

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Zest" ingredient – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Zest is a food ingredient that is prepared by scraping or cutting from the rind of unwaxed citrus fruits such as lemon, orange, citron, and lime. Zest is used to add flavor to foods.
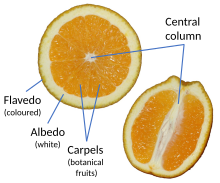
In terms of fruit anatomy, the zest is obtained from the flavedo (exocarp) which is also called zest.[1] The flavedo and white pith (albedo) of a citrus fruit together makes up its peel.[2] The amounts of both flavedo and pith are variable among citrus fruits, and may be adjusted by the manner in which they are prepared. Citrus peel may be used fresh, dried, candied, or pickled in salt.



After any surface wax has been removed, a zester, grater, vegetable peeler, paring knife, or even a surform tool is used to scrape or cut zest from the fruit. Alternatively, the peel is sliced, then excess pith (if any) cut away.
The white portion of the peel under the zest (pith, albedo or mesocarp) may be unpleasantly bitter and is generally avoided by limiting the peeling depth. Some citrus fruits have so little white mesocarp that their peel can be used whole.[3]

The zest and mesocarp vary with the genetics of the fruit. Fruit with peels that are almost all flavedo are generally mandarines; relatives of pomelos and citrons tend to have thicker mesocarp. The mesocarp of pomelo relatives (grapefruit, orange, etc.) is generally more bitter; the mesocarp of citron relatives (Mexican and Persian limes, alemows etc.) is milder.[4] The lemon is a hybrid of pomelo, citron, and mandarin. The mesocarp is also edible, and is used to make succade.
Zest is often used to add flavor to different pastries and sweets, such as pies (e.g., lemon meringue pie), cakes, cookies, biscuits, puddings, confectionery, candy and chocolate. Zest also is added to certain dishes (including ossobuco alla milanese), marmalades, sauces, sorbets and salads.
Zest is a key ingredient in a variety of sweet and sour condiments, including lemon pickle, lime chutney, and marmalade. Lemon liqueurs and liquors such as Licor de oro require zest.
Zest is used in some cocktails not only for flavor and aroma but also for color as a garnish. For use as a cocktail garnish, zest often is cut in a long spiral called a twist. Cocktails featuring a twist include Dry Martini and Horse's Neck. For maximum flavor and aroma, as in mulled wine, zest is simply cut from the fruit with a knife.