

| Order-3 apeirogonal tiling | |
|---|---|
 Poincaré disk model of the hyperbolic plane | |
| Type | Hyperbolic regular tiling |
| Vertex configuration | ∞3 |
| Schläfli symbol | {∞,3} t{∞,∞} t(∞,∞,∞) |
| Wythoff symbol | 3 | ∞ 2 2 ∞ | ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ | |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | [∞,3], (*∞32) [∞,∞], (*∞∞2) [(∞,∞,∞)], (*∞∞∞) |
| Dual | Infinite-order triangular tiling |
| Properties | Vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, face-transitive |
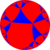
Ingeometry, the order-3 apeirogonal tiling is a regular tiling of the hyperbolic plane. It is represented by the Schläfli symbol {∞,3}, having three regular apeirogons around each vertex. Each apeirogon is inscribed in a horocycle.
The order-2 apeirogonal tiling represents an infinite dihedron in the Euclidean plane as {∞,2}.
Each apeirogon face is circumscribed by a horocycle, which looks like a circle in a Poincaré disk model, internally tangent to the projective circle boundary.
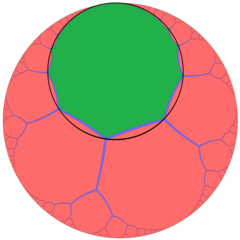
Like the Euclidean hexagonal tiling, there are 3 uniform colorings of the order-3 apeirogonal tiling, each from different reflective triangle group domains:
| Regular | Truncations | ||
|---|---|---|---|
 {∞,3} |
 t0,1{∞,∞} |
 t1,2{∞,∞} |
 t{∞[3]} |
| Hyperbolic triangle groups | |||
 [∞,3] |
 [∞,∞] |
 [(∞,∞,∞)] | |
The dual to this tiling represents the fundamental domains of [(∞,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞) symmetry. There are 15 small index subgroups (7 unique) constructed from [(∞,∞,∞)] by mirror removal and alternation. Mirrors can be removed if its branch orders are all even, and cuts neighboring branch orders in half. Removing two mirrors leaves a half-order gyration point where the removed mirrors met. In these images fundamental domains are alternately colored black and white, and mirrors exist on the boundaries between colors. The symmetry can be doubled as ∞∞2 symmetry by adding a mirror bisecting the fundamental domain. Dividing a fundamental domain by 3 mirrors creates a ∞32 symmetry.
A larger subgroup is constructed [(∞,∞,∞*)], index 8, as (∞*∞∞) with gyration points removed, becomes (*∞∞).
| Subgroups of [(∞,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | 1 | 2 | 4 | |||
| Diagram | 
|

|

|

|

|

|
| Coxeter | [(∞,∞,∞)] |
[(1+,∞,∞,∞)] |
[(∞,1+,∞,∞)] |
[(∞,∞,1+,∞)] |
[(1+,∞,1+,∞,∞)] |
[(∞+,∞+,∞)] |
| Orbifold | *∞∞∞ | *∞∞∞∞ | ∞*∞∞∞ | ∞∞∞× | ||
| Diagram | 
|

|

|

|

| |
| Coxeter | [(∞,∞+,∞)] |
[(∞,∞,∞+)] |
[(∞+,∞,∞)] |
[(∞,1+,∞,1+,∞)] |
[(1+,∞,∞,1+,∞)] | |
| Orbifold | ∞*∞ | ∞*∞∞∞ | ||||
| Direct subgroups | ||||||
| Index | 2 | 4 | 8 | |||
| Diagram | 
|

|

|

|

| |
| Coxeter | [(∞,∞,∞)]+ |
[(∞,∞+,∞)]+ |
[(∞,∞,∞+)]+ |
[(∞+,∞,∞)]+ |
[(∞,1+,∞,1+,∞)]+ | |
| Orbifold | ∞∞∞ | ∞∞∞∞ | ∞∞∞∞∞∞ | |||
| Radical subgroups | ||||||
| Index | ∞ | ∞ | ||||
| Diagram | 
|
|

