セイヨウオトギリ
表示
(セント・ジョーンズ・ワートから転送)
| セイヨウオトギリ | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Hypericum perforatum | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 分類 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| 学名 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Hypericum perforatum L. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 和名 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| セイヨウオトギリ | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 英名 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Common St. John's wort | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 亜種 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
本文参照 |
セイヨウオトギリ︵西洋弟切; 学名: Hypericum perforatum; 英語名: St. John's wort、Klamath weed、Goat weed︶は、オトギリソウ科オトギリソウ属の多年草である。英語におけるセント・ジョーンズ・ワート (St. John's wort) は、本種の一般名だが、様々な修飾語とともに、オトギリソウ属の他種を指すこともあり、英語ではそれらと区別するために、本種を Common St. John's wort と呼ぶ場合もある。
セイヨウオトギリはリンネの﹃植物の種﹄(1753年) で記載された植物の一つである[1]。
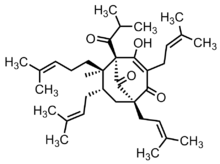
ヒペルホリン︵ハイパフォリン︶

ヒペリシン
ハーブと花は異なるポリフェノールを含んでいる: フラボノイド類︵ルチン、ヒペロシド、イソケルセチン、ケルシトリン、ケルセチン、I3,II8-ビアピゲニン、アメントフラボン、アスチルビン、ミクエリアニン︶、フェノール酸︵クロロゲン酸、3-O-クマロイルキナ酸︶、ナフトジアントロン類︵ヒペリシン、プソイドヒペリシン、プロトヒペリシン、プロトプソイドヒペリシン︶、フロログルシノール類︵ヒペルホリン、アドヒペルホリン︶。
ヒペリシン、プソイドヒペリシンならびにヒペルホリンは活性成分であると考えられている[17][18][19]。その他精油成分︵主にセスキテルペン︶も含まれている。
植物[編集]
セイヨウオトギリは黄色い花を咲かせる根茎性の多年草であり、ヨーロッパに自生し、後にアメリカへも伝播し多くの草地で野生化している。聖ヨハネの日︵6月24日︶の頃までに花が咲き、伝統的にその日に収穫されたためその名が付いた。地上部全体が刈られ乾燥させられハーブティーとして用いられる。そのハーブティーは若干苦いものの嗜好品としてまたその薬理的性質のため長い間愛好されてきた。種小名の perforatum は光にかざすと見える葉にある小さな窓︵油点︶に由来する。 キュー植物園系データベース Plants of the World Online は亜種として以下のものを認めている[2]。 ●コゴメバオトギリ Hypericum perforatum subsp. chinense N.Robson - 中華人民共和国原産。 ●セイヨウオトギリ Hypericum perforatum subsp. perforatum - ヨーロッパからシベリア中央部およびトルコ北西部にかけて自生。 ●Hypericum perforatum subsp. songaricum (Ledeb.exRchb.) N.Robson - ウクライナから新疆にかけて自生。 ●Hypericum perforatum subsp. veronense (Schrank) H.Lindb. - マカロネシア、中欧、地中海地域からスーダン南西部およびヒマラヤ西部にかけて自生。 セイヨウオトギリが商業的に栽培されている地域はあるものの20以上の国では毒草としてリストされている。家畜による摂取は光過敏感反応、中枢神経抑圧、流産または最悪死をもたらす場合もある。セイヨウオトギリの除草剤には 2,4-D、ピクロラム、グリホサートが有効である。生物的駆除の目的で、オトギリソウ類を食べることで知られる3種の甲虫︵ハムシ科・ヨモギハムシ属の2種‥Chrysolina quadrigeminaとChrysolina hyperici、およびタマムシ科の1種‥Agrilus hyperici︶が北米西部で使われている。ハーブとしての利用[編集]
