

This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this articlebyadding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
Find sources: "Rubin vase" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
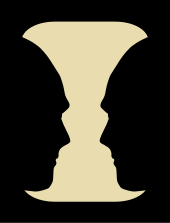
Rubin's vase (sometimes known as the Rubin face or the figure–ground vase) is a famous example of ambiguous or bi-stable (i.e., reversing) two-dimensional forms developed around 1915 by the Danish psychologist Edgar Rubin.[1]
The depicted version of Rubin's vase can be seen as the black profiles of two people looking towards each other or as a white vase, but not both.
Another example of a bistable figure Rubin included in his Danish-language, two-volume book was the Maltese cross.

Rubin presented in his doctoral thesis (1915) a detailed description of the visual figure-ground relationship, an outgrowth of the visual perception and memory work in the laboratory of his mentor, Georg Elias Müller.[2] One element of Rubin's research may be summarized in the fundamental principle, "When two fields have a common border, and one is seen as figure and the other as ground, the immediate perceptual experience is characterized by a shaping effect which emerges from the common border of the fields and which operates only on one field or operates more strongly on one than on the other".

The visual effect generally presents the viewer with two shape interpretations, each of which is consistent with the retinal image, but only one of which can be maintained at a given moment. This is because the bounding contour will be seen as belonging to the figure shape, which appears interposed against a formless background. If the latter region is interpreted instead as the figure, then the same bounding contour will be seen as belonging to it.
These types of stimuli are both interesting and useful because they provide an excellent and intuitive demonstration of the figure–ground distinction the brain makes during visual perception. Rubin's figure–ground distinction, since it involved higher-level cognitive pattern matching, in which the overall picture determines its mental interpretation, rather than the net effect of the individual pieces, influenced the Gestalt psychologists, who discovered many similar percepts themselves.
Normally the brain classifies images by which object surrounds which – establishing depth and relationships. If one object surrounds another object, the surrounded object is seen as figure, and the presumably further away (and hence background) object is the ground, and reversed. This makes sense, since if a piece of fruit is lying on the ground, one would want to pay attention to the "figure" and not the "ground".[3] However, when the contours are not so unequal, ambiguity starts to creep into the previously simple inequality, and the brain must begin "shaping" what it sees; it can be shown that this shaping overrides and is at a higher level than feature recognition processes that pull together the face and the vase images – one can think of the lower levels putting together distinct regions of the picture (each region of which makes sense in isolation), but when the brain tries to make sense of it as a whole, contradictions ensue, and patterns must be discarded.

The distinction is exploited by devising an ambiguous picture, whose contours match seamlessly the contours of another picture (sometimes the same picture; a practice M.C. Escher used on occasion). The picture should be "flat" and have little (if any) texture to it. The stereotypical example has a vase in the center, and a face matching its contour (since it is symmetrical, there is a matching face on the other side).
|
| ||
|---|---|---|
| Illusions |
| |
| Popular culture |
| |
| Related |
| |