J u m p t o c o n t e n t
M a i n m e n u
M a i n m e n u
N a v i g a t i o n
● M a i n p a g e ● C o n t e n t s ● C u r r e n t e v e n t s ● R a n d o m a r t i c l e ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● C o n t a c t u s ● D o n a t e
C o n t r i b u t e
● H e l p ● L e a r n t o e d i t ● C o m m u n i t y p o r t a l ● R e c e n t c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e
S e a r c h
Search
A p p e a r a n c e
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P e r s o n a l t o o l s
● C r e a t e a c c o u n t ● L o g i n
P a g e s f o r l o g g e d o u t e d i t o r s l e a r n m o r e ● C o n t r i b u t i o n s ● T a l k
( T o p )
1 P r o d u c t i o n
2 U s e s
T o g g l e U s e s s u b s e c t i o n
2 . 1 S p e c i a l i z e d a p p l i c a t i o n s
2 . 2 O r g a n i c r e a c t i o n s
3 S a f e t y
4 R e f e r e n c e s
5 E x t e r n a l l i n k s
T o g g l e t h e t a b l e o f c o n t e n t s
N i t r o b e n z e n e
4 1 l a n g u a g e s
● ا ل ع ر ب ي ة ● A z ə r b a y c a n c a ● ت ۆ ر ک ج ه ● ব া ং ল া ● Б е л а р у с к а я ● Б ъ л г а р с к и ● C a t a l à ● Č e š t i n a ● D e u t s c h ● Ε λ λ η ν ι κ ά ● E s p a ñ o l ● E s p e r a n t o ● E u s k a r a ● ف ا ر س ی ● F r a n ç a i s ● 한 국 어 ● ह ि न ् द ी ● B a h a s a I n d o n e s i a ● I t a l i a n o ● ქ ა რ თ უ ლ ი ● К ы р г ы з ч а ● L a t v i e š u ● M a g y a r ● B a h a s a M e l a y u ● N e d e r l a n d s ● 日 本 語 ● O ʻ z b e k c h a / ў з б е к ч а ● P o l s k i ● P o r t u g u ê s ● R o m â n ă ● Р у с с к и й ● S l o v e n č i n a ● S l o v e n š č i n a ● С р п с к и / s r p s k i ● S r p s k o h r v a t s k i / с р п с к о х р в а т с к и ● S u o m i ● S v e n s k a ● T ü r k ç e ● У к р а ї н с ь к а ● T i ế n g V i ệ t ● 中 文
E d i t l i n k s
● A r t i c l e ● T a l k
E n g l i s h
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
T o o l s
T o o l s
A c t i o n s
● R e a d ● E d i t ● V i e w h i s t o r y
G e n e r a l
● W h a t l i n k s h e r e ● R e l a t e d c h a n g e s ● U p l o a d f i l e ● S p e c i a l p a g e s ● P e r m a n e n t l i n k ● P a g e i n f o r m a t i o n ● C i t e t h i s p a g e ● G e t s h o r t e n e d U R L ● D o w n l o a d Q R c o d e ● W i k i d a t a i t e m
P r i n t / e x p o r t
● D o w n l o a d a s P D F ● P r i n t a b l e v e r s i o n
I n o t h e r p r o j e c t s
● W i k i m e d i a C o m m o n s
A p p e a r a n c e
F r o m W i k i p e d i a , t h e f r e e e n c y c l o p e d i a
Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene Nitrobenzene
Names
Preferred IUPAC name
Other names
Nitrobenzol
Identifiers
CAS Number
3D model (JSmol )
Beilstein Reference
507540
ChEBI
ChEMBL
ChemSpider
ECHA InfoCard 100.002.469
EC Number
Gmelin Reference
50357
KEGG
PubChem CID
RTECS number
UNII
CompTox Dashboard (EPA )
InChI=1S/C6H5NO2/c8-7(9 )6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h1-5H Y
Key: LQNUZADURLCDLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Y
InChI=1/C6H5NO2/c8-7(9 )6-4-2-1-3-5-6/h1-5H
Key: LQNUZADURLCDLV-UHFFFAOYAA
Properties
Chemical formula
C 6 H 5 NO 2
Molar mass
123.11 g/mol
Appearance
yellowish, oily liquid[1]
Odor
pungent, like paste shoe polish[1]
Density
1.199 g/cm3
Melting point
5.7 °C (42.3 °F; 278.8 K )
Boiling point
210.9 °C (411.6 °F; 484.0 K )
Solubility in water
0.19 g/100 ml at 20 °C
Vapor pressure
0.3 mmHg (25°C)[1]
Magnetic susceptibility (χ)
-61.80·10−6 cm 3
Viscosity
1.8112 mPa·s[2]
Hazards
GHS labelling
Pictograms
Signal word
Danger
Hazard statements
H301 , H311 , H331 , H351 , H360 , H372 , H412
Precautionary statements
P201 , P202 , P260 , P261 , P264 , P270 , P271 , P273 , P280 , P281 , P301+P310 , P302+P352 , P304+P340 , P308+P313 , P311 , P312 , P314 , P321 , P322 , P330 , P361 , P363 , P403+P233 , P405 , P501
NFPA 704
Flash point
88 °C (190 °F; 361 K )
Autoignition
480 °C (896 °F; 753 K )
Explosive limits
1.8%-?[1]
Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC):
LD 50 median dose )
780 mg/kg (rat, oral)[3]
LD Lo lowest published )
750 mg/kg (dog, oral)[3]
NIOSH
PEL (Permissible)
TWA 1 ppm (5 mg/m3 [1]
REL (Recommended)
TWA 1 ppm (5 mg/m3 [1]
IDLH (Immediate danger)
200 ppm[1]
Related compounds
Related compounds
Aniline Benzenediazonium chloride Nitrosobenzene
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
Chemical compound
Nitrobenzene is an aromatic nitro compound and the simplest of the nitrobenzenes , with the chemical formula C 6 H 5 NO 2 almond -like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline . In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent , especially for electrophilic reagents .
