

|
BI Cygni is the small very red dot right on the left edge of this image. The bright star at the centre is γ Cygni and north is to the right. Credit: Erik Larsen | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cygnus |
| Right ascension | 20h21m 21.8869s[1] |
| Declination | 36° 55′ 55.729″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 8.4 – 9.9[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Evolutionary stage | Red supergiant |
| Spectral type | M4 Iab[2] |
| Variable type | Lc[2] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −7.48±0.42[1] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −2.751[1] mas/yr Dec.: −5.459[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.3541 ± 0.0377 mas[1] |
| Distance | 4,349+548 −440 ly (1,334+168 −135 pc)[3] |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −6.78[4] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 17[5] M☉ |
| Radius | 852+12 −9 – 908+12 −10[3] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 89,300[5] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | -0.35[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 3,575[3][5] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | +0.40[6] dex |
| Age | >12[5] Myr |
| Other designations | |
RAFGL 2559, BI Cyg, BD+36 4025, WDS J20214+3656, TIC 13249363, TYC 2684-522-1, GSC 02684-00522, IRAS 20194+3646, 2MASS J20212192+3655555 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
BI Cygni (BI Cyg, IRC +40408, BD+36 4025) is a red supergiant in the constellation Cygnus. It is an irregular variable star with a maximum brightness of magnitude 8.4 and a minimum of magnitude 9.9. It is considered a member of the Cygnus OB1 stellar association,[4] its distance is around 1,300 parsecs (4,200 ly) of the Solar System. It is less than a degree south of another variable red supergiant, BC Cygni.
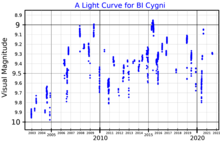
BI Cyg is a slow irregular variable star classified as type Lc, an irregular supergiant. Its brightness changes between extremes of magnitude 8.4 and 9.9.[2] Frequency analysis of its light curve shows no significant periods.[8]
BI Cyg is one of the largest known stars with a radius around 850 R☉, measured by its angular diameter by the CHARA array.[3] It is about 90,000 times more luminous that the Sun and has a cool effective temperature of 3,535 K.[5] Its mass is estimated at 17 solar masses, and it took 12 million years to enter the red supergiant phase.[5]