

This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (September 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message)
|
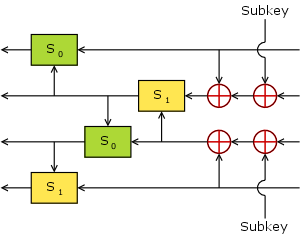
The FEAL Feistel function
| |
| General | |
|---|---|
| Designers | Akihiro Shimizu and Shoji Miyaguchi (NTT) |
| First published | FEAL-4 in 1987; FEAL-N/NX in 1990 |
| Cipher detail | |
| Key sizes | 64 bits (FEAL), 128 bits (FEAL-NX) |
| Block sizes | 64 bits |
| Structure | Feistel network |
| Rounds | Originally 4, then 8, then variable (recommended 32) |
| Best public cryptanalysis | |
| Linear cryptanalysis can break FEAL-4 with 5 known plaintexts (Matsui and Yamagishi, 1992). A differential attack breaks FEAL-N/NX with fewer than 31 rounds (Biham and Shamir, 1991). | |
Incryptography, FEAL (the Fast data Encipherment Algorithm) is a block cipher proposed as an alternative to the Data Encryption Standard (DES), and designed to be much faster in software. The Feistel based algorithm was first published in 1987 by Akihiro Shimizu and Shoji Miyaguchi from NTT. The cipher is susceptible to various forms of cryptanalysis, and has acted as a catalyst in the discovery of differential and linear cryptanalysis.
There have been several different revisions of FEAL, though all are Feistel ciphers, and make use of the same basic round function and operate on a 64-bit block. One of the earliest designs is now termed FEAL-4, which has four rounds and a 64-bit key.
Problems were found with FEAL-4 from the start: Bert den Boer related a weakness in an unpublished rump session at the same conference where the cipher was first presented. A later paper (den Boer, 1988) describes an attack requiring 100–10000 chosen plaintexts, and Sean Murphy (1990) found an improvement that needs only 20 chosen plaintexts. Murphy and den Boer's methods contain elements similar to those used in differential cryptanalysis.
The designers countered by doubling the number of rounds, FEAL-8 (Shimizu and Miyaguchi, 1988). However, eight rounds also proved to be insufficient — in 1989, at the Securicom conference, Eli Biham and Adi Shamir described a differential attack on the cipher, mentioned in (Miyaguchi, 1989). Gilbert and Chassé (1990) subsequently published a statistical attack similar to differential cryptanalysis which requires 10000 pairs of chosen plaintexts.
In response, the designers introduced a variable-round cipher, FEAL-N (Miyaguchi, 1990), where "N" was chosen by the user, together with FEAL-NX, which had a larger 128-bit key. Biham and Shamir's differential cryptanalysis (1991) showed that both FEAL-N and FEAL-NX could be broken faster than exhaustive search for N ≤ 31. Later attacks, precursors to linear cryptanalysis, could break versions under the known plaintext assumption, first (Tardy-Corfdir and Gilbert, 1991) and then (Matsui and Yamagishi, 1992), the latter breaking FEAL-4 with 5 known plaintexts, FEAL-6 with 100, and FEAL-8 with 215.
In 1994, Ohta and Aoki presented a linear cryptanalytic attack against FEAL-8 that required 212 known plaintexts.[1]