ヘビの鱗

ヘビの鱗︵ヘビのうろこ、英語: Snake scale︶は、爬虫類有鱗目に属するヘビ︵ヘビ亜目︶が持つ鱗である。魚類の鱗が生きた組織に覆われ、そのまま成長するのに対し、爬虫類の鱗は表皮起源であり、細胞としては既に死んだものが強化・硬化したものである[1]。爬虫類ではしたがって、鱗の下にだけ生きた組織があるため、皮下で周期的に新しい角質が生成され、外側の古くなった部分は新しい角質層との間の層で剥がれて脱落する︵脱皮︶。脱皮には、摩耗した部分の交換や寄生虫の排除だけでなく、身体の成長にも関わると考えられている。また、鱗の配列は種の識別に用いられる。
他の爬虫類と同様、ヘビ亜目には鱗で覆われた皮膚がある[2]。ヘビは全身が様々な形状や大きさの鱗甲で覆われており、その集合体は蛇革として知られている。鱗はヘビの身体を防護し、移動を行い、水分を体内に留めることができ、凹凸など表面特性を変えることでカモフラージュに役立つばかりではなく、ヤスリヘビなどでは獲物の捕獲にも役立っている。鱗の色彩パターンには単純なものと複雑なものがあり、いずれも鱗より内側の層によっており、カモフラージュや捕食者に対する警告として機能する。また、発達した筋肉を用いて皮膚を縮め、鱗を重ねることによって鱗と鱗の間の皮膚を隠しておくことができ、皮膚を急に広げて明るい色を露わにすることで捕食者を驚かせることもできる。
一部の鱗は長い時を経て、﹁まつげ﹂にあたる眼の縁や眼球そのものを保護被覆するといった別の機能[3][4] を果たすべく変化している。最も特徴的な例に北米産ガラガラヘビの尾の﹁ラトル﹂がある。これは、危険を感じたとき、脱皮殻の積み重なった尾を激しく振るわせて音を出して警告を発するというものである。

クサリヘビ属に属する Vipera renardi の蛇行運動
腹側の板状の鱗︵﹁腹板﹂︶によりヘビ特有の蛇行が可能であると考えられている。
ヘビの鱗は特に、﹁はう﹂というヘビに特徴的な運動に大きくかかわっている[1][5]。﹁はう﹂という運動も陸上でのほかの移動方法︵歩く、走る、ジャンプする︶と原理的には同じであり、地面を後方に押し出すことによる前進運動である[5]。他の﹁はう﹂動物、たとえばミミズは剛毛と呼ばれるかたいトゲがあり、これを地面にひっかけて進み、カタツムリは﹁足﹂の裏から分泌される粘液を用いる[5]。
ヘビの鱗は背中側と腹側は形状が異なり、腹側の板状を呈する長方形の鱗は﹁腹板﹂と呼ばれ、断面形状がフック︵鉤︶状になっており、これを地面にひっかけることによって蛇行を可能にしていると考えられる[1]。すなわち、腹板と地面との摩擦によって前進しているのである[5]。近年、カリフォルニアキングヘビの脱皮殻の詳細な調査より、ヘビの鱗はきわめて薄い脂質の層により被覆されていることが確認され、その脂質層は背中側よりも腹側の方が緻密な層を形成し、蛇行の際の潤滑油の役割を果たしていることが判明した[6]。
民俗学の吉野裕子によれば、ヘビの脱皮こそ永生と新生をもたらすものの象徴で、日本では古くから縁起物と考えられ、財布などに入れておくと財産運や金運が開けると信じられてきた[7]。
世界的には、色鮮やかな鱗の模様は初期の芸術にも大きな影響を与えたと考えられている。現在、蛇革の財布、衣服、その他小物への利用はヘビの大量殺害に繋がっており、人工蛇革の使用が提唱されている。

ニジボアは虹色変色を引き起こす鱗の色彩が名称の由来である。

﹁キスジヒバァ (Amphiesma stolatum) ﹂の鱗にある筋状突起︵キー ルとも︶。
ヘビの鱗は、皮膚の表皮の分化によって形成される[15]。鱗にはそれぞれ外表面と内表面がある。前の鱗と次の鱗の基部との間には空間があり、前の鱗の内表面からは皮膚が出て繋がっている[16]。ヘビの鱗の数は孵化した時から定まっており、加齢による増減はないが、成長して大きさを増し、脱皮の前後で形状が変わる場合もある[12]。
口の周囲と胴体側面の鱗は小さく、口や胴体を広げるられるようになっており、自分自身より遥かに大きな獲物を飲み込むことが可能な場合もある。

ホソメクラヘビやその他メクラヘビ種の円鱗は蛍光性で、低周波紫外線 ︵ブラックライト︶の下に置かれると鱗が輝く。
ヘビの鱗には様々な形状がある。メクラヘビ科では時に円形で[17]、ハナナガムチヘビでは長くて先端が尖った先細り形[18]、シロクチアオハブでは幅広な木の葉形[18]、またナンダなどのネズミヘビ︵ナミヘビ科︶では鱗が幅広で長い[18]。時にはキスジヒバァのように、大なり小なりの筋状突起︵キール︶が見られる場合もある[18]。ユウダ属の一部の種では、時に先端に2つの歯状突起がみられる[注釈 1][18]。トゲウミヘビ等では並列した棘状の鱗を持っている場合があり[16]、一方でミツウロコヘビ︵ドラゴンスネーク︶のように重なり合わない大きな突起[注釈 2]になった鱗をもつ場合もある[16]。
特殊化した鱗の例としては、ヘビの眼球を覆うブリル (brille) と呼ばれる透明な鱗が挙げられる。これは脱皮の際には古い皮膚の一部として脱落する[4]。英語圏では、ブリルはしばしば﹁癒合したまぶた (fused eyelid)﹂と呼ばれることがある[注釈 3]。

変容した尾の鱗がニシダイヤ︵又はセイブヒシモン︶ガラガラヘビの音 が鳴るラトルを形成する
ヘビの鱗で最も特殊化した例は、ガラガラヘビ属やヒメガラガラヘビ属などのガラガラヘビ類にある﹁ラトル (rattle)﹂[注釈 4]である。ラトルは、連動する複数の空洞が節状にゆるく繋がった構造をしており、基部だけが尾の先端に強固に付いている[19]。これを振ると、互いに振動し擦り合うことで、ガラガラヘビ特有の警戒音を発する。
孵化したてのガラガラヘビの尾の先端には、小さなボタン状の﹁ラトル原基﹂だけが強固に付着している[19]。最初の節は、幼体が初めて脱皮した時に付加され、[20] 脱皮のたびに更に節が付加されて、ラトルが形成される。このようにラトルは加齢と共に成長するものの、節自体が分離しやすいため、ラトルの長さでヘビの年齢を推定するのは不確実である[21]。

長さ1メートル超に及ぶヨーロッパヤマカガシの抜け殻︵脱皮殻︶
鱗を含む外皮が剥落することを脱皮という。ヘビの場合、皮膚の外側の層全体が1つの層を形成する[22]。ヘビの鱗はこの表皮の延長であるため別々に剥落せず、皮膚の外側の層が完全に繋がったものの一部であり、この皮は脱皮の際に靴下が裏返されるように脱ぎ捨てられる[12]。
脱皮は多くの役目を果たしている。第一に摩耗した皮膚を交換し、第二にダニ類などの寄生虫を除去する。脱皮による皮膚の更新は、昆虫などでは体の成長に必須のものとなっているが、ヘビにも当てはまるかについては議論が続いている[12][23]。
脱皮はヘビの生涯にわたって定期的に繰り返される。脱皮の前になると、ヘビは摂食を控え、隠れるか安全な場所に移動する。脱皮の直前には、皮膚は色がくすんで乾いた外観になり、目は曇るか青みがかる。古い表皮の内側は溶けており、新しい表皮から分離する。数日後、澄んだ目をしたヘビが古い皮膚から現れる。古い皮膚は口の付近で破れ、ヘビは周りの粗い表面に身を擦り付けるようにして身をよじらせながら脱ぎ進める。多くの場合、脱け殻は古い靴下のように一連なりになり、頭から尾まで全身が裏返しになっている。脱皮するより先に、より大きく明るい新しい皮膚が形成されている[12][24]。
老齢のヘビは年に1-2回しか脱皮しないこともあるが、若齢で成長途上のヘビは年に最大4回まで脱皮する場合がある[24]。脱皮して残された皮には鱗の配列が完全に保存されているため、ほぼ完全で無傷な抜け殻であれば、通常はそれで種を識別できる[12]。

頭部にある鱗の命名︵頭頂部の写真︶
鱗の配列は、分類学的な有用性のみならず、法医学や種の保全においても重要である[25]。頭部を除き、ヘビは瓦重ね状の鱗を有する[26]。ヘビには体に沿って全身または一部に鱗列があり、頭部などの部位に特殊な鱗が多くあり、それらは単一ないし左右一対である。
ヘビの体躯にある体鱗[注釈 5]は、胴に沿って列を作る。隣り合う体鱗列は互いに斜め方向へと列をなす[27]。大半のヘビでは体鱗列は奇数だが、カサントウ属などでは偶数になっている[16]。一部の水生・海生ヘビでは鱗が粒状になっており、列を数えることはできない[26]。
体鱗列数の幅は広く、フミキリヘビで10、キノボリアトバ属、スベハダヘビ属 、ヒメヘビ属、ワモンベニヘビで13、日本に生息するアカマタで17、アオダイショウでは23や25[27] である。大きなものだとニシキヘビ属で65から75、オオアタマウミヘビ属で74から93、ヤスリヘビ属で130から150ある。ヘビの大部分を占めるナミヘビ科は15、17、19の鱗列を持つ[16][28]。列は胴体中央で最も数が多く、頭・尾に向かうほど数が減る。
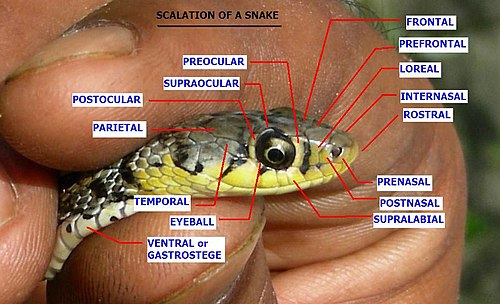
鱗の命名︵頭部を横から見たもの︶
ヘビの頭部および体にある様々な鱗を以下に示す。右の写真は南アジアの一般的な草むらに生息するナミヘビ科のキスジヒバァの鱗の名称︵英語︶[注釈 6]。

鱗の命名︵頭部を下から見たもの︶
頭部の鱗の識別は、鼻孔を基準に考えるのが最も分かりやすい。1つの鼻孔は2つの鱗に囲まれており、鼻板[注釈 7]と呼ばれる。 ナミヘビ科では鼻孔が前後の鼻板の間に位置するが、クサリヘビ科では鼻板が単一で、その中央に位置する[29]。前後の鼻板はそれぞれ前鼻板[注釈 8]、後鼻板[注釈 9]と呼ばれる。 左右両側の鼻板をつなぐ鱗にも名称があり、上側で繋ぐものを鼻間板[注釈 10]、前方で2つの前鼻板を繋ぐものを吻端板[注釈 11]と呼ぶ[29]。
眼窩の鱗[注釈 12]には、日本では定訳がみられない[注釈 3]。この鱗は眼球を覆う透明なもので、英語圏ではブリル[注釈 13]、スペクタクル[注釈 14]、アイキャップ[注釈 15]などと呼ばれる[12][31]。眼窩を囲む鱗のうち、前方のものを眼前板[注釈 16]と、後方のものを眼後板[注釈 17]、上側︵背側︶のものは眼上板[注釈 18]と呼ばれる[32]。また、眼窩下側︵腹側︶も囲むように鱗がある場合があり、眼下板[注釈 19]と呼ばれる。眼前板と後鼻板の間には、頬板[注釈 20][32]と呼ばれる鱗が1-2個ある[29]。コブラ科には頬板がない。
ヘビの唇沿いにある鱗は唇板[注釈 21]と呼ばれる。上唇にあるものは上唇板[注釈 22]、下唇にあるものは下唇板[注釈 23]と呼ばれる[32]。頭頂部と目の間で、左右の眼上板に隣接するのが1枚の額板[注釈 24]である[32]。額板の前方には2枚の前額板[注釈 25]が接しており、これはさらに前方で鼻孔間板とも接している。2つの前額板の間にもう1枚鱗がある場合もある[29]。 頭頂部の後部には額板に接する鱗が2枚あり、頭頂板[注釈 26]と呼ばれる。 後頭部の側面で頭頂板と上唇板の間にあるものは側頭板[注釈 27]と呼ばれる[29]。
頭部の下側には前方端にオトガイ板[注釈 28][注釈 29]と呼ばれる鱗がある[32]、下唇板に接している。顎下では鱗が対になって下唇板に挟まれており、前咽頭板[注釈 30][注釈 31]と後咽頭板[注釈 32] がある[32]。
中央部の喉部には、咽頭板及び胴体の第一腹板に隣接する複数の鱗があり、これらは喉板[注釈 33]と呼ばれる。顎下には鱗の間に縦方向の溝があり、オトガイ溝[注釈 34]とよばれる。これは左右の咽頭板の間から喉板の間を走っている。

黄色と黒の帯模様があるマルオアマガサの胴体の一部。胴体は断面が三 角形で、脊椎の畝の頂点には特徴的な鱗がある。

鱗の命名︵胴体を下から見たもの︶
ヘビの腹板の終点、尾部付近の腹側には総排出腔︵排泄口と生殖口を兼ねる器官︶の開口部を保護する肛板[注釈 37]がある。この肛板は1つの場合も左右2つに分かれている場合もある。肛板の後ろからが尾部とみなされる[19]。
種によっては尾部下側に1列ないし2列の大型の鱗を持ち、これらは尾下板[注釈 38]と呼ばれる[29][33]。これらの尾下板は滑らかな場合もあるが、パフアダーのように線状突起︵キール︶がある場合もある。尾の終端は先端に向かって単純に先細りになっていることが多いが、デスアダー属などでは棘になっており、終端がブッシュマスター属のように骨棘になる場合や、ガラガラヘビ属のようにラトルになる場合、多くの海生ヘビのように、舵の役割を果たす場合がある。

鱗の機能と特性[編集]

機能[編集]
上述したように、ヘビの鱗は﹁這︵は︶う﹂という移動方法を支えている。地面を後ろに押し出して進むためには、地面に引っかかるような器官が必要であり、それが腹側の、断面が鈎状になっている大型の板状の鱗︵腹板︶である[5]。脊椎動物であるヘビは蠕虫のような流体骨格ではないので、ミミズのように大幅に身体を伸び縮みさせることはできない。しかし、発達した筋肉によって全身をくねらせ、そうすることで頭と尾の間の距離をうまく縮め、同様の効果を上げている[5]。身体のくねりが大きければ大きいほど、地面と身体の接触する面積が広くなり、それだけ動く速度も速くなる[5]。同時に筋肉がうろこを立てて、身体を押し当てている面との摩擦を大きくしているのである[5]。また、身体をくねらせることにより、水中を﹁泳ぐ﹂ことも可能になったのである。 樹上性の種の一部は側稜を使って枝をつかむことが可能である。ヘビの皮と鱗は乾燥を防ぎ、水分を体内に保持する役割も果たしている[8]。ヘビは空気と地面の両方から振動を拾い、内部共振の複雑なシステムを使って両者を区別することができる[9] が、これにも鱗が関わっていると考えられている。成分と特性[編集]
爬虫類は両生類のうち、水中生活から陸上生活に移行したものから進化した。両生類の皮膚は柔らかく潤っているが、爬虫類の皮膚は水分の損失を防ぐためにそうした性質を失っている。また、多層の脂肪をともなった分厚い角質が発達しており、皮膚に不透水性を与え、紫外線を防ぐのに役立っている[10]。進化の過程で、爬虫類の皮膚細胞は非常に角質化した、頑強で乾燥したものとなった。全ての爬虫類において、鱗を含め表皮は一続きのシート状になっており[11]、ヘビが全身を脱皮する際にはそれがよく現れる。 ヘビの鱗は、他の生物における毛髪や爪などと同様、基本的には硬質タンパクのケラチンを主体とした角質で構成されているため﹁角鱗﹂と呼ばれる[12]。触るとひんやりしていて乾燥している[13]。 多くの有鱗目では、鱗は互いに重なり合い、外側から見える部分は硬いβケラチンで覆われ、鱗の付け根の部分はやわらかいαケラチンで覆われている。また、付け根部分の、隣の鱗との連結部はヒンジ状の構造になっていて、柔軟性を高めている。ヘビは、きわめて柔軟な体を持ち、大きな獲物を飲み込めるように皮膚を伸縮させることができるが、このため、鱗同士は強固に連結せず、一つ一つの鱗が先端は重なり合いながらも、基部は独立して皮膚に癒着している。皮膚を伸ばしたときには鱗同士の間隔が広がり、柔軟な皮膚が露出する。皮膚を縮めると鱗同士はもとどおりにすき間なく重なり合う。潤滑油の発見[編集]
足もないのに木に登ったり、砂漠を走ったり、泳いだり、また、木から木へ飛び移ったりできるヘビの多様な運動能力については長年にわたって謎とされてきた[14]。また、そうした激しい運動にかかわらず鱗が落剥することがほとんどないことも不思議とされてきた。さらに、腹側の鱗が背中側の鱗よりもはるかにすべすべしており、滑らかなのは一目瞭然であるにもかかわらず、それがどうしてなのかは従来説明がつかなかったのである[14]。 2015年12月9日の "Journal of the Royal Society Interface" は、ヘビの鱗の表面がわずか数ナノメートルというきわめて薄い潤滑油でコーティングされているという新発見の事実を発表した[14]。オレゴン州立大学の化学工学者ジョー・バイオとドイツのマックス・プランク高分子研究所のトビアス・ヴァイドナーが共同研究チームをつくり、カリフォルニアキングヘビ︵Lampropeltis californiae︶の脱皮殻にレーザーを照射し、鱗の表面分子がレーザー光線をどのように反射・散乱するかを調べたことにより得られた知見であり、その結果、ヘビの鱗が極薄の脂質︵生体内で脂肪の形で存在する炭化水素鎖︶の層によってコーティングされていること、さらに腹側が背中側よりはるかに滑らかで整然とした層をかたちづくっていることが判明したのである[14]。鱗の形態[編集]

表面と形状[編集]
ヘビの鱗の形状や大きさは様々である。鱗はザラザラの場合もあるし、滑らかであったり、縦方向の筋状突起︵リッジやキールと呼ばれる︶がある場合もある︵左上の写真参照︶。多くの場合、鱗には肉眼または顕微鏡で視認可能な鱗孔、結節、その他の微細構造がある。ヘビの鱗は、ブッシュバイパー属のAtheris ceratophoraのようにフリンジ状に変化したり、北米にいるガラガラヘビの尾のようにラトルに変化している場合もある[16]。 ボア属やニシキヘビ属といった原始的なヘビや、クサリヘビ属のような派生的なヘビの中には、頭部に小さな鱗が不規則に並ぶものもある。より派生的なヘビの頭部には、英語圏で﹁シールド﹂や﹁プレート﹂と呼ばれる大きな対称形の特殊な鱗がある[16]。
ラトル[編集]

色[編集]
ヘビの鱗は透明な硬いβケラチンでほとんど構成されている。青や緑を除いて、鱗の色は全て皮膚内側層の色素に起因するもので、鱗の成分や構造自体によるものではないが、青色は鱗自体の微細構造が光の回折によって生じ、緑色や玉虫色はこの仕組みによる青色と皮膚内側に由来する黄色が重なることで生じる。 一部のヘビは鱗の色をゆっくり変化させる能力を持っており、典型例は体色が季節変化と共に明るくなったり暗くなったりするものである。同様の変化が昼と夜の間で起こる例もある[12]。脱皮[編集]

鱗の配列[編集]

鱗の名称[編集]

頭部の鱗[編集]


胴部の鱗[編集]
ヘビの胴部にある鱗は、背骨側が体鱗、肋骨側が腹板と呼ばれる。背側中央に特別な列をなす大きな鱗があり、これは脊椎板[注釈 35]と呼ばれる︵右の写真参照︶。 ヘビの腹側には大型の鱗があり、腹板[注釈 36]と呼ばれる。腹板の数は種を識別に用いられる[29]。派生的なヘビ︵ナミヘビ上科︶では、腹板と背側の体鱗列が脊椎に対応しており、専門家は解剖せずとも脊椎の数を数えることができる。尾部の鱗[編集]

鱗の名称一覧[編集]

ag-前咽頭板
f -額板
in -鼻間板
l -頬板
la -上唇板
la'-下唇板
m -頤板
n -鼻板
p -頭頂板
pf -前額板
pg -後咽頭板
pro -眼前板
pso -眼前下板
pto -眼後板
r -吻端板
so -眼上板
t -側頭板
v -第一腹板
f -額板
in -鼻間板
l -頬板
la -上唇板
la'-下唇板
m -頤板
n -鼻板
p -頭頂板
pf -前額板
pg -後咽頭板
pro -眼前板
pso -眼前下板
pto -眼後板
r -吻端板
so -眼上板
t -側頭板
v -第一腹板
- 頭部の鱗
- 吻端板 (Rostral scale)
- 鼻吻板 (Nasorostral scale)
- 鼻板 (Nasal scale)
- 前鼻板 (Prenasal)
- 後鼻板 (Postnasal)
- 上鼻板 (Supranasal)
- 前頭鼻板 (Fronto-nasal)
- 鼻間板 (Internasal scales)
- ブリル (Brille)
- 眼窩の鱗 (Ocular scales)
- 眼前板 (preocular)
- 眼後板 (postocular)
- 眼上板 (supraocular)
- 眼下板 (subocular)
- 頬板 (loreal)
- 眼間板 (Interorbital scales)
- 額板 (Frontal scale)
- 前額板 (Prefrontal scales)
- 頭頂板 (Parietal scales)
- 後頭板 (Occipital scales)
- 後頭間板 (Interoccipital)
- 側頭板 (Temporal scales)
- 唇板 (Labial scales)
- 上唇板 (supralabial)
- 下唇板 (subralabial)
- 頤(オトガイ)板 (Mental scale)
- 咽頭板 (Chin shields)
- 前咽頭板 (anterior chin shields)
- 後咽頭板 (posterior chin shields)
- 咽頭間板 (Intergeneial)
- 喉板 (Gular scales)
- 胴部の鱗
- 体鱗 (Dorsal scales)
- 椎板 (Vertebral scales)
- 腹板 (Ventral scales)
- 尾部の鱗
- 肛板 (Anal scale)
- 尾下板 (Subcaudal scales)
分類学上の重要性[編集]
鱗は、科の識別にはあまり貢献しないが、属および種のレベルでは重要となり、鱗の命名法は精巧に定められている。鱗の配列に加え、鱗の表面及び手触り、模様と色彩、肛板の状態といった形態学的な特徴とを組み合わせることで、ヘビを種レベルまで分類するための主な手段となる[34]。
北米の、ヘビの多様性がさほど高くないような地域では、一般人が毒ヘビかどうかを区別できるよう、単純な鱗の識別に基づく簡単な方法が考案されている[35][36]。一方で、ミャンマーなど多様性の高い地域では、慎重に検討しなければ識別することはできないとされる[37]。
鱗の配列はフィールド調査における個体識別にも使用される場合がある。尾下板など特定の鱗を切り取ることで個々のヘビに印をつけるクリッピングは、標識再捕獲法によって生息数を推定する際に用いられる手法として一般的である[38]。

コブラ科のマルオアマガサには、鼻板と眼前板の間にあるべき頬板がな い
一般的には、鱗の特徴だけで毒ヘビかどうかを識別する単純な方法はない。毒蛇かどうかを調べるには、専門家の助けを借りて種を同定するのが正確だが[39]:190、専門家がいない場合は、形態を詳細に調べて、その地域にいるヘビについての信頼できる参考文献と照らし合わせて同定する。鱗の配列は種の同定に有用であり、毒ヘビかどうかは︵既に調べられていれば︶参考文献で確認できる。
鱗を用いた種の識別には、ヘビそのものだけでなく、その分類や鱗の名称に関する知識を持ち、科学的な文献にアクセスし読解できることが求められる。図表で鱗を照らし合わせる場合は、捕獲しなければ毒ヘビかどうかを使って識別することはできないが、これは現場では推奨されない[39]:190。大半の書籍やウェブサイトでは、鱗の図表よりも、その地域で見られる種の特徴を記述している[34][40]:52。
一部の地域には、毒ヘビかどうかを特定の鱗の有無によって素早く識別する方法もあるが、注意深さと例外について知識が必要とされる。例えばミャンマーでは、比較的無害なナミヘビ科と致死的な毒を持つコブラ科を識別するのに頬板の有無が使用されているが、これはコブラ科が鼻板と眼前板の間に頬板がないことを利用している[37]。しかし、こうしたやり方は、頭に小さな鱗が多数あるクサリヘビ科の毒ヘビ︵日本に生息するマムシやハブなど︶には適用できないので、その点を頭に入れずに使ってはならない。ナミヘビ科にもヤマカガシなどの毒ヘビがおり、こうした種を見分ける際にも注意深く検討する必要がある[37]。
南アジアでは、医療従事者が鱗の図表に基づいてヘビを同定できるよう、噛んだヘビが死んでいれば病院まで持ち込むことが推奨されており、それによってどの抗毒血清を投与すべきかを正確に判断することが可能になる。ただし、二次被害を防ぐため、そのためにヘビを捕獲・殺傷することは推奨されていない[41]。
毒ヘビと毒を持たないヘビの識別[編集]

脚注[編集]
注釈[編集]
(一)^ 英: bidentate。
(二)^ 英: knob。
(三)^ ab日本では名称を使わずに﹁眼球をカバーする透明な鱗がある﹂と紹介されることが多い[3]。なお、長崎国際大学の岩堀修明︵解剖学教授︶によると、発生初期は上下のまぶた︵の原基︶だが、やがて両者が﹁癒合したまま大きくなり、発生が進むに従って次第に透明になってくる。最終的に一枚の透明な眼瞼になったもの﹂[30] と解説されている。
(四)^ 和名の﹁ガラガラヘビ﹂は赤ちゃんをあやすがらがら (玩具)が由来だが、英名の﹁ラトルスネーク (rattlesnake)﹂は振ると音が出る打楽器ラトルが由来。この鱗部位については英名に基づき﹁ラトル﹂と記す。
(五)^ 英: Body scale, dorsal scale。
(六)^ 日本では、爬虫類の鱗を﹁身体部位+板︵ばん︶﹂で表記する通例があり、ヘビの鱗もこれに倣った表記となる。なお、写真と照合できるよう英語名も併記した。
(七)^ 英: nasals。
(八)^ 英: prenasal。
(九)^ 英: postnasal。
(十)^ 英: internasals。
(11)^ 英: rostral。
(12)^ 英: circumorbitalやocular。
(13)^ 英: brille。
(14)^ 英: spectacle。
(15)^ 英: eyecap。
(16)^ 英: preocular。
(17)^ 英: postocular。
(18)^ 英: supraocular。
(19)^ 英: subocular。
(20)^ 英: loreal。
(21)^ 英: labials。
(22)^ 英: supralabialsやupper labials。
(23)^ 英: infralabialsやlower labials。
(24)^ 英: frontal。
(25)^ 英: prefrontal。
(26)^ 英: parietal。
(27)^ 英: temporal。
(28)^ 英: mental。
(29)^ この位置にヘビの顎を制御するオトガイ神経が通っていることから、こう呼ばれる。
(30)^ 英: anterior chin shields。
(31)^ 英語名と訳語がやや不釣り合いなのは、この部位が英語圏では鱗よりもさらに固い盾板︵じゅんばん、英: shield︶に分類されている︵submaxillaryという鱗だとする一部テキストもあり︶ため[29]。
(32)^ 英: posterior chin shields。
(33)^ 英: gular。
(34)^ 英: mental groove。
(35)^ 英: vertebral。
(36)^ 英: ventralやgastrosteges。
(37)^ 英: anal。
(38)^ 英: subcaudalsやurosteges。
出典[編集]
(一)^ abcうろこのはなし ︵千葉県松戸市21世紀の森と広場パークセンターだより第81号︵2016年︶
(二)^ Boulenger, George A. 1890 The Fauna of British India. p. 1
(三)^ ab﹁意外と知らない知識-ヘビにまぶたはない﹂マイナビウーマン、2014年4月5日。
(四)^ abThe Snakes of Indiana Archived 2012-04-19 at the Wayback Machine. at The Centre for Reptile and Amphibian Conservation and Management, Indiana. Retrieved 14 August 2006.
(五)^ abcdefghネイチャー・ワークス︵1994︶pp.214-215
(六)^ ヘビのウロコに新発見!︵講談社 ﹁動く図鑑MOVE﹂︶
(七)^ 縁起物百科事典﹁蛇の抜け殻が縁起物と言われている理由﹂ ︵全国寺社観光協会︶
(八)^ Barnes, Thomas G. Snakes: Information for Kentucky Homeowners. University of Kentucky.
(九)^ Hartline, PH (1971). “Physiological basis for detection of sound and vibration in snakes”. The Journal of Experimental Biology 54 (2): 349-71. PMID 5553415.
(十)^ Cheng Chang; Ping Wu; Ruth E. Baker; Philip K. Maini; Lorenzo Alibardi; Cheng-Ming Chuong (21 May 2010). “Reptile scale paradigm: Evo-Devo, pattern formation and regeneration”. International Journal of Developmental Biology 53 (5-6): 813-826. doi:10.1387/ijdb.072556cc. PMC 2874329. PMID 19557687.
(11)^ “integument”. Encyclopædia Britannica Online (2014年). 2014年9月23日閲覧。
(12)^ abcdefghAre snakes slimy?atSingapore Zoological Garden's Docent. Retrieved 14 August 2006.
(13)^ Herpetology FAQatSan Diego Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 14 August 2006.
(14)^ abcdナショナル・ジオグラフィック﹁ヘビのウロコに﹃剥がれない潤滑油﹄初の発見:するすると滑らかに動ける驚きの秘密が判明﹂
(15)^ Alibardi, Lorenzo (2005). “Differentiation of snake epidermis, with emphasis on the shedding layer”. Journal of Morphology 264 (2): 178-90. doi:10.1002/jmor.10326. PMID 15761820.
(16)^ abcdefgGreene, Harry W. (2004) Snakes - The Evolution of Mystery in Nature. University of California Press, pp. 22-23 ISBN 0520224876.
(17)^ Boulenger, George A. The Fauna of British India... page 234
(18)^ abcdeSmith, Vol III, p. 6
(19)^ abcReptiles - Snake facts. Columbus Zoo & Aquarium. Retrieved on 2013-01-21.
(20)^ Young Snake Rattles! Ask a scientist! (Zoology archive). Newton BBS, Argonne National Laboratory. Newton.dep.anl.gov. Retrieved on 2013-01-21.
(21)^ Rhoades, Dusty. Spring rattles in! Desert USA website.
(22)^ Smith, Vol I, p. 30
(23)^ ZooPax Scales Part 3. Whozoo.org. Retrieved on 2013-01-21.
(24)^ abGeneral Snake Information. Division of Wildlife, South Dakota
(25)^ Baker, Barry W (2006). “Forensic implications of dorsal row counts on Puff-faced Water-snakes (Colubridae: Homalopsinae: Homalopsis buccata)”. Herpetological Review 37 (2): 171-173.
(26)^ abSmith, Vol III, p. 5
(27)^ ab加藤英明﹁鱗の数でヘビの種類を見分けよう!体鱗列数﹂、加藤英明の﹁静岡ぐるっと生き物探検!﹂、2020年1月25日閲覧。
(28)^ Smith, Vol III, p. 7
(29)^ abcdefghIdentifying snakes by scalation and other details. Wildsideholidays
(30)^ 岩堀修明、ドクター岩堀の﹁私設動物資料室﹂、爬虫類の眼瞼︵まぶた︶、2015年9月5日。
(31)^ Evolution of snakes. Arachnophiliac.co.uk (2007-02-12). Retrieved on 2013-01-21.
(32)^ abcdef柴田保彦ほか﹁男女群島から発見されたシロマダラ﹂大阪市立自然史博物館、42巻、1987年3月、27-28頁。
(33)^ 星野 一三雄﹁#6.ヘビの尻尾﹂、All About、2006年12月03日
(34)^ abHow To Identify Snakes. kentuckysnakes.org.
(35)^ North Carolina State Wildlife Damage Notes - Snakes Archived 2015-01-15 at the Wayback Machine.. Ces.ncsu.edu. Retrieved on 2013-01-21.
(36)^ Pennsylvania State University - Wildlife Damage Control 15 (pdf). (PDF) . Retrieved on 2013-01-21.
(37)^ abc“The Dangerously Venomous Snakes of Myanmar, Illustrated Checklist with Keys”. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 54 (24): 407-462. (2003).
(38)^ Resources Inventory Branch, Ministry of Environment, Lands and Parks Resources Inventory Branch for the Terrestrial Ecosystems Task Force Resources Inventory Committee . (1998). Inventory Methods for Snakes Standards for Components of British Columbia's Biodiversity No. 38.
(39)^ abThorpe, Roger S.; Thorpe, R. S.;Wüster, Wolfgang & Malhotra, Anita (1997). Venomous snakes: ecology, evolution, and snakebite. Vol. 70 of Symposia of the Zoological Society of London. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-854986-5.
(40)^ Berger, Cynthia. (2007). Venomous Snakes. Stackpole books. ISBN 0-8117-3412-9.
(41)^ Directorate General Armed Forces Medical Services, India. Memorandum No 102 : Snakebite. Undated.pdf available [ online]. Accessed on 21 Feb 2010.
参考資料[編集]
●青木薫・山口陽子監訳 編﹁動物はどのようにはうのか﹂﹃ネイチャー・ワークス‥地球科学館﹄同朋舎出版、1994年7月。ISBN 4-8104-1778-6。 ●小林達雄﹃縄文の思考﹄筑摩書房︿ちくま新書﹀、2008年4月。ISBN 4-88621-293-X。 ●能登健﹃列島の考古学 縄文時代﹄河出書房新社、2011年6月。ISBN 978-4-309-71442-4。 ●Smith, Malcolm A. (1943) The Fauna of British India, Ceylon and Burma including the whole of the Indo-Chinese Sub-region, Reptilia and Amphibia. Vol I - Loricata and Testudines, Vol II-Sauria, Vol III-Serpentes. Taylor and Francis, London.鱗名称の説明図にて使用。関連項目[編集]
外部リンク[編集]
- Are snakes slimy - Singapore Zoological Garden's Docent site
- Microscopic structure of smooth and keeled scales in snakes
- General Snake Information - Division of Wildlife, South Dakota
- Reptiles - Snake facts. Columbus Zoo & Aquarium.
- North Carolina State Wildlife Damage Notes - Snakes
- Pennsylvania State University - Wildlife Damage Control 15 (pdf)
- ZooPax Scales Part 3
- Species in Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) -2006年8月14日閲覧。
- The Endangered Species Handbook - Trade (chapter) Reptile Trade - Snakes and Lizards (section) -2006年8月15日閲覧。
