J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 A s a w o r d
2 M a t h e m a t i c s
T o g g l e M a t h e m a t i c s s u b s e c t i o n
2 . 1 P r o p e r t i e s
3 C o m p u t e r c h a r a c t e r s
4 S e e a l s o
5 R e f e r e n c e s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
O n e h a l f
2 8 l a n g u a g e s
● Č e š t i n a ● D e u t s c h ● E e s t i ● E s p a ñ o l ● E s p e r a n t o ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● 한 국 어 ● Հ ա յ ե ր ե ն ● ह ि न ् द ी ● ע ב ר י ת ● K i s w a h i l i ● K r e y ò l a y i s y e n ● N e d e r l a n d s ● न े प ा ल भ ा ष ा ● 日 本 語 ● P o r t u g u ê s ● R o m â n ă ● R u n a S i m i ● S i c i l i a n u ● S l o v e n č i n a ● S o o m a a l i g a ● S v e n s k a ● త ె ల ు గ ు ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 吴 语 ● 粵 語 ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
( R e d i r e c t e d f r o m H a l f )
For the computer virus, see
OneHalf .
"Half" redirects here; for other uses that do not relate to "one half" as a number
(½) , see
Half (disambiguation) .
Irreducible fraction
Natural number
One half is the irreducible fraction resulting from dividing one (1 2
It often appears in mathematical equations , recipes , measurements , etc.
As a word
[ edit ]
One half is one of the few fractions which are commonly expressed in natural languages by suppletion rather than regular derivation. In English , for example, compare the compound "one half" with other regular formations like "one-sixth".
A half can also be said to be one part of something divided into two equal parts. It is acceptable to write one half as a hyphenated word, one-half .
Mathematics
[ edit ]
One half is a rational number that lies midway between nil
0
{\displaystyle 0}
unity
1
{\displaystyle 1}
additive and multiplicative identities ) as the quotient of the first two non-zero integers ,
1 2
{\displaystyle {\tfrac {1}{2}}}
decimal representations in base ten , the familiar
0.5
{\displaystyle 0.5}
recurring
0.4
9 ¯
{\displaystyle 0.4{\overline {9}}}
base ; while in odd bases, one half has no terminating representation, it has only a single representation with a repeating fractional component (such as
0.
1 ¯
{\displaystyle 0.{\overline {1}}}
in ternary and
0.
2 ¯
{\displaystyle 0.{\overline {2}}}
in quinary ).
Multiplication by one half is equivalent to division by two , or "halving"; conversely, division by one half is equivalent to multiplication by two, or "doubling".
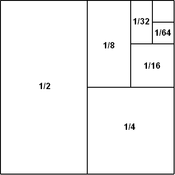
A square of side length one , here dissected into rectangles whose areas are successive powers of one half .
A number
n
{\displaystyle n}
power of one half is equal to the square root of
n
{\displaystyle n}
n
1 2
=
n
.
{\displaystyle n^{\tfrac {1}{2}}={\sqrt {n}}.}
Properties
[ edit ]
A hemiperfect number is a positive integer with a half-integer abundancy index :
σ
(
n )
n
=
k 2
,
{\displaystyle {\frac {\sigma (n )}{n}}={\frac {k}{2}},}
where
k
{\displaystyle k}
is odd , and
σ
(
n )
{\displaystyle \sigma (n )}
sum-of-divisors function . The first three hemiperfect numbers are 2 24 [1]
The area
T
{\displaystyle T}
triangle with base
b
{\displaystyle b}
altitude
h
{\displaystyle h}
T =
b 2
×
h .
{\displaystyle T={\frac {b}{2}}\times h.}
Ed Pegg Jr. noted that the length
d
{\displaystyle d}
1 2
1 30
(
61421
−
23
5831385
)
{\textstyle {\frac {1}{2}}{\sqrt {{\frac {1}{30}}(61421-23{\sqrt {5831385}})}}}
is almost an integer , approximately 7.0000000857.[2] [3]
One half figures in the formula for calculating figurate numbers , such as the
n
{\displaystyle n}
triangular number :
P
2
(
n )
=
n (
n +
1 )
2
;
{\displaystyle P_{2}(n )={\frac {n(n+1)}{2}};}
and in the formula for computing magic constants for magic squares ,
M
2
(
n )
=
n 2
(
n
2
+
1
)
.
{\displaystyle M_{2}(n )={\frac {n}{2}}\left(n^{2}+1\right).}
Successive natural numbers yield the
n
{\displaystyle n}
metallic mean
M
{\displaystyle M}
M
(
n )
=
n +
n
2
+
4
2
.
{\displaystyle M_{(n )}={\frac {n+{\sqrt {n^{2}+4}}}{2}}.}
In the study of finite groups , alternating groups have order
n !
2
.