セント・ジョーンズ・ワートの医療的利用の最初の記録は古代ギリシアにまでさかのぼり、以来利用されてきている。またネイティブアメリカンも人工妊娠中絶薬、抗炎症剤、収斂剤、消毒剤として使用してきた。 現代医学において標準的なセント・ジョーンズ・ワートの抽出物はうつ病や不安障害の一般的な処置として用いられている。ホメオパシーにおいては多くの医学的な問題に対する処置として用いられるが、その効果の程は正確には記載されていない。歴史的にはセント・ジョーンズ・ワートの花や茎は赤や黄色の色素を作るために用いられてきた。 今日セント・ジョーンズ・ワートはうつ病への処置法︵あるいはその可能性︶として最も知られている。ドイツをはじめいくつかの国では軽度のうつに対して従来の抗うつ薬より広く処方されている[3]。標準的な抽出物はタブレット、カプセル、ティーバッグとして一般の薬局等で購入することが可能である。 欧州では、伝統的医薬品として流通しているが[4]日本においては、薬事法上、薬効を標榜しない限りは﹁食品﹂扱いであり、ハーブとして市販されている。しかし、多くの薬物と相互作用をするので、厚生労働省からも注意が必要であると喚起されている[4]。臨床的効果についての研究[編集]
セント・ジョーンズ・ワートについての臨床研究は、うつ病に対する効果を調査したものが多い。その結論は現在のところ成否さまざまである。軽症から中等症のうつに対して有効でかつ従来の抗うつ薬よりも副作用が少ないとするイギリスの診療ガイドラインにおける合意がある一方で、偽薬以上の効果は見られないとするアメリカで行われた研究もある。 英国国立医療技術評価機構︵NICE︶の2009年のうつ病に対する診療ガイドラインは、軽症から中等症のうつ病に対し危険性が利益を上回るため抗うつ薬は使用してはならないが、セント・ジョーンズ・ワートには利益がある可能性があるという証拠が存在するとしている[5]。効果があるとする報告[編集]
コクランレビューによる2008年の報告[6]は以下のように結論している。 (一)うつ病患者に対して偽薬群より優れた効果を示す。 (二)標準的な抗うつ薬と同等に効果がある。 (三)標準的な抗うつ薬と比較して副作用が小さい。 なお以下の点が解釈を複雑にしていると記されている[6]。 (一)厳密な臨床試験では偽薬群に対する優位性が、より質の低い臨床試験に比べ小さくなること (二)セント・ジョーンズ・ワートに効果があるとする報告がほぼドイツ語圏からの報告であること 1996年の初期のメタアナリシスでは、セント・ジョーンズ・ワートの抽出物は軽症から中等症のうつ病に対して偽薬より有意に有効であると報告された[7]。この研究は、23個のより小規模な先行研究をメタアナリシスしたものである。 このメタアナリシスは、後に27の研究を含めるように改訂され、コクランレビューへ掲載された。この改訂されたレビューはセント・ジョーンズ・ワートの抽出物は偽薬に有意に勝り︵率比2.47: 95%信頼区間1.69から3.61︶、標準的な抗うつ薬と同等の有効性であるとした︵単独使用 1.01:0.87 から 1.16、複合使用1.52:0.78から2.94︶[8]。 包含する研究をより厳密な基準により選んだ1999年の別のメタアナリシスでは、セント・ジョーンズ・ワートは偽薬より効果があり︵奏功率73.2 対 37.9%、相対危険率 1.48: 95% 信頼区間 1.03-1.92︶、三環系抗うつ剤と同等の効果がある一方で、悪影響が少ないことを見いだした︵64対 66.4%, 相対危険率 1.11 95% 信頼区間 0.92-1.29︶[9]。1998年と1999年の2つの︵大規模な︶多施設平行研究でも、偽薬以上の有効性、標準的抗うつ剤と同等の効果、より少ない副作用などを示している[10][11][12]。効果がないとする報告[編集]
米国国立衛生研究所 (NIH) に属する米国国立補完代替医療センター (NCCAM) やその他の機関はうつ病に対しては、セント・ジョーンズ・ワートは偽薬と比較して極めて小さい効果しか示さないか、あるいはまったく効果を示さないとしている[13][14]。これらの結論は、NCCAMによって行われた大規模な臨床試験の結果に基づいている[15]。この研究は、DSM-IVに基いて大うつ病性障害と診断された340人の患者を対象に、ハミルトンうつ病評価尺度 (HAM-D) と臨床全般印象尺度 (CGI) を症状評価尺度として用いた、多施設無作為二重盲検偽薬対照試験である。対照として、セルトラリン︵SSRI︶と偽薬を用いている。その結果、セント・ジョーンズ・ワートは中程度のうつ病に対して、偽薬に比べて有効性があることは示されなかった。しかし、抗うつ薬のセルトラリンも偽薬に比べて有効性があることは示されなかった。より軽度のうつ病における効果の調査がNIHにより計画されていると記されている。 代替医療についての他の多くの研究と同様に、これらの多くは方法論や研究デザインが不十分であり、有効性について結論づけることができない状態である。有効性を報告している研究者の一人も、今後より精密な調査が必要であることを2003年の論文中で述べてられている[8]。 DSM-IV基準を満たした注意欠陥多動性障害ADHDの小児および青年に対して、セント・ジョーンズ・ワート300mgによる改善効果を検討した無作為比較試験では臨床的に有効な改善効果は認められなかった[16]。成分[編集]


