J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 S t r u c t u r e
T o g g l e S t r u c t u r e s u b s e c t i o n
1 . 1 S p h i n c t e r s
1 . 2 V a r i a t i o n
2 C l i n i c a l s i g n i f i c a n c e
3 E t y m o l o g y
4 A d d i t i o n a l i m a g e s
5 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
A m p u l l a o f V a t e r
1 9 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● C a t a l à ● E s p a ñ o l ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● H r v a t s k i ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● I t a l i a n o ● ע ב ר י ת ● K a p a m p a n g a n ● L a t i n a ● M a g y a r ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● S u o m i ● த ம ி ழ ் ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Not to be confused with the
Duodenal cap also known as the duodenal ampulla, the first part of the duodenum.
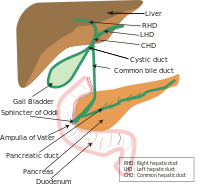
The ampulla of Vater , hepatopancreatic ampulla or hepatopancreatic duct is the common duct that is usually formed by a union of the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct within the wall of the duodenum . This common duct usually features a dilation ("ampulla "). The common duct then opens medially into the descending part of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla . The common duct usually measures 2-10mm in length.[1]
The ampulla of Vater is an important landmark halfway along the second part of the duodenum marking the transition from foregut to midgut .[citation needed
Structure [ edit ]
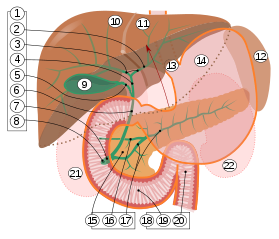
1. Bile ducts Intrahepatic bile ducts Left and right hepatic ducts Common hepatic duct Cystic duct Common bile duct Ampulla of Vater Major duodenal papilla Gallbladder Right and left lobes of liver Spleen Esophagus Stomach Pancreas Accessory pancreatic duct Pancreatic duct Small intestine Duodenum Jejunum kidneys [2]
Sphincters [ edit ]
Various smooth muscle sphincters regulate the flow of bile and pancreatic juice through the ampulla: the sphincter of the pancreatic duct , the sphincter of the bile duct , and the sphincter of Oddi .[3]
Variation [ edit ]
The common bile duct and pancreatic duct may sometimes unite outside the duodenal wall, creating an unusually long common duct. The two ducts may also drain into the duodenum separately, or may fuse yet retain their separate lumens separated by a septum.[1]
Clinical significance [ edit ]
Thomas' sign is the production of silver stools and can be indicative of cancer of the Ampulla of Vater . The silver-colored stool is a combination of the white stool of obstructive jaundice combined with black stool of melena or bleeding. It was first described in the British Medical Journal by Dr. H. Ogilvie in 1955.[4]
Etymology [ edit ]
The eponymic term "ampulla of Vater" is named after Abraham Vater (1684–1751),[5] a German anatomist who first published a description of it in 1723.[6]
Additional images [ edit ]
The pancreatic duct.
Carcinoma of Ampulla
References [ edit ]
^ Standring S, Borley NR, eds. (2008). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice . Brown JL, Moore LA (40th ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 1163, 1177, 1185–6. ISBN 978-0-8089-2371-8
^ Allescher, H. D. (1989). "Papilla of Vater: Structure and Function" . Endoscopy . 21 doi :10.1055/s-2007-1012982 . PMID 2691236 . S2CID 38457896 . Archived from the original . Retrieved March 27, 2020 – via www.thieme-connect.de.
^ Ogilvie, H (1955). "Thomas's sign, or the silver stool in cancer of the ampulla of Vater" . Br Med J . 1 doi :10.1136/bmj.1.4907.208 . PMC 2060824 PMID 13219383 .
^ Lerch, MM; Domschke, W (2000). "Abraham Vater of the ampulla (papilla) of Vater" . Gastroenterology . 118 (2 ): 379. doi :10.1016/s0016-5085(00 )70243-5 PMID 10691372 .
^ Vater A. Dissertation in auguralis medica, poes diss. Qua Scirris viscerum dissert, C.S. Ezlerus. Vol 70. 1723.
"Ampulla, hepatopancreatic." Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed. (2000). ISBN 0-683-40007-X
Moore, Keith L. and Arthur F. Dalley. Clinically Oriented Anatomy, 4th ed. (1999). ISBN 0-683-06141-0
Medicine
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Ampulla_of_Vater&oldid=1194348578 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● P a n c r e a s a n a t o m y ● G a l l b l a d d e r H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● C S 1 m a i n t : l o c a t i o n m i s s i n g p u b l i s h e r ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● U s e m d y d a t e s f r o m S e p t e m b e r 2 0 2 1 ● U s e A m e r i c a n E n g l i s h f r o m F e b r u a r y 2 0 1 9 ● A l l W i k i p e d i a a r t i c l e s w r i t t e n i n A m e r i c a n E n g l i s h ● A l l a r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h u n s o u r c e d s t a t e m e n t s f r o m J u l y 2 0 2 3 ● A r t i c l e s w i t h T A 9 8 i d e n t i f i e r s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 8 J a n u a r y 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 5 : 1 2 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w