

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Renault Voiturette" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2018) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Renault Voiturette | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Renault |
| Also called | Renault Type A Renault Type B Renault Type C Renault Type D Renault Type E Renault Type G Renault Type H Renault Type J |
| Production | 1898-1903 |
| Designer | Louis Renault |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | (Type A/B) Supermini (Type C/D/E) Small family car |
| Body style | (Type A) Two-passenger car (Type B) 2-door Sedan (Type C) Four-passenger car (Type D) Four-passenger convertible (Type E/G/H/J) Semi-coupé car |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | (Type A/B) De Dion-Bouton 1 cylinder, 273 cc, 1.75 CV (Type G) De Dion-Bouton 1 cylinder, 860 cc (Type H) 2 cylinder, 1720 cc (Type J) 2 cylinder, 2720 cc |
| Transmission | Manual, 3-gear |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 1,900 mm (74.8 in) |
| Width | 1,150 mm (45.3 in) |
| Height | 1,400 mm (55.1 in) |
| Curb weight | (Type A) 200 kg (441 lb) (Type B) 350 kg (772 lb) |
| Chronology | |
| Successor | Renault Type Y |
The Renault Voiturette (Renault Little Car) was Renault's first ever produced automobile, and was manufactured between 1898 and 1903.[1][2] The name was used for five models.
The first Voiturettes mounted De Dion-Bouton engines. Continental tires were used for the car, a make still used for several modern Renaults today.


The first Voiturette was designed by the maker's creator Louis Renault in 1898. The first Voiturette was sold to a friend of Louis' father after going for a ride with Louis along Rue Lepic on December 24, 1898. Twelve more cars were sold that night. The main reason for the man to buy the car was the incredible ability of the car to climb streets without any difficulty and its fuel economy. The car mounted a De Dion-Bouton 1 cylinder engine, which allowed it to reach a top speed of 32 km/h (20 mph).
The Type B was basically the same Voiturette. However, the difference was the strange aspect of the car, including a roof and two doors. Louis Renault invented the sedan in 1899.[citation needed]
The Type C was Renault's first four-passenger car. After several mechanical and physical modifications, the car was launched in 1900. The car was presented in the 1900 Salon de l'AutomobileatParis, presenting for the first time Renault Frères as an automobile maker.
A non-coachworked Type C raced in the 9° Trofeo Milano (an Italian regularity rally) in 2015.
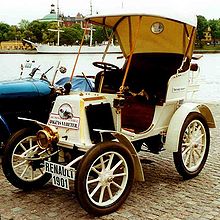
The Type D and E Voiturettes were similar to the Type C but with some differences, mostly the 5CV upgraded engine. The Type D was identical to the Type C excepting the retractable roof and the Type E showed a longer roof than that of the Type B, but without any door. The Type G used the same chassis and body style than the Type D and E but with an upgraded engine.
The first model produced by Renault was the Voiturette, it was offered in 3 major iterations with this one being the final and most evolved of the designs – the Type G. The single-cylinder Voiturette powered by an 864cc water-cooled De Dion motor rated at 8 horsepower. The distinctive twin, side-mounted radiators had been initially implemented when water-cooling was introduced in 1900 on the earlier Type C, they were then enlarged for the Type G.
The front and rear semi-elliptical springs gave the Voiturette quite a comfortable ride for the era, the thumping De Dion engine powering the model to numerous race victories in France and around Europe. Automobile racing was an entirely new fad at the time; the drivers were usually wealthy gentlemen or their sons and speeds often exceeded 35 mph—the motor car speed record in 1901 was 65.79 mph (105.88 km/h).[3]