ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験

ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験︵ケネディ・ソーンダイクのじっけん、Kennedy–Thorndike experiment︶は、1932年にロイ・ケネディ (Roy J. Kennedy) とエドワード・ソーンダイク (Edward M. Thorndike) により初めて行われた、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験の手順を改良した特殊相対性理論を検証する実験である[1]。改良点は、古典的なマイケルソン・モーリーの実験の装置の一方のアームをもう一方のアームよりも短くした点である。マイケルソン・モーリーの実験は光の速度が装置の﹁向き﹂に依存しないことを示したが、ケネディ・ソーンダイク実験は、異なる慣性系における装置の﹁速度﹂にも依存しないことを示した。これにより時間の遅れが間接的に検証された。マイケルソン・モーリーの実験の否定的結果は長さの収縮だけで説明できるが、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の否定的結果の説明には、地球が太陽の周りを公転する間の位相シフトが検出されない理由を説明するために、長さの収縮だけでなく時間の遅れも必要である。時間の遅れは、アイヴズ・スティルウェルの実験により、初めて直接確認された。これら3つの実験の結果を組み合わせると、完全なローレンツ変換を導出することができる[2]。
ケネディ・ソーンダイク実験を改良し、光キャビティまたは月レーザー測距を使用して行われた実験がある。
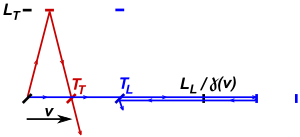
図2. 垂直のアームを使用する光路
ローレンツ収縮は、それ自体でマイケルソン・モーリーの実験の否定的結果を完全に説明できるが、それ自体でケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の否定的結果を説明できない。ローレンツ収縮は次の式で与えられる。
 ここで
ここで
 は固有長︵静止座標系における物体の長さ︶
は固有長︵静止座標系における物体の長さ︶
 は物体に対して相対運動している観測者により観測される長さ
は物体に対して相対運動している観測者により観測される長さ
 は観測者と移動する物体の間、つまり仮想のエーテルと移動物体の間の相対速度である。
は観測者と移動する物体の間、つまり仮想のエーテルと移動物体の間の相対速度である。
 は光速
であり、ローレンツ因子は以下のように定義される。
は光速
であり、ローレンツ因子は以下のように定義される。
 .
図2は、垂直なアームを備えるケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の装置を示しており、ローレンツ収縮が有効であることを仮定している[3]。装置が仮想のエーテルに対して﹁静止している﹂場合、光が縦のアームと横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間の差は次の式で与えられる。
.
図2は、垂直なアームを備えるケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の装置を示しており、ローレンツ収縮が有効であることを仮定している[3]。装置が仮想のエーテルに対して﹁静止している﹂場合、光が縦のアームと横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間の差は次の式で与えられる。
実験[編集]
元のマイケルソン・モーリーの実験は、ローレンツ収縮の仮説のみを検証するのに役立った。ケネディは、1920年代にマイケルソン・モーリーの実験を洗練したものをいくつか作っていたが、時間の遅れも検証する方法を思いついた。以下のように記している[1]。 この実験の基礎となっている原理は、均一な光のビームが2つに分割され、異なる長さの経路を通過した後に再び結合される場合、相対性理論が要求するように光の周波数が速度に依存しない限り、相対的な位相は装置の速度に依存するというものである。 図1を参照すると、主要な光学部品は真空チャンバーVの内部にある熱膨張係数が極めて低い溶融石英の基盤上に取り付けられた。水ジャケットWにより、温度変化は±0.001 °C以内に制御された。水銀源Hgからの単色緑色光は真空チャンバーに入る前にニコルプリズムを通過し、不要な背面反射を防ぐためにブリュースター角に設定されたビームスプリッタBにより分割された。2つのビームは、5461 Å水銀線のコヒーレンス長を考慮して、可能な限り発散する距離に設定された2つのミラーM1及びM2に向けられた︵コヒーレンス長はおよそ32 cmであり、アームの長さの差ΔL ≈ 16 cmを許容する︶。反射されたビームは再結合して円形の干渉縞を形成し、Pで撮影された。スリットSにより、リングの直径にわたる複数の露光が、1日の異なる時間に単一の写真乾板に記録された。 一方のアームをもう一方のアームよりもずっと短くすると、地球の速度の変化により光線の移動時間が変化し、光源の周波数が同じ値に変わらない限り干渉縞が移動する。このような干渉縞の移動があったかどうかを判断するために、干渉計を非常に安定させ、後の比較のために干渉パターンを撮影した。検証は何か月間も行われたが、大きな干渉縞の移動は見つからなかったため︵誤差の範囲内である10±10 km/sの速度に相当︶、特殊相対性理論により予測されたように時間の遅れが生じていると結論付けられた。理論[編集]
実験の基本的な理論[編集]

 ここで
ここで
 は固有長︵静止座標系における物体の長さ︶
は固有長︵静止座標系における物体の長さ︶
 は物体に対して相対運動している観測者により観測される長さ
は物体に対して相対運動している観測者により観測される長さ
 は観測者と移動する物体の間、つまり仮想のエーテルと移動物体の間の相対速度である。
は観測者と移動する物体の間、つまり仮想のエーテルと移動物体の間の相対速度である。
 は光速
であり、ローレンツ因子は以下のように定義される。
は光速
であり、ローレンツ因子は以下のように定義される。
 .
