

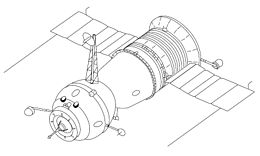
Soyuz 7K-OKS spacecraft
| |
| Manufacturer | Experimental Design Bureau (OKB-1) |
|---|---|
| Country of origin | Soviet Union |
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| Applications | Crewed spacecraft to dock with space station |
| Specifications | |
| Dimensions |
|
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Design life | Up to 35 days |
| Production | |
| Status | No longer in service |
| Launched | 2 |
| Maiden launch | Soyuz 10 22 April 1971 |
| Last launch | Soyuz 11 6 June 1971 |
| Related spacecraft | |
| Derived from | Soyuz 7K-OK |
Soyuz 7K-OKS (also known as Soyuz 7KT-OK)[1] is a version of the Soyuz spacecraft and was the first spacecraft designed for space station flights. Its only crewed flights were conducted in 1971, with Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11.
The two craft of the Soyuz 7K-OKS generation were modified from the original Soyuz 7K-OK. The new "probe and drogue" docking mechanism, which was first used by these two missions, featured an internal docking hatch that allowed for the first time internal transfer between Soviet spacecraft. This "probe and drogue" docking mechanism introduced with Soyuz 7K-OKS is still in use today at the International Space Station (ISS). The external toroidal fuel tank, a holdover from the original lunar mission models of the Soyuz, was dropped from the 7K-OKS since it was unneeded for Earth orbital flights.[1]
The Soyuz 7K-OKS flew only twice, Soyuz 10 and Soyuz 11.[1]
On its maiden flight, the Soyuz 7K-OKS successfully launched into Earth orbit, but failed to dock completely with the Salyut 1 space station. Upon reentry, the spacecraft encountered problems with toxic fumes.[2]
This generation of Soyuz spacecraft is notable for the first successful delivery of crew to the first space station Salyut 1 by Soyuz 11 – this success was however overshadowed by the death of the crew, who were killed when the capsule depressurised during the re-entry phase.[3]
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main topics |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Past missions (by spacecraft type) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current missions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Future missions |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Uncrewed missions are designated as Kosmos instead of Soyuz; exceptions are noted "(uncrewed)". | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |
|---|---|
| Active |
|
| In development |
|
| Past |
|
| Cancelled |
|
| Related |
|