薬理学[編集]
セント・ジョーンズ・ワートが機能する機構は正確には不明であるが、従来の選択的セロトニン再取り込み阻害薬 (SSRI) 系の抗うつ薬と同様にセロトニンの再吸収を阻害することが関係すると信じられている[20]。 セント・ジョーンズ・ワートの主要な有効成分はハイパフォリンとヒペリシンだと考えられているが、フラボノイドやタンニンのような他の生理活性物質が関与している可能性もある[21][22][23]。 ハイパフォリンは抗うつ作用の主要な有効成分だと信じられており、セロトニン、ドーパミン、ノルアドレナリン、γ-アミノ酪酸 (GABA)、グルタミン酸の取込みを阻害することが示されている[24]。用量反応関係の不一致からハイパフォリン以外の成分の関与も示唆されている[25]。また、ハイパフォリンを含まないセント・ジョンズ・ワート抽出物 (Ze 117 - Remotiv) が顕著な抗うつ作用を示すという報告も成されている[26][27]。投与/処方[編集]
セント・ジョーンズ・ワートの投与量は処方間で大きく隔たりがあり、それは植物原料と調整過程の違いによるものである。臨床試験で一般的に用いられる投与量は一日当たり350から1800mgである︵これはヒペリシンで0.4から2.7mgに相当する︶[8]。 英国ハーブ医学連合科学委員会により推薦されている様々な形態のセント・ジョーンズ・ワートの用量は以下の通りである [28]。 ●乾燥ハーブ - 2-4 g または煎じ薬として1日3回 ●液体抽出物 - 2-4 mL (1対1 25% アルコール中) 1日3回 ●チンキ剤 - 2-4 mL (1対10 45% アルコール中) 1日3回 標準化された抽出物を入手できない市場では、物によってその強度が大きく異なる。薬局で手に入る某ブランドのものは、他のものより強い場合がある。また同じブランドでも、バッチが異なると用量が異なる場合がある。標準化されたものが手に入る場所でも、ヘパフォリンが主要な活性成分だと考えられているため、ヒペリシンを基準に用いるのには議論がある。 他の抗うつ薬と同様に、セント・ジョーンズ・ワートの効果を適切に評価するためには、最低4週間は取り続けなければならない。副作用[編集]
セント・ジョーンズ・ワートは一般に良好な耐容性を示し、プラセボと同程度の副作用しか示さない[29]。報告されている最も一般的な副作用は胃腸症状、目まい、意識混濁、けん怠、鎮静である[30]。また、ヒペリシンは、通常では日焼けを起こさないような状況でも日焼け様の症状を呈する、光線過敏症の原因となることが知られているが、通常の摂取量の範囲においてそれが起きることは非常に稀である[29]。カンプト(イリノテカン)の作用を弱めるため、抗癌剤のFOLFIRI療法などの際は併用を避けるべきであるとされている。統合失調症を患っている人では精神病症状を悪化と関連があると思われる。[31]薬物相互作用[編集]
セント・ジョーンズ・ワートは、シトクロームP450酵素 CYP3A4を誘導することで、ジゴキシン︵強心薬︶、シクロスポリン︵免疫抑制薬︶、テオフィリン︵気管支拡張薬︶、インジナビル︵抗HIV薬︶、ワルファリン︵血液凝固防止薬︶、パキロビッド︵新型コロナウイルス感染症治療薬︶など、いくつもの薬物相互作用をすることが知られている。ハイパフォリンが主要な原因物質で、それが有効成分でもある。 セント・ジョーンズ・ワートは、ある種の薬物の量を体の中で減少させ、その薬物の効果を減じさせる作用がある。例えば、他の抗うつ薬︵SSRIや三環系抗うつ薬︶、避妊薬、高脂血治療薬等[32]抗てんかん薬[33]は影響を受ける。脚注[編集]
(一)^ Linnaeus, Carolus (1753) (ラテン語). Species Plantarum. Holmia[Stockholm]: Laurentius Salvius. p. 785
(二)^ POWO (2019). Plants of the World Online. Facilitated by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on the Internet; http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:433719-1 Retrieved 30 September 2021.