図2は、垂直なアームを備えるケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の装置を示しており、ローレンツ収縮が有効であることを仮定している[3]。装置が仮想のエーテルに対して﹁静止している﹂場合、光が縦のアームと横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間の差は次の式で与えられる。
.
図2は、垂直なアームを備えるケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の装置を示しており、ローレンツ収縮が有効であることを仮定している[3]。装置が仮想のエーテルに対して﹁静止している﹂場合、光が縦のアームと横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間の差は次の式で与えられる。
光がローレンツ収縮した縦のアームを往復するのにかかる時間は、次の式で与えられる。
 T1は運動方向の移動時間、T2は反対方向の移動時間、vはエーテルの速度成分、cは光速、LLは縦方向のアームの長さである。光が横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間は、次の式で与えられる。
T1は運動方向の移動時間、T2は反対方向の移動時間、vはエーテルの速度成分、cは光速、LLは縦方向のアームの長さである。光が横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間は、次の式で与えられる。
 光が縦のアームと横のアームを通過するのにかかる時間の差は、次の式で与えられる。
光が縦のアームと横のアームを通過するのにかかる時間の差は、次の式で与えられる。
 T1は運動方向の移動時間、T2は反対方向の移動時間、vはエーテルの速度成分、cは光速、LLは縦方向のアームの長さである。光が横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間は、次の式で与えられる。
T1は運動方向の移動時間、T2は反対方向の移動時間、vはエーテルの速度成分、cは光速、LLは縦方向のアームの長さである。光が横のアームを往復するのにかかる時間は、次の式で与えられる。
 光が縦のアームと横のアームを通過するのにかかる時間の差は、次の式で与えられる。
光が縦のアームと横のアームを通過するのにかかる時間の差は、次の式で与えられる。
ΔL=c(TL-TT)であるため、次の移動距離の差が与えられる︵ΔLAは初期の移動距離の差、vAは装置の初速度、ΔLBとvBは、地球自体の自転または太陽の周りの公転による回転または速度変化後の移動距離の差と初速度である︶[4]
 .
否定的結果を得るためには、ΔLA−ΔLB=0という結果を得る必要がある。ただし、速度が同じ (vA=vB) である限り、両方の式が互いに打ち消しあうだけである。しかし、速度が異なる場合、ΔLAとΔLBは等しくなくなる︵マイケルソン・モーリーの実験においては、LLとLTの差がゼロであるため、速度の変化の影響を受けない。そのため、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験では、光速が装置の向きに依存するかどうかを検証するだけである︶。しかし、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験では、最初からLLとLTが異なるため、装置の﹁速度﹂に対する光速の依存性も測定できる[2]。
前式によれば、移動距離の差ΔLA−ΔLBとその結果として予想される干渉縞の移動 (fringe shift) ΔNは次の式で与えられる。
.
