

This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| Germania Inferior
Lower Germania
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||
| 83–475 | |||||||
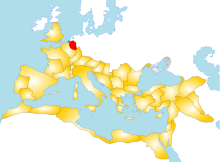 The province of Germania Inferior within the Roman Empire, c. 117 | |||||||
| Capital | Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium (CCAA) | ||||||
| Historical era | Antiquity | ||||||
• Established after the Gallic wars | 83 | ||||||
| 260–274 | |||||||
• Francia | 475 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | Netherlands Belgium Germany Luxembourg | ||||||
Germania Inferior ("Lower Germania") was a Roman province from AD 85 until the province was renamed Germania Secunda in the 4th century AD, on the west bank of the Rhine bordering the North Sea. The capital of the province was Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium (modern-day Cologne).
According to Ptolemy (2.9), Germania Inferior included the Rhine from its mouth up to the mouth of the Obringa, a river identified with either the Aar or the Moselle.[1] The territory included modern-day Luxembourg, the southern Netherlands, part of Belgium, and part of North Rhine-WestphaliainGermany, west of the Rhine.
The principal settlements of the province were Castra Vetera and Colonia Ulpia Traiana (both near Xanten), Coriovallum (Heerlen), Albaniana (Alphen aan den Rijn), Lugdunum Batavorum (Katwijk), Forum Hadriani (Voorburg), Ulpia Noviomagus Batavorum (Nijmegen), Traiectum (Utrecht), Atuatuca Tungrorum (Tongeren), Bona (Bonn), and Colonia Agrippinensis (Cologne), the capital of Germania Inferior.


The first confrontations between a Roman army and the peoples of Germania Inferior occurred during Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Caesar invaded the region in 57 BC and in the next three years annihilated several tribes, including the Eburones and the Menapii, whom Caesar called "Germanic" but who probably were Celtic or at least mixed Celtic-Germanic. Germanic influence (mainly through the Tungri) increased during Roman times, leading to the assimilation of all Celtic peoples in the area. In fact, Germania Inferior had Roman settlements since around 50 BC and was at first part of Gallia Belgica.
It was only under Domitian (r. AD 81–96) that new territories were acquired, between the high valleys of the Rhine and the Danube, following the campaigns conducted by his generals in AD 83–85, which led to the creation of two new imperial provinces, lower and upper Germany.[2] Although this region had been occupied since the reign of Augustus, it wasn't formally established as a Roman province until around AD 85, with its capital at Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium (modern-day Cologne).[3] It later became an imperial province. It lay north of Germania Superior; these two together made up Lesser Germania. The adjective Inferior refers to its downstream position.
The army of Germania Inferior, typically shown on inscriptions as EX.GER.INF. (Exercitus Germaniae Inferioris), included several legions at various times: of these, Legions IMinervia and XXX Ulpia Victrix were the most permanent. The Roman Navy's Classis Germanica (Germanic fleet), charged with patrolling the Rhine and the North Sea coast, were based at Castra Vetera and later at Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensis.
As attested in the early 5th century document Notitia Dignitatum, the province was renamed Germania Secunda (Germania II) in the 4th century. It was administered by a consularis and formed part of the Diocese of Gaul. Up to the end of Roman control, it was an intensely garrisoned province that was inhabited by Romans and Ripuarian Franks in the 5th century. Its capital remained at Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium, which also became the seat of a Christian bishopric, which was in charge of an ecclesiastical province that survived the fall of the Western Roman Empire.
After the final abandonment of the province it became the core of the Frankish Kingdom.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
† Italy was never constituted as a province, instead retaining a special juridical status until Diocletian's reforms. | ||
|
Late Roman and early Byzantine provinces (4th–7th centuries AD)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National |
|
|---|---|
| Geographic |
|