the product is used in biosynthesis, e.g. for the production of cysteine. The latter process is called assimilatory sulfate reduction because the sulfate sulfur is assimilated.[5]
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active forms |
| ||||||
| Base forms |
| ||||||