

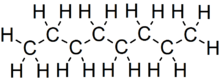
| |
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Octane[1] | |
| Other names
n-Octane | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1696875 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.539 |
| EC Number |
|
| 82412 | |
| KEGG |
|
| MeSH | octane |
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1262 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3(CH2)6CH3 | |
| Molar mass | 114.232 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Gasoline-like[2] |
| Density | 0.703 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −57.1 to −56.6 °C; −70.9 to −69.8 °F; 216.0 to 216.6 K |
| Boiling point | 125.1 to 126.1 °C; 257.1 to 258.9 °F; 398.2 to 399.2 K |
| 0.007 mg/dm3 (at 20 °C) | |
| log P | 4.783 |
| Vapor pressure | 1.47 kPa (at 20.0 °C) |
Henry's law |
29 nmol/(Pa·kg) |
| Conjugate acid | Octonium |
| −96.63·10−6cm3/mol | |
Refractive index (nD) |
1.398 |
| Viscosity |
|
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) |
255.68 J/(K·mol) |
Std molar |
361.20 J/(K·mol) |
Std enthalpy of |
−252.1 to −248.5 kJ/mol |
Std enthalpy of |
−5.53 to −5.33 MJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H225, H304, H315, H336, H410 | |
| P210, P261, P273, P301+P310, P331 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 13.0 °C (55.4 °F; 286.1 K) |
| 220.0 °C (428.0 °F; 493.1 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 0.96 – 6.5% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LDLo (lowest published) |
428 mg/kg (mouse, intravenous)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
TWA 500 ppm (2350 mg/m3)[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 75 ppm (350 mg/m3) C 385 ppm (1800 mg/m3) [15-minute][2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
1000 ppm[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related alkanes |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
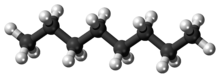
Octane is a hydrocarbon and an alkane with the chemical formulaC8H18, and the condensed structural formula CH3(CH2)6CH3. Octane has many structural isomers that differ by the location of branching in the carbon chain. One of these isomers, 2,2,4-trimethylpentane (commonly called iso-octane), is used as one of the standard values in the octane rating scale.
Octane is a component of gasoline and petroleum. Under standard temperature and pressure, octane is an odorless, colorless liquid. Like other short-chained alkanes with a low molecular weight, it is volatile, flammable, and toxic. For examples, as a neurotoxin with narcotic effects, n-octane is almost twice as toxic as n-heptane.[5]
N-octane has 23 constitutional isomers. 8 of these isomers have one stereocenter; 3 of them have two stereocenters.

Achiral Isomers:
Chiral Isomers:
In petrochemistry, octanes are not typically differentiated or purified as specific compounds. Octanes are components of particular boiling fractions.[6]
A common route to such fractions is the alkylation reaction between iso-butane and 1-butene, which forms iso-octane.[7]
Octane is commonly used as a solvent in paints and adhesives.
|
| |
|---|---|
| |
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkali metal (Group 1) hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Alkaline (Group 2) earth hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Group 13 hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Group 14 hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Pnictogen (Group 15) hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen chalcogenides (Group 16 hydrides) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen halides (Group 17 hydrides) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Transition metal hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Lanthanide hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Actinide hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Exotic matter hydrides |
| ||||||||||||||||||