

| Thermodynamics | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

The classical Carnot heat engine
| ||||||||||||
|
Branches |
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
Note: Conjugate variablesinitalics
|
||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
   |
||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
|
Scientists |
||||||||||||
|
Other |
||||||||||||
|
|

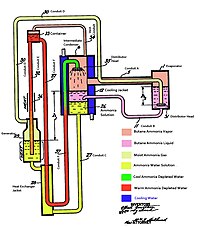
The Einstein–SzilardorEinstein refrigerator is an absorption refrigerator which has no moving parts, operates at constant pressure, and requires only a heat source to operate. It was jointly invented in 1926 by Albert Einstein and his former student Leó Szilárd, who patented it in the U.S. on November 11, 1930 (U.S. patent 1,781,541). The three working fluids in this design are water, ammonia, and butane.[1] The Einstein refrigerator is a development of the original three-fluid patent by the Swedish inventors Baltzar von Platen and Carl Munters.
From 1926 until 1934 Einstein and Szilárd collaborated on ways to improve home refrigeration technology. The two were motivated by contemporary newspaper reports of a Berlin family who had been killed when a seal in their refrigerator failed and leaked toxic fumes into their home. Einstein and Szilárd proposed that a device without moving parts would eliminate the potential for seal failure, and explored practical applications for different refrigeration cycles. Einstein had worked in the Swiss Patent Office, and used his experience to apply for valid patents for their inventions in several countries. The two were eventually granted 45 patents in six countries for three different models.[2]
It has been suggested that most of the actual inventing was done by Szilárd, with Einstein merely acting as a consultant and helping with the patent-related paperwork,[2] but others assert that Einstein contributed design work to the project.[3]
The refrigerator was less efficient than existing appliances, although having no moving parts made it more reliable; the introduction of Freon to replace refrigerant gases toxic to humans made it even less attractive commercially.[2] The Great Depression of 1929 dried up funding for development, and the widespread political violence in Nazi Germany, where the inventors lived, particularly towards Jews such as Einstein and Szilard, contributed to the device's lack of commercial success. (The inventors fled Germany in the early 1930s.)[4] It was not immediately put into commercial production, although the most promising of the patents were quickly bought up by the Swedish company Electrolux. Einstein and Szilárd earned $750 (the equivalent of $10,000 in 2017).[3] A few demonstration units were constructed from other patents.
One variant, the Einstein–Szilard electromagnetic refrigerator used a Einstein–Szilard electromagnetic pump to compress a working gas, pentane.[2] Although the refrigerator was not a commercial success, the Einstein–Szilard pump was later used for cooling breeder reactors, where its inherent reliability and safety were important.[2]
In 2008, electrical engineers at Oxford University's Energy and Power Group, part of the university's Department of Engineering Science,[5] revived the Einstein refrigerator as an attempt to produce a refrigerator suitable for use in rural areas without electricity.[1] The group, led by Malcolm McCulloch noted that the design was still "nowhere near commercialised",[1] but might allow the efficiency of the original Einstein–Szilárd design to be quadrupled.[6]
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
|
| |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| External combustion / thermal |
| ||||
| Internal combustion / thermal |
| ||||
| Mixed |
| ||||
| Refrigeration |
| ||||