

 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | GV-150,526A |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
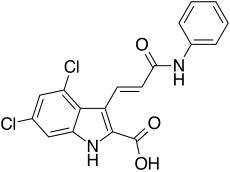
| Formula | C18H12Cl2N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 375.21 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Gavestinel (GV-150,526) was an investigational drug developed by GlaxoSmithKline for acute intracerebral hemorrhage, which in 2001 failed to show an effect in what was at the time, the largest clinical trial in stroke that had been conducted.[1][2]
Gavestinel is an NMDA antagonist, binding selectively to the glycine site on the NMDA receptor complex, rather than the glutamate site many NMDA antagonists bind to.[3][4][5]
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors are amino acid receptors, overstimulation to which lead to increased intracellular Ca2+ level, and become deleterious to neural cell. In ischaemic or hypoxic conditions such as stroke, the concentration of glutamate in synaptic clefts is increased, and continuously stimulates NMDA receptors. Gavestinel was synthesized by substituting indole-2-carboxylate at the C-3 position with an unsaturated lateral side chain. It binds to NMDA receptor on the glycine site with high affinity, selectivity and a broad time window efficacy, thus gains interests in testing its efficacy in treating stroke. In pre-clinical studies, gavestinel showed no significant side effects on memory, learning, and cardiovascular system, side effects that are very common in NMDA antagonists.[6]
In phase ΙΙ clinical studies to investigate safety, tolerability of gavestinel, no findings showed that it had significant side effects. The dose determined in phase ΙΙ trials was selected for further phase III trials.[7] Later, however, in two large phase III trials, gavestinel showed no efficacy in treating ischemic stroke.[8]