(三)^ Fegert JM, Kölch M, Zito JM, Glaeske G, Janhsen K (2006). “Antidepressant use in children and adolescents in Germany”. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 16 (1-2): 197-206. doi:10.1089/cap.2006.16.197. PMID 16553540.
(四)^ ab厚生労働省 (2000年5月10日). “セント・ジョーンズ・ワートと医薬品の相互作用について”. 2010年10月6日閲覧。
(五)^ 英国国立医療技術評価機構 (28 October 2009). CG90: Depression in adults (Report). pp. Chapt.1.4.4.
(六)^ abLinde K, Berner MM, Kriston L (2008). “St John's wort for major depression”. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 4: CD000448. PMID 18843608.
(七)^ Linde K, Ramirez G, Mulrow CD, Pauls A, Weidenhammer W, Melchart D year=1996. “St John's wort for depression - an overview and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials”. BMJ 313: 253-258. PMID 8704532.
(八)^ abcLinde K, Mulrow CD (2003). “St John's wort for depression (Cochrane Review)”. The Cochrane Library. 3. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
(九)^ Kim HL, Streltzer J, Goebert D (1999). “St. John's wort for depression: a meta-analysis of well-defined clinical trials”. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 187 (9): 532-538. PMID 10496508.
(十)^ Laakmann G, Schüle C, Baghai T, Kieser M (1998). “St. John's wort in mild to moderate depression: the relevance of hyperforin for the clinical efficacy”. Pharmacopsychiatry 31 Suppl 1: 54-59. doi:10.1055/s-2007-979346. PMID 9684948.
(11)^ Harrer G, Schmidt U, Kuhn U, Biller A (1999). “Comparison of equivalence between the St. John's wort extract LoHyp-57 and fluoxetine”. Arzneimittelforschung. 49 (4): 289-296. PMID 10337446.
(12)^ Philipp M, Kohnen R, Hiller KO (1999). “Hypericum extract versus imipramine or placebo in patients with moderate depression: randomised multicentre study of treatment for eight weeks”. BMJ 319 (7224): 1534-1538. PMID 10591711.
(13)^ 米国国立補完代替医療センター (NCCAM) (作成2005年7月:更新:2012年4月). “St. John's Wort”. 2010年10月7日閲覧。
(14)^ 米国国立精神衛生研究所 (NIMH). “How is depression detected and treated?”. 2010年10月7日閲覧。
(15)^ Hypericum Depression Trial Study Group (2002). “Effect of Hypericum perforatum (St John's wort) in major depressive disorder: a randomized controlled trial”. JAMA 287 (14): 1807-1814. PMID 11939866.
(16)^ Weber W, Vander Stoep A, McCarty RL, Weiss NS, Biederman J, McClellan J (2008). “Hypericum perforatum (St John's wort) for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a randomized controlled trial”. JAMA 299 (22): 2633-2641. PMID 18544723.
(17)^ Umek A, Kreft S, Kartnig T, Heydel B (1999). “Quantitative phytochemical analyses of six hypericum species growing in Slovenia”. Planta medica 65 (4): 388-390. doi:10.1055/s-2006-960798. PMID 17260265.
(18)^ Tatsis EC, Boeren S, Exarchou V, Troganis AN, Vervoort J, Gerothanassis IP, (2007). “Identification of the major constituents of Hypericum perforatum by LC/SPE/NMR and/or LC/MS.”. Phytochemistry 68 (3): 383-393. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.11.026. PMID 17196625.
