

Israeli music |
|---|
| Religious |
| Secular |
| Israel |
| Dance |
| Music for holidays |
|
|
Yigdal (Hebrew: יִגְדַּל yīgdal, "be exalted") is a Jewish hymn which in various rituals shares with Adon 'Olam the place of honor at the opening of the morning and the close of the evening service. It is based on the 13 principles of faith (sometimes referred to as "the 13 Creeds") formulated by Maimonides. This was not the only metrical presentment of the Creeds, but it has outlived all others, whether in Hebrew or in the vernacular. A translation can be found in any bilingual siddur.
Among Ashkenazim only thirteen lines are sung, one for each creed; the last line, dealing with the resurrection of the dead, is repeated to complete the antiphony when the hymn is responsorially sung by the Chazzan and congregation. Sephardim, who sing the hymn in congregational unison throughout, use the following line as the 14th: "These are the 13 bases of the Rule of Moses and the tenets of his Law".
There is scholarly debate as to the hymn's author. Leopold Zunz contends that it was written by Daniel ben Yehudah Dayan,[1] who spent eight years in improving it, completing it in 1404.[2] Some see in the last line of "Yigdal" a signature, "Yechiel b'Rav Baruch", though it is unclear who this might be. Hartwig Hirschfeld argues that the famous poet Immanuel of Rome is the author. Immanuel made several attempts at putting the 13 Principles into verse, e.g. a 72-line version entitled “Poem Based on the 13 Articles”. "Yigdal" shares rhythm, rhyme and a number of phrases with this poem.[3]
| Hebrew | English |
|---|---|
|
|
Yigdal far surpasses Adon Olam in the number of its traditional tunes and the length of time during which they have been traditional. In the Spanish ritual, in its Dutch-and English-speaking tradition, the hymn is often sung, according to the general Sephardic custom (compare e.g., Yah Shimkha), to some "representative" melody of the particular day. Thus, for example, it is chanted at the close of evening service on Rosh Hashana to the tune of 'Et Sha'are Raẓon. On Friday evening the Sabbath Yigdal is customarily sung to the same melody as are Adon Olam and Ein Keloheinu. On the three pilgrimage festivals, the melody shown here is the tune favored. Its old Spanish character is evident.
![\relative c' {
\language "english"
\key g \minor
\time 2/2
\autoBeamOff
\tempo "Moderato." 4 = 140
\partial 4 f4^"Allegretto" |
bf4. c8 d4 ef8[( d)] |
c2. d8[( c)] |
bf2 g |
f2. bf8[( a)] |
g4. f8 ef4 g |
f4.( g8 f4) ef'4 |
d2 c |
bf2. \bar "|."
}
\addlyrics {
Yig -- |
dal E -- lo -- him __ |
hay. we -- |
yish -- tab -- |
bab. Nim -- |
za we -- en 'et |
el __ me -- |
zi -- 'u -- |
to.
}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/score/r/q/rqxsco4g044sgo5cwgyr9xepribxj12/rqxsco4g.png)
In the Ashkenazic ritual Yigdal, though always commencing the morning prayer, is not invariably sung at the close of the evening service on Sabbaths and festivals, being often, especially in Germany, replaced by Adon Olam. In Polish use, however, it is more regularly employed as the closing hymn. In the synagogues of northwestern Germany, the Netherlands, and England, where the influence of the Sephardic ritual has been felt by that of the Ashkenazim, Yigdal is considered an integral portion of the Sabbath and festival evening prayer. In London for fully two centuries there has been allotted to the hymn, according to the occasion, a definite tradition of tunes, all of which are antiphonal between chazzan and congregation. The most familiar of these tunes is the Friday evening Yigdal. It is utilized also in Germany and in some parts of Poland and Bohemia as a festival Yigdal. The melody may date from the 17th century or perhaps earlier. The tune was also used by the hazzan Myer Lyon (who also sang on the London opera stage as 'Michael Leoni') at the Great Synagogue of London, where it was heard by the Methodist Thomas Olivers; he adapted the tune for the English hymn The God of Abraham Praise (see below).
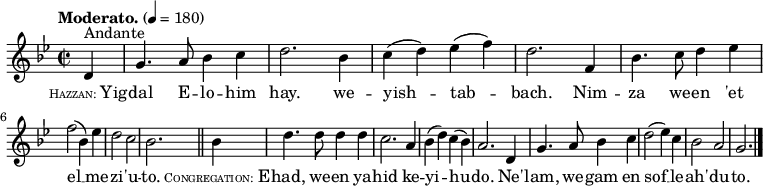
Next in importance comes the melody reserved for the solemn evenings of Rosh Hashana and Yom Kippur, and introduced, in the spirit of Psalm 137:6, into the service of Simchath Torah. This melody is constructed in the harmonic major scale (EFG # ABCD # E) with its two augmented seconds (see synagogue music), and is the inspiration of some Polish precentor, dating perhaps from the early 17th century, and certainly having spread westward from the Slavonic region.
In the German use of Bavaria and the Rhineland, the old tradition has preserved a contrasting "Yigdal" for Rosh Hashana and Yom Kippur that is of equally antique character, but built on a diatonic scale and reminiscent of the morning service of the day.
For the evenings of the three festivals (shalosh regalim) the old London tradition has preserved, from at least the early 18th century, three characteristic melodies, probably brought from north Germany or Bohemia. That for Passover illustrates the old custom according to which the precentor solemnly dwells on the last creed, that on the resurrection of the dead (in this case to a "representative" theme common to Passover and to Purim), and is answered by the choristers with an expression of confident assurance. The choral response here given received its final shaping from David Mombach. Yigdal for Shavu`oth has a solemn tone, strikingly contrasting with those for the other festivals.
The tune for Sukkot displays a gaiety quite rare in synagogal melody. It was employed by Isaac Nathan, in 1815, as the air for one of Lord Byron's "Hebrew Melodies", being set by him to the verses "The Wild Gazelle" in such a manner as to utilize the contrasting theme then chanted by the chazzan to the last line as in the Passover "Yigdal".
Other old tunes for the hymn, such as the melody of Alsatian origin used on "Shabbat Hagadol" before Passover, are preserved in local or family tradition (cf. Zemirot).
Most Hasidic Jews do not recite Yigdal as part of their liturgy, as the Arizal omitted it (and most other Spanish piyyutim) from his siddur. However, based on the teachings of Rabbi Isaiah Horowitz, most do consider it to be a sacred hymn, even if they do not sing it. For similar reasons, Syrian Jews omit both Adon Olam and Yigdal at the end of the morning and evening services, but sing them on other occasions (Adon Olam at the end of the Baqashot and Yigdal before Kiddush on Friday night).
Yigdal appears in translation in several Christian hymnals. The hymn The God of Abraham Praise written by Thomas Olivers around 1770 is based on one of the traditional melodies for Yigdal, the words are recognizable as a paraphrase of it.[5][6] As originally printed in John Wesley's Hymnbook for the use of Christians of all Denominations in 1785, it was very Christianized.[7][8]

In the late 19th century, Rabbi Max Landsberg and Rev. Newton M. Mann (Unitarian) produced a new translation of Yigdal, known as Praise To the Living God. This first appeared in the Union Hymnal (Reform Jewish).[10] This translation, while far less Christianized than the Olivers version, has been used in many Christian hymnals, although some contain hybrids of the Olivers and the Landsberg-Mann texts and have confusing attributions.[11] All Christian versions stick closely to the melody known as "Leoni", collected from Hazzan Myer Lyon at the Great Synagogue of London in 1770, although the meters printed in different hymnals differ considerably.[12]
![]() This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Adler, Cyrus; Cohen, Francis L. (1901–1906). "Yigdal". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls. Its bibliography:
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Adler, Cyrus; Cohen, Francis L. (1901–1906). "Yigdal". In Singer, Isidore; et al. (eds.). The Jewish Encyclopedia. New York: Funk & Wagnalls. Its bibliography:
|
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
| Mincha |
| ||||||||||
| Maariv |
| ||||||||||
| Shabbat / Holiday additions |
| ||||||||||
| Seasonal additions |
| ||||||||||
| Other prayers |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|