否定的結果を得るためには、ΔLA−ΔLB=0という結果を得る必要がある。ただし、速度が同じ (vA=vB) である限り、両方の式が互いに打ち消しあうだけである。しかし、速度が異なる場合、ΔLAとΔLBは等しくなくなる︵マイケルソン・モーリーの実験においては、LLとLTの差がゼロであるため、速度の変化の影響を受けない。そのため、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験では、光速が装置の向きに依存するかどうかを検証するだけである︶。しかし、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験では、最初からLLとLTが異なるため、装置の﹁速度﹂に対する光速の依存性も測定できる[2]。
前式によれば、移動距離の差ΔLA−ΔLBとその結果として予想される干渉縞の移動 (fringe shift) ΔNは次の式で与えられる。
 .
v/cで2次より大きい項を無視すると、次の式になる。
.
v/cで2次より大きい項を無視すると、次の式になる。
 ΔNが定数になる、つまり干渉縞の移動が装置の速度や向きに依存しないためには、波長λがローレンツ因子により修正される必要がある。周波数に対する時間の遅れの影響を考慮した場合にはこのことが実際に生じる。そのため、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の否定的結果を説明するためには、長さの収縮と時間の遅れの両方が必要である。
ΔNが定数になる、つまり干渉縞の移動が装置の速度や向きに依存しないためには、波長λがローレンツ因子により修正される必要がある。周波数に対する時間の遅れの影響を考慮した場合にはこのことが実際に生じる。そのため、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の否定的結果を説明するためには、長さの収縮と時間の遅れの両方が必要である。
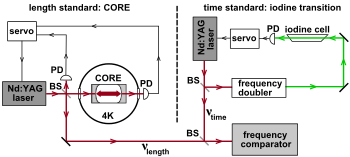
図3. Braxmaier et al. 2002の単純化した図
近年、レーザー、メーザー、低温光共振器を使用して、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験やケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の精度を高めた実験が行われている。時間の遅れと長さの収縮の間の関係を示すRobertson-Mansouri-Sexl(RMS)検証理論による速度依存性の限界が大きく改善されている。例えば、元のケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験ではRMS速度依存性の限界が~10−2であったが、現在の限界は~10−8の範囲である[5]。
図3は、Braxmaierらが2002年に行ったケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の単純化した図を示す[6]。左側において、光検出器 (PD) がサファイア低温光共振器 (CORE) 長さ基準の共振を監視し、COREはNd:YAGレーザの周波数を1064nmに安定させるために、液体ヘリウム温度に保たれた。右側においては、低圧ヨウ素基準の532 nm吸収度線が、2番目のNd:YAGレーザの︵2倍の︶周波数を安定させるための時間標準として使用されている。
 .
否定的結果を得るためには、ΔLA−ΔLB=0という結果を得る必要がある。ただし、速度が同じ (vA=vB) である限り、両方の式が互いに打ち消しあうだけである。しかし、速度が異なる場合、ΔLAとΔLBは等しくなくなる︵マイケルソン・モーリーの実験においては、LLとLTの差がゼロであるため、速度の変化の影響を受けない。そのため、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験では、光速が装置の向きに依存するかどうかを検証するだけである︶。しかし、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験では、最初からLLとLTが異なるため、装置の﹁速度﹂に対する光速の依存性も測定できる[2]。
前式によれば、移動距離の差ΔLA−ΔLBとその結果として予想される干渉縞の移動 (fringe shift) ΔNは次の式で与えられる。
.
否定的結果を得るためには、ΔLA−ΔLB=0という結果を得る必要がある。ただし、速度が同じ (vA=vB) である限り、両方の式が互いに打ち消しあうだけである。しかし、速度が異なる場合、ΔLAとΔLBは等しくなくなる︵マイケルソン・モーリーの実験においては、LLとLTの差がゼロであるため、速度の変化の影響を受けない。そのため、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験では、光速が装置の向きに依存するかどうかを検証するだけである︶。しかし、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験では、最初からLLとLTが異なるため、装置の﹁速度﹂に対する光速の依存性も測定できる[2]。
前式によれば、移動距離の差ΔLA−ΔLBとその結果として予想される干渉縞の移動 (fringe shift) ΔNは次の式で与えられる。
 .
v/cで2次より大きい項を無視すると、次の式になる。
.