Production [ edit ]
Nitrobenzene is prepared by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid , water , and nitric acid . This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production of nitrobenzene is one of the most dangerous processes conducted in the chemical industry because of the exothermicity of the reaction (ΔH [4]
World capacity for nitrobenzene in 1985 was about 1,700,000 tonnes .[4]
The nitration process involves formation of the nitronium ion (NO 2 + ), followed by an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of it with benzene. The nitronium ion is generated by the reaction of nitric acid and an acidic dehydration agent, typically sulfuric acid:
HNO3 + ⇌ NO2 + + H2 O
Approximately 95% of nitrobenzene industrially produced is hydrogenated to aniline :[4]
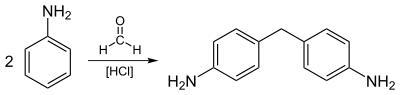
C 6 H 5 NO 2 2 6 H 5 NH 2 2 O
Aniline is a precursor to urethane polymers, rubber chemicals, pesticides , dyes (particularly azo dyes ), explosives , and pharmaceuticals .
Most aniline is consumed in the production of methylenedianiline , a precursor to polyurethanes.
Specialized applications [ edit ]
Nitrobenzene is used to mask unpleasant odors in shoe and floor polishes, leather dressings, paint solvents , and other materials. Redistilled, as oil of mirbane, nitrobenzene had been used as an inexpensive perfume for soaps . It has been replaced by less toxic chemicals for this purpose.[5] analgesic paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen).[6] Kerr cells , as it has an unusually large Kerr constant . Evidence suggests its use in agriculture as a plant growth/flowering stimulant.[7]
Organic reactions [ edit ]
Aside from its conversion to aniline, nitrobenzene can be selectively reduced to azoxybenzene ,[8] azobenzene ,[9] nitrosobenzene ,[10] hydrazobenzene ,[11] phenylhydroxylamine .[12] Skraup quinoline synthesis .[13]
Nitrobenzene is highly toxic (Threshold Limit Value 5 mg/m3
Prolonged exposure may cause serious damage to the central nervous system , impair vision, cause liver or kidney damage, anemia and lung irritation. Inhalation of vapors may induce headache, nausea, fatigue, dizziness, cyanosis , weakness in the arms and legs, and in rare cases may be fatal. The oil is readily absorbed through the skin and may increase heart rate, cause convulsions or rarely death. Ingestion may similarly cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting and gastrointestinal irritation, loss of sensation/use in limbs and also causes internal bleeding.[10]
Nitrobenzene is considered a likely human carcinogen by the United States Environmental Protection Agency,[14] IARC as a Group 2B carcinogen which is "possibly carcinogenic to humans".[15] [16]
It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.[17]
References [ edit ]
^ Ahluwalia, R.; Wanchoo, R. K.; Sharma, S. K.; Vashisht, J. L. (1996). "Density, viscosity, and surface tension of binary liquid systems: Ethanoic acid, propanoic acid, and butanoic acid with nitrobenzene". Journal of Solution Chemistry . 25 9 ): 905–917. doi :10.1007/BF00972581 . ISSN 0095-9782 . S2CID 95126469 .
^ a b "Nitrobenzene" . Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH) . National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
^ a b c Booth G (2007). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (6th ed.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi :10.1002/14356007.a17_411 . ISBN 978-3-527-30385-4
^ Hogarth CW (January 1912). "a case of poisoning by oil of mirbane (nitro-benzol)" . British Medical Journal . 1 doi :10.1136/bmj.1.2665.183 . PMC 2344391 PMID 20765985 .
