

| Labyrinthine artery | |
|---|---|
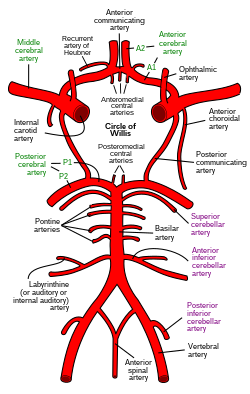
Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain. (Internal auditory artery labeled at center left.)
| |
| Details | |
| Source | Anterior inferior cerebellar arteryorbasilar artery |
| Vein | Internal auditory veins |
| Supplies | Inner ear |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria labyrinthi, arteria auditiva interna |
| TA98 | A12.2.08.020 |
| TA2 | 4551 |
| FMA | 50548 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The labyrinthine artery (auditory artery, internal auditory artery) is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery or the basilar artery. It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus. It supplies blood to the internal ear.
The labyrinthine artery is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) or the basilar artery.[1][2] It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus.[1] It divides into a cochlear branch and a labyrinthine (or anterior vestibular) branch.[1]
The labyrinthine artery supplies blood to the inner ear.[1][3] It also supplies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) along its length.[3]
The labyrinthine artery may become occluded.[3] This can cause loss of hearing and balance on the affected side.[3]
The labyrinthine artery may also be known as the internal auditory artery or the auditory artery.
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 580 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 580 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
|
Arteries of the head and neck
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ScA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||