(19)^ Schwob I, Bessière JM, Viano J (2002). “Composition of the essential oils of Hypericum perforatum L. from southeastern France”. C. R. Biol. 325 (7): 781-785. doi:10.1016/S1631-0691(02)01489-0. PMID 12360846.
(20)^ Leuner K, Kazanski V, Müller M, Essin K, Henke B, Gollasch M, Harteneck C, Müller WE (2007). “Hyperforin--a key constituent of St. John's wort specifically activates TRPC6 channels”. FASEB J. 21 (14): 4101-4111. doi:10.1096/fj.07-8110com. PMID 1766645.
(21)^ Nahrstedt A, Butterweck V (1997). “Biologically active and other chemical constituents of the herb of Hypericum perforatum L.”. Pharmacopsychiatry 30 Suppl 2: 129-134. doi:10.1055/s-2007-979533. PMID 9342774.
(22)^ Butterweck V (2003). “Mechanism of action of St John's wort in depression : what is known?”. CNS Drugs 17 (8): 539-562. doi:10.2165/00023210-200317080-00001. PMID 12775192.
(23)^ Müller WE (2003). “Current St John's wort research from mode of action to clinical efficacy”. Pharmacol. Res. 47 (2): 101-109. doi:10.1016/S1043-6618(02)00266-9. PMID 12543057.
(24)^ Chatterjee SS, Bhattacharya SK, Wonnemann M, Singer A, Müller WE (1998). “Hyperforin as a possible antidepressant component of hypericum extracts”. Life Sci. 63 (6): 499-510. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(98)00299-9. PMID 9718074.
(25)^ Chatterjee SS, Nöldner M, Koch E, Erdelmeier C (1998). “Antidepressant activity of hypericum perforatum and hyperforin: the neglected possibility”. Pharmacopsychiatry 31 Suppl 1: 7-15. doi:10.1055/s-2007-979340. PMID 9684942.
(26)^ Woelk H (2000). “Comparison of St John's wort and imipramine for treating depression: randomised controlled trial”. BMJ 321 (7260): 536-539. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7260.536. PMC 27467. PMID 10968813.
(27)^ Schrader E (2000). “Equivalence of St John's wort extract (Ze 117) and fluoxetine: a randomized, controlled study in mild-moderate depression”. Int. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 15 (2): 61-68. doi:10.1097/00004850-200015020-00001. PMID 10759336.
(28)^ British Herbal Medicine Association Scientific Committee (1983). British Herbal Pharmacopoeia. West Yorkshire: British Herbal Medicine Association. ISBN 0-903032-07-4
(29)^ abErnst E, Rand JI, Barnes J, Stevinson C (1998). “Adverse effects profile of the herbal antidepressant St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum L.)”. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 54 (8): 589-594. doi:10.1007/s002280050519. PMID 9860144.
(30)^ Barnes J, Anderson LA, Phillipson JD (2002). Herbal Medicines: A guide for healthcare professionals (2 ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 0-85369-474-5
(31)^ Singh, Simon and Edzard Ernst (2008). Trick or Treatment: The Undeniable Facts About Alternative Medicine. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 218. ISBN 978-0-393-33778-5
(32)^ 独立行政法人 国立健康・栄養研究所 (2010年8月25日). “セイヨウオトギリソウ”. 健康食品等の素材情報データベース. 2010年10月6日閲覧。
(33)^ 国立医薬品食品衛生研究所 (2008年1月10日). “医薬品安全性情報 Vol.6 No.01”. 2010年10月6日閲覧。
関連項目[編集]
- グレープフルーツジュース - 飲むと医薬品の効果・効能が増強する薬がある。
外部リンク[編集]
- セイヨウオトギリソウ(セントジョーンズワート) - 素材情報データベース<有効性情報>(国立健康・栄養研究所)
- 健康食品に用いられるセントジョーンズワートの栽培と鑑別について 東京都健康安全研究センター 東京都薬用植物園
- St. John's Wort - 米国国立補完代替医療センター (NCCAM)
- セントジョンズワート(セイヨウオトギリソウ)メルクマニュアル家庭版