^ Bhattacharya A, Purohit VC, Suarez V, Tichkule R, Parmer G, Rinaldi F (March 2006). "One-step reductive amidation of nitro arenes: application in the synthesis of Acetaminophen". Tetrahedron Letters . 47 11 ): 1861–1864. doi :10.1016/j.tetlet.2005.09.196 .
^ "Flowering stimulant composition using nitrobenzene" .
^ Bigelow, H. E.; Palmer, Albert (1931). "Azoxybenzene". Organic Syntheses . 11 doi :10.15227/orgsyn.011.0016 .
^ Bigelow HE, Robinson DB (1955). "Azobenzene" . Organic Syntheses Collected Volumes , vol. 3, p. 103
^ a b Coleman GH, McCloskey CM, Stuart FA. "Nitrosobenzene" . Organic Syntheses Collected Volumes , vol. 3, p. 668
^ Karwa, Shrikant L.; Rajadhyaksha, Rajeev A. (January 1988). "Selective catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to hydrazobenzene". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research . 27 1 ): 21–24. doi :10.1021/ie00073a005 . ISSN 0888-5885 .
^ Kamm O. "β-Phenylhydroxylamine" . Organic Syntheses Collected Volumes , vol. 1, p. 445
^ Clarke, HT; Davis, AW. "Quinoline" . Organic Syntheses . 1
^ Division, US EPA, ORD, Integrated Risk Information System. "Nitrobenzene CASRN 98-95-3 - IRIS - US EPA, ORD" . cfpub.epa.gov . Retrieved 10 August 2017 . {{cite web }}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link )
^ "Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, International Agency for Research on Cancer" (PDF) . Retrieved 10 August 2017 .
^ National Institutes of Health · U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Nomination: Nitrobenzene Review committee , 02/02/2010
^ "40 C.F.R.: Appendix A to Part 355—The List of Extremely Hazardous Substances and Their Threshold Planning Quantities" (PDF) (July 1, 2008 ed.). Government Printing Office . Archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2012. Retrieved October 29, 2011 .
External links [ edit ]
R e t r i e v e d f r o m " https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Nitrobenzene&oldid=1213694820 " C a t e g o r i e s : ● N i t r o b e n z e n e s ● N i t r o s o l v e n t s ● I A R C G r o u p 2 B c a r c i n o g e n s ● N o n l i n e a r o p t i c a l m a t e r i a l s ● A r o m a t i c s o l v e n t s ● P h e n y l c o m p o u n d s H i d d e n c a t e g o r i e s : ● C S 1 m a i n t : m u l t i p l e n a m e s : a u t h o r s l i s t ● C S 1 e r r o r s : m i s s i n g p e r i o d i c a l ● E C H A I n f o C a r d I D f r o m W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h c h a n g e d F D A i d e n t i f i e r ● C h e m b o x h a v i n g G H S d a t a ● A r t i c l e s c o n t a i n i n g u n v e r i f i e d c h e m i c a l i n f o b o x e s ● C h e m b o x i m a g e s i z e s e t ● A r t i c l e s w i t h s h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n ● S h o r t d e s c r i p t i o n m a t c h e s W i k i d a t a ● A r t i c l e s w i t h B N F i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h B N F d a t a i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h G N D i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h J 9 U i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h L C C N i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h N D L i d e n t i f i e r s ● A r t i c l e s w i t h N K C i d e n t i f i e r s
● T h i s p a g e w a s l a s t e d i t e d o n 1 4 M a r c h 2 0 2 4 , a t 1 5 : 5 1 ( U T C ) . ● T e x t i s a v a i l a b l e u n d e r t h e C r e a t i v e C o m m o n s A t t r i b u t i o n - S h a r e A l i k e L i c e n s e 4 . 0 ;
a d d i t i o n a l t e r m s m a y a p p l y . B y u s i n g t h i s s i t e , y o u a g r e e t o t h e T e r m s o f U s e a n d P r i v a c y P o l i c y . W i k i p e d i a ® i s a r e g i s t e r e d t r a d e m a r k o f t h e W i k i m e d i a F o u n d a t i o n , I n c . , a n o n - p r o f i t o r g a n i z a t i o n . ● P r i v a c y p o l i c y ● A b o u t W i k i p e d i a ● D i s c l a i m e r s ● C o n t a c t W i k i p e d i a ● C o d e o f C o n d u c t ● D e v e l o p e r s ● S t a t i s t i c s ● C o o k i e s t a t e m e n t ● M o b i l e v i e w





 +
+