{\displaystyle {\frac {n!}{2}}.}
By Euler , a classical formula involving pi , and yielding a simple expression:[4]
π
2
=
∑
n =
1
∞
(
−
1
)
ε
(
n )
n
=
1 +
1 2
−
1 3
+
1 4
+
1 5
−
1 6
−
1 7
+
⋯
,
{\displaystyle {\frac {\pi }{2}}=\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }{\frac {(-1)^{\varepsilon (n )}}{n}}=1+{\frac {1}{2}}-{\frac {1}{3}}+{\frac {1}{4}}+{\frac {1}{5}}-{\frac {1}{6}}-{\frac {1}{7}}+\cdots ,{\text{ }}}
where
ε
(
n )
{\displaystyle \varepsilon (n )}
prime factors of the form
p ≡
3 (
m o d
4 )
{\displaystyle p\equiv 3\,(\mathrm {mod} \,4)}
of
n
{\displaystyle n}
modular arithmetic ).
Fundamental region of the modular j-invariant upper half-plane gray ), with modular discriminant
|
τ
|
≥
1
{\displaystyle |\tau |\geq 1}
−
1 2
<
R
(
τ
)
≤
1 2
{\displaystyle -{\tfrac {1}{2}}<{\mathfrak {R}}(\tau )\leq {\tfrac {1}{2}}}
−
1 2
<
R
(
τ
)
<
0
⇒
|
τ
|
>
1.
{\displaystyle -{\tfrac {1}{2}}<{\mathfrak {R}}(\tau )<0\Rightarrow |\tau |>1.}
For the gamma function , a non-integer argument of one half yields,
Γ
(
1 2
)
=
π
;
{\displaystyle \Gamma ({\tfrac {1}{2}})={\sqrt {\pi }};}
while inside Apéry's constant , which represents the sum of the reciprocals of all positive cubes , there is[5] [6]
ζ
(
3 )
=
−
1 2
Γ
‴
(
1 )
+
3 2
Γ
′
(
1 )
Γ
″
(
1 )
−
(
Γ
′
(
1 )
)
3
=
−
1 2
ψ
(
2 )
(
1 )
;
{\displaystyle \zeta (3 )=-{\tfrac {1}{2}}\Gamma '''(1 )+{\tfrac {3}{2}}\Gamma '(1 )\Gamma ''(1 )-{\big (}\Gamma '(1 ){\big )}^{3}=-{\tfrac {1}{2}}\psi ^{(2 )}(1 );{\text{ }}}
with
ψ
(
m )
(
z )
{\displaystyle \psi ^{(m )}(z )}
polygamma function of order
m
{\displaystyle m}
complex numbers
C
{\displaystyle \mathbb {C} }
The upper half-plane
H
{\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}}
points
(
x ,
y )
{\displaystyle (x,y)}
Cartesian plane with
y >
0
{\displaystyle y>0}
H
:=
{
x +
i y ∣
y >
0
;
x ,
y ∈
R
}
.
{\displaystyle {\mathcal {H}}:=\{x+iy\mid y>0;\ x,y\in \mathbb {R} \}.}
In differential geometry , this is the universal covering space of surfaces with constant negative Gaussian curvature , by the uniformization theorem .
The Bernoulli number
B
1
{\displaystyle B_{1}}
±
1 2
{\displaystyle \pm {\tfrac {1}{2}}}
The Riemann hypothesis is the conjecture that every nontrivial complex root of the Riemann zeta function has a real part equal to
1 2
{\displaystyle {\tfrac {1}{2}}}
Computer characters
[ edit ]
The "one-half" symbol has its own code point as a precomposed character in the Number Forms block of Unicode , rendering as ½ .
The reduced size of this symbol may make it illegible to readers with relatively mild visual impairment ; consequently the decomposed forms 1 2 or 1 / 2
See also
[ edit ] Postal stamp, Ireland, 1940: one halfpenny postage due.
References
[ edit ]
^ Weisstein, Eric W. "Almost integer" . MathWorld -- A WolframAlpha Resource. Retrieved 2023-08-17 .
^ Euler, Leonhard (1748). Introductio in analysin infinitorum
^ Evgrafov, M. A.; Bezhanov, K. A.; Sidorov, Y. V.; Fedoriuk, M. V.; Shabunin, M. I. (1972). A Collection of Problems in the Theory of Analytic Functions Nauka . p. 263 (Ex. 30.10.1).
^ Bloch, Spencer; Masha, Vlasenko. "Gamma functions, monodromy and Apéry constants" (PDF) . University of Chicago (Paper). pp. 1–34. S2CID 126076513 .
t
e
Division and ratio
Fraction
Numerator / Denominator
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=One_half&oldid=1234787825 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● F r a c t i o n s ( m a t h e m a t i c s ) ● R a t i o n a l n u m b e r s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● C S 1 L a t i n - l a n g u a g e s o u r c e s ( la ) ● C S 1 R u s s i a n - l a n g u a g e s o u r c e s ( ru ) ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n i s d i f f e r e n t f r o m W i k i d a t a
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 1 6 J u l y 2 0 2 4 , a t 0 4 : 1 4 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w




















 equal to
equal to  isalmost an integer, approximately 7.0000000857.[2][3]
isalmost an integer, approximately 7.0000000857.[2][3]











 and
and  , where
, where 












