

|
Rescuing 2 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.9.2
|
Add: bibcode. | Use this bot. Report bugs. | Suggested by Whoop whoop pull up | #UCB_webform 1278/3660
|
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
==Main fullerenes== |
==Main fullerenes== |
||
Below is a table of main closed carbon fullerenes synthesized and characterized so far, with their [[Chemical Abstract Service|CAS]] number when known.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=W. L. F. Armarego |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PTXyS7Yj6zUC&pg=PA214 |title=Purification of laboratory chemicals |last2=Christina Li Lin Chai |date=11 May 2009 |publisher=Butterworth-Heinemann |isbn=978-1-85617-567-8 |pages=214– |access-date=26 December 2011}}</ref> Fullerenes with fewer than 60 carbon atoms have been called "lower fullerenes",<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Sun |first1=Marc C. Nicklaus |last2=Rui-hua |first2=Xie |title=Structure, Stability, and NMR Properties of Lower Fullerenes C38−C50 and Azafullerene C44N6 |journal=J. Phys. Chem. |date=2005 |volume=109 |issue=20 |pages=4617–4622 |doi=10.1021/jp0450181|pmid=16833800 }}</ref> and those with more than 70 atoms "higher fullerenes".<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Thilgen |first1=Carlo |last2=Herrmann |first2=Andreas |last3=Diederich |first3=François |title=The Covalent Chemistry of Higher Fullerenes: C70 and Beyond |journal=Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English |date=14 November 1997 |volume=36 |issue=21 |pages=2268–2280 |doi=10.1002/anie.199722681}}</ref> |
Below is a table of main closed carbon fullerenes synthesized and characterized so far, with their [[Chemical Abstract Service|CAS]] number when known.<ref>{{Cite book |last1=W. L. F. Armarego |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=PTXyS7Yj6zUC&pg=PA214 |title=Purification of laboratory chemicals |last2=Christina Li Lin Chai |date=11 May 2009 |publisher=Butterworth-Heinemann |isbn=978-1-85617-567-8 |pages=214– |access-date=26 December 2011}}</ref> Fullerenes with fewer than 60 carbon atoms have been called "lower fullerenes",<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Sun |first1=Marc C. Nicklaus |last2=Rui-hua |first2=Xie |title=Structure, Stability, and NMR Properties of Lower Fullerenes C38−C50 and Azafullerene C44N6 |journal=J. Phys. Chem. |date=2005 |volume=109 |issue=20 |pages=4617–4622 |doi=10.1021/jp0450181|pmid=16833800 |bibcode=2005JPCA..109.4617S }}</ref> and those with more than 70 atoms "higher fullerenes".<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Thilgen |first1=Carlo |last2=Herrmann |first2=Andreas |last3=Diederich |first3=François |title=The Covalent Chemistry of Higher Fullerenes: C70 and Beyond |journal=Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English |date=14 November 1997 |volume=36 |issue=21 |pages=2268–2280 |doi=10.1002/anie.199722681}}</ref> |
||
{|class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
{|class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" |
||
!Formula <!--!![[CAS number]]--> !! Num.<br/>Isom.[http://www.nanotube.msu.edu/fullerene/fullerene-isomers.html] ||Mol.<br/>Symm.!! Cryst.<br/>Symm. !![[Space group]]!! No !! Pearson <br/>symbol!!''a'' (nm)!!''b'' (nm)!!''c'' (nm)!!β°!!''Z''!! ρ<br/>(g/cm<sup>3</sup>) |
!Formula <!--!![[CAS number]]--> !! Num.<br/>Isom.[http://www.nanotube.msu.edu/fullerene/fullerene-isomers.html] ||Mol.<br/>Symm.!! Cryst.<br/>Symm. !![[Space group]]!! No !! Pearson <br/>symbol!!''a'' (nm)!!''b'' (nm)!!''c'' (nm)!!β°!!''Z''!! ρ<br/>(g/cm<sup>3</sup>) |
||


| Part of a series of articles on |
| Nanomaterials |
|---|
 |
| Carbon nanotubes |
| Fullerenes |
| Other nanoparticles |
| Nanostructured materials |
|
|
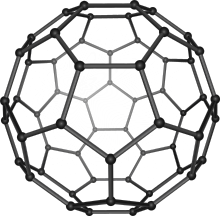
Afullerene is an allotrope of carbon whose molecule consists of carbon atoms connected by single and double bonds so as to form a closed or partially closed mesh, with fused rings of five to seven atoms. The molecule may be a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, tube, or many other shapes and sizes. Graphene (isolated atomic layers of graphite), which is a flat mesh of regular hexagonal rings, can be seen as an extreme member of the family.
Fullerenes with a closed mesh topology are informally denoted by their empirical formulaCn, often written Cn, where n is the number of carbon atoms. However, for some values of n there may be more than one isomer.
The family is named after buckminsterfullerene (C60), the most famous member, which in turn is named after Buckminster Fuller. The closed fullerenes, especially C60, are also informally called buckyballs for their resemblance to the standard ballofassociation football ("soccer"). Nested closed fullerenes have been named bucky onions. Cylindrical fullerenes are also called carbon nanotubesorbuckytubes.[1] The bulk solid form of pure or mixed fullerenes is called fullerite.[2]
Fullerenes had been predicted for some time, but only after their accidental synthesis in 1985 were they detected in nature[3][4] and outer space.[5][6] The discovery of fullerenes greatly expanded the number of known allotropes of carbon, which had previously been limited to graphite, diamond, and amorphous carbon such as soot and charcoal. They have been the subject of intense research, both for their chemistry and for their technological applications, especially in materials science, electronics, and nanotechnology.[7]

The icosahedral C
60H
60 cage was mentioned in 1965 as a possible topological structure.[8] Eiji Osawa predicted the existence of C
60 in 1970.[9][10] He noticed that the structure of a corannulene molecule was a subset of the shape of a football, and hypothesised that a full ball shape could also exist. Japanese scientific journals reported his idea, but neither it nor any translations of it reached Europe or the Americas.
Also in 1970, R. W. Henson (then of the UK Atomic Energy Research Establishment) proposed the C
60 structure and made a model of it. Unfortunately, the evidence for that new form of carbon was very weak at the time, so the proposal was met with skepticism, and was never published. It was acknowledged only in 1999.[11][12]
In 1973, independently from Henson, a group of scientists from the USSR made a quantum-chemical analysis of the stability of C
60 and calculated its electronic structure. The paper was published in 1973,[13] but the scientific community did not give much importance to this theoretical prediction.
Around 1980, Sumio Iijima identified the molecule of C
60 from an electron microscope image of carbon black, where it formed the core of a particle with the structure of a "bucky onion".[14]
Also in the 1980's at MIT, Mildred Dresselhaus and Morinobu Endo, collaborating with T. Venkatesan, directed studies blasting graphite with lasers, producing carbon clusters of atoms, which would be later identified as "fullerenes."[15]
In 1985, Harold Kroto of the University of Sussex, working with James R. Heath, Sean O'Brien, Robert Curl and Richard Smalley from Rice University, discovered fullerenes in the sooty residue created by vaporising carbon in a helium atmosphere. In the mass spectrum of the product, discrete peaks appeared corresponding to molecules with the exact mass of sixty or seventy or more carbon atoms, namely C
60 and C
70. The team identified their structure as the now familiar "buckyballs".[16]
The name "buckminsterfullerene" was eventually chosen for C
60 by the discoverers as an homage to American architect Buckminster Fuller for the vague similarity of the structure to the geodesic domes which he popularized; which, if they were extended to a full sphere, would also have the icosahedral symmetry group.[17] The "ene" ending was chosen to indicate that the carbons are unsaturated, being connected to only three other atoms instead of the normal four. The shortened name "fullerene" eventually came to be applied to the whole family.
Kroto, Curl, and Smalley were awarded the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry[18] for their roles in the discovery of this class of molecules.
Kroto and the Rice team already discovered other fullerenes besides C60,[16] and the list was much expanded in the following years. Carbon nanotubes were first discovered and synthesized in 1991.[19][20]
After their discovery, minute quantities of fullerenes were found to be produced in sooty flames,[21] and by lightning discharges in the atmosphere.[4] In 1992, fullerenes were found in a family of mineraloids known as shungitesinKarelia, Russia.[3]
The production techniques were improved by many scientists, including Donald Huffman, Wolfgang Krätschmer, Lowell D. Lamb, and Konstantinos Fostiropoulos.[22] Thanks to their efforts, by 1990 it was relatively easy to produce gram-sized samples of fullerene powder. Fullerene purification remains a challenge to chemists and to a large extent determines fullerene prices.
In 2010, the spectral signatures of C60 and C70 were observed by NASA's Spitzer infrared telescope in a cloud of cosmic dust surrounding a star 6500 light years away.[5] Kroto commented: "This most exciting breakthrough provides convincing evidence that the buckyball has, as I long suspected, existed since time immemorial in the dark recesses of our galaxy."[6] According to astronomer Letizia Stanghellini, "It’s possible that buckyballs from outer space provided seeds for life on Earth."[23] In 2019, ionized C60 molecules were detected with the Hubble Space Telescope in the space between those stars.[24][25]
There are two major families of fullerenes, with fairly distinct properties and applications: the closed buckyballs and the open-ended cylindrical carbon nanotubes.[26] However, hybrid structures exist between those two classes, such as carbon nanobuds — nanotubes capped by hemispherical meshes or larger "buckybuds".

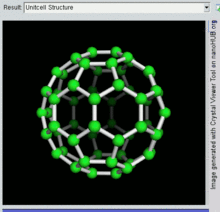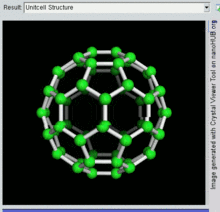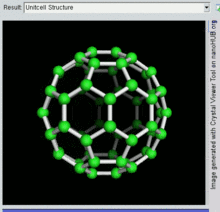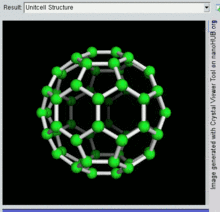
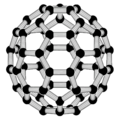
Buckminsterfullerene is the smallest fullerene molecule containing pentagonal and hexagonal rings in which no two pentagons share an edge (which can be destabilizing, as in pentalene). It is also most common in terms of natural occurrence, as it can often be found in soot.
The empirical formula of buckminsterfullerene is C
60 and its structure is a truncated icosahedron, which resembles an association football ball of the type made of twenty hexagons and twelve pentagons, with a carbon atom at the vertices of each polygon and a bond along each polygon edge.
The van der Waals diameter of a buckminsterfullerene molecule is about 1.1 nanometers (nm).[27] The nucleus to nucleus diameter of a buckminsterfullerene molecule is about 0.71 nm.
The buckminsterfullerene molecule has two bond lengths. The 6:6 ring bonds (between two hexagons) can be considered "double bonds" and are shorter than the 6:5 bonds (between a hexagon and a pentagon). Its average bond length is 1.4 Å.
Another fairly common fullerene has empirical formula C
70,[28] but fullerenes with 72, 76, 84 and even up to 100 carbon atoms are commonly obtained.
The smallest possible fullerene is the dodecahedral C
20. There are no fullerenes with 22 vertices.[29] The number of different fullerenes C2n grows with increasing n = 12, 13, 14, ..., roughly in proportion to n9 (sequence A007894 in the OEIS). For instance, there are 1812 non-isomorphic fullerenes C
60. Note that only one form of C
60, buckminsterfullerene, has no pair of adjacent pentagons (the smallest such fullerene). To further illustrate the growth, there are 214,127,713 non-isomorphic fullerenes C
200, 15,655,672 of which have no adjacent pentagons. Optimized structures of many fullerene isomers are published and listed on the web.[30]
Heterofullerenes have heteroatoms substituting carbons in cage or tube-shaped structures. They were discovered in 1993[31] and greatly expand the overall fullerene class of compounds and can have dangling bonds on their surfaces. Notable examples include boron, nitrogen (azafullerene), oxygen, and phosphorus derivatives.
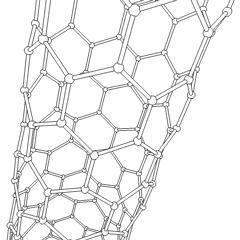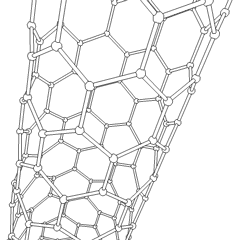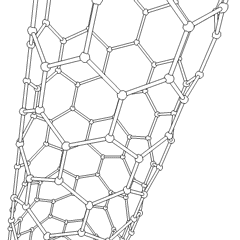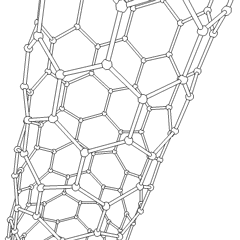
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical fullerenes. These tubes of carbon are usually only a few nanometres wide, but they can range from less than a micrometer to several millimeters in length. They often have closed ends, but can be open-ended as well. There are also cases in which the tube reduces in diameter before closing off. Their unique molecular structure results in extraordinary macroscopic properties, including high tensile strength, high electrical conductivity, high ductility, high heat conductivity, and relative chemical inactivity (as it is cylindrical and "planar" — that is, it has no "exposed" atoms that can be easily displaced). One proposed use of carbon nanotubes is in paper batteries, developed in 2007 by researchers at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.[32] Another highly speculative proposed use in the field of space technologies is to produce high-tensile carbon cables required by a space elevator.
Buckyballs and carbon nanotubes have been used as building blocks for a great variety of derivatives and larger structures, such as[26]
After the discovery of C60, many fullerenes have been synthesized (or studied theoretically by molecular modeling methods) in which some or all the carbon atoms are replaced by other elements. Non-carbon nanotubes, in particular, have attracted much attention.
A type of buckyball which uses boron atoms, instead of the usual carbon, was predicted and described in 2007. The B
80 structure, with each atom forming 5 or 6 bonds, was predicted to be more stable than the C
60 buckyball.[38] However, subsequent analysis found that the predicted Ih symmetric structure was vibrationally unstable and the resulting cage would undergo a spontaneous symmetry break, yielding a puckered cage with rare Th symmetry (symmetry of a volleyball).[39] The number of six-member rings in this molecule is 20 and number of five-member rings is 12. There is an additional atom in the center of each six-member ring, bonded to each atom surrounding it. By employing a systematic global search algorithm, it was later found that the previously proposed b
80 fullerene is not a global maximum for 80-atom boron clusters and hence can not be found in nature; the most stable configurations have complex.[40] The same paper concluded that boron's energy landscape, unlike others, has many disordered low-energy structures, hence pure boron fullerenes are unlikely to exist in nature.[40]
However, an irregular B
40 complex dubbed borospherene was prepared in 2014. This complex has two hexagonal faces and four heptagonal faces with in D2d symmetry interleaved with a network of 48 triangles.[41]
Inorganic (carbon-free) fullerene-type structures have been built with the molybdenum(IV) sulfide (MoS2), long used as a graphite-like lubricant