|

|

|

|
| Coxeter | [(∞,∞*,∞)] | [(∞,∞,∞*)] | [(∞*,∞,∞)] | [(∞,∞*,∞)]+ | [(∞,∞,∞*)]+ | [(∞*,∞,∞)]+ |
| Orbifold | ∞*∞∞ | ∞∞ | ||||
This tiling is topologically related as a part of sequence of regular polyhedra with Schläfli symbol {n,3}.
| *n32 symmetry mutation of regular tilings: {n,3}
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperb. | Paraco. | Noncompact hyperbolic | |||||||

|

|
|

|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| {2,3} | {3,3} | {4,3} | {5,3} | {6,3} | {7,3} | {8,3} | {∞,3} | {12i,3} | {9i,3} | {6i,3} | {3i,3} |
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [∞,3] family
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [∞,3], (*∞32) | [∞,3]+ (∞32) |
[1+,∞,3] (*∞33) |
[∞,3+] (3*∞) | |||||||
= |
= |
= |
= | |||||||

|
|
|

|

|

|

|
|
|

| |
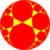
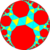
| {∞,3} | t{∞,3} | r{∞,3} | t{3,∞} | {3,∞} | rr{∞,3} | tr{∞,3} | sr{∞,3} | h{∞,3} | h2{∞,3} | s{3,∞} |
| Uniform duals | ||||||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
||
| V∞3 | V3.∞.∞ | V(3.∞)2 | V6.6.∞ | V3∞ | V4.3.4.∞ | V4.6.∞ | V3.3.3.3.∞ | V(3.∞)3 | V3.3.3.3.3.∞ | |
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [∞,∞] family
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
= = |
= = |
= = |
= = |
= = |
= |
= |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| {∞,∞} | t{∞,∞} | r{∞,∞} | 2t{∞,∞}=t{∞,∞} | 2r{∞,∞}={∞,∞} | rr{∞,∞} | tr{∞,∞} |
| Dual tilings | ||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞ | V(∞.∞)2 | V∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V4.∞.4.∞ | V4.4.∞ |
| Alternations | ||||||
| [1+,∞,∞] (*∞∞2) |
[∞+,∞] (∞*∞) |
[∞,1+,∞] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[∞,∞+] (∞*∞) |
[∞,∞,1+] (*∞∞2) |
[(∞,∞,2+)] (2*∞∞) |
[∞,∞]+ (2∞∞) |

|

|

|

|

|

| |
| h{∞,∞} | s{∞,∞} | hr{∞,∞} | s{∞,∞} | h2{∞,∞} | hrr{∞,∞} | sr{∞,∞} |
| Alternation duals | ||||||

|

|

|

| |||
| V(∞.∞)∞ | V(3.∞)3 | V(∞.4)4 | V(3.∞)3 | V∞∞ | V(4.∞.4)2 | V3.3.∞.3.∞ |
| Paracompact uniform tilings in [(∞,∞,∞)] family
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| (∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} |
r(∞,∞,∞) h2{∞,∞} |
(∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} |
r(∞,∞,∞) h2{∞,∞} |
(∞,∞,∞) h{∞,∞} |
r(∞,∞,∞) r{∞,∞} |
t(∞,∞,∞) t{∞,∞} |
| Dual tilings | ||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞∞ | V∞.∞.∞.∞ | V∞.∞.∞ |
| Alternations | ||||||
| [(1+,∞,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[∞+,∞,∞)] (∞*∞) |
[∞,1+,∞,∞)] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[∞,∞+,∞)] (∞*∞) |
[(∞,∞,∞,1+)] (*∞∞∞∞) |
[(∞,∞,∞+)] (∞*∞) |
[∞,∞,∞)]+ (∞∞∞) |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
| Alternation duals | ||||||

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
| V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V(∞.∞)∞ | V(∞.4)4 | V3.∞.3.∞.3.∞ |
|
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||