v/cで2次より大きい項を無視すると、次の式になる。
 ΔNが定数になる、つまり干渉縞の移動が装置の速度や向きに依存しないためには、波長λがローレンツ因子により修正される必要がある。周波数に対する時間の遅れの影響を考慮した場合にはこのことが実際に生じる。そのため、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の否定的結果を説明するためには、長さの収縮と時間の遅れの両方が必要である。
ΔNが定数になる、つまり干渉縞の移動が装置の速度や向きに依存しないためには、波長λがローレンツ因子により修正される必要がある。周波数に対する時間の遅れの影響を考慮した場合にはこのことが実際に生じる。そのため、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の否定的結果を説明するためには、長さの収縮と時間の遅れの両方が必要である。
相対性理論に対する重要性[編集]
1905年、アンリ・ポアンカレとアルベルト・アインシュタインにより、ローレンツ変換が相対性原理を満たす群を形成する必要があることを示した。このことは、長さの収縮と時間の遅れが正確な相対論的値を有することを必要とする。ケネディとソーンダイクは、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験とケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の実験データのみから、完全なローレンツ変換を導出できると主張した。しかし、正確な相対論的値を有する長さの収縮と時間の遅れは十分であるが、両方の実験の説明には必要ないため、厳密には正しくない。運動方向のみでの長さの収縮は、マイケルソン・モーリーの実験を説明する可能性の1つにすぎないためである。一般的に、否定的結果は、横方向と縦方向の長さの﹁比﹂がローレンツ因子に対応する必要があり、これには、横方向と縦方向の長さの変化の無限に多くの組み合わせが含まれる。このことは、その値が実験の解析で使用される長さの収縮の値に依存するため、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験における時間の遅れの役割にも影響する。したがって、実験データのみからローレンツ変換を導出するには、3番目の実験であるアイヴズ・スティルウェルの実験を考慮する必要がある[2]。 より正確には、Robertson-Mansouri-Sexl検証理論の枠組みにおいて[2][5]、次のスキームを使用して実験を記述することができる。αは時間変化を表し、βは運動方向の長さ変化を表し、δは運動方向に垂直な方向の長さ変化を表す。マイケルソン・モーリーの実験はβとδの関係を検証し、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験はαとβとの関係を検証する。すなわち、αはβに依存し、βはδに依存する。これら2つの実験ではこれらの量の組み合わせのみが測定でき、個々の値は測定できない。これらの量のいずれかの値を﹁直接﹂測定するには、別の実験が必要である。これは実際に、相対論的時間の遅れにより予測される値を持つαを測定したアイヴズ・スティルウェルの実験で達成された。このαの値とケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験の否定的結果を組み合わせると、βは必然的に相対論的長さの収縮の値を仮定する必要があることがわかる。さらに、このβの値とマイケルソン・モーリーの実験の否定的結果を組み合わせると、δはゼロでなければならないことがわかる。したがって、ローレンツ変換に必要な要素は、群論の理論的要件と一致して、実験により提供される。近年の実験[編集]
キャビティ︵光共振器︶による検証[編集]

| 著者 | 年 | 説明 | 最大速度依存性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hils and Hall[7] | 1990 | 光ファブリ・ペロー共振器の周波数と、I2基準線に安定化されたレーザーの周波数を比較する。 | |
| Braxmaier et al.[6] | 2002 | 2つのNd:YAGレーザーを使用して、低温光共振器の周波数をI2周波数基準と比較する。 | |
| Wolf et al.[8] | 2003 | whispering gallery modeで動作するサファイア結晶により構成される定置低温マイクロ波発振器の周波数が水素メーザーの周波数と比較され、その周波数はセシウムとルビジウムの原子泉時計と比較された。地球の自転中の変化が調べられた。2001年から2002年までのデータが分析された。 | |
| Wolf et al.[9] | 2004 | Wolf et al. (2003)参照。温度制御をアクティブに行った。2002年から2003年までのデータが分析された。 | |
| Tobar et al.[10] | 2009 | Wolf et al. (2003)参照。2002年から2008年までのデータが、恒星変動と年変動の両方を考慮して分析された |
月レーザー測距[編集]
地上での測定に加え、Müller & Soffel (1995)[11]やMüller et al. (1999)[12]により、地球と月の距離をセンチメートルの精度で評価した月レーザー測距データを使用して、ケネディ・ソーンダイクの実験が行われた。好ましい座標系(en:preffered frame)があり、光速が観測者の速度に依存する場合、地球と月の間の距離測定で異常振動が観測できるはずである。時間の遅れはすでに高精度で確認されているため、このような振動が観測されれば光速が観測者の速度に依存していることや、長さの収縮の方向依存性が実証される。しかしながら、どちらの研究でもそのような振動は観測されず、RMS速度限界はHils and Hall (1990)により設定された限界に匹敵する~10−5[12]であった。したがって、長さの収縮と時間の遅れは両方とも相対性理論により予測された値を有する必要がある。





