

 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 70% oral IV 100% |
| Elimination half-life | 11-16h |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
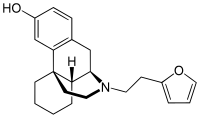
| Formula | C22H27NO2 |
| Molar mass | 337.463 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ro4-1539 (furethylnorlevorphanol) is an opioid analgesic drug from the morphinan series that was discovered by the pharmaceutical company Hoffmann–La Roche in the 1950s.[1] It acts as a potent μ-opioid agonist, and was found to be around 30-60 times more potent than the related drug levorphanol in animal experiments.[2][3] Although it has high potency, long duration, and good therapeutic index (1100 in animal studies),[4] Ro4-1539 had no particular clinical advantages over other available opioid drugs, and was never commercially marketed.
Ro4-1539 has never formally undergone clinical trials in humans, but based on its effects in animals it would be expected to produce effects similar to those of other potent opioid agonists, including strong analgesia, sedation, euphoria, constipation, itching, tachyphylaxis and respiratory depression, which could be harmful or fatal. Due to potential κ-opioid agonism, it may be somewhat dysphoric and cause dissociation.
This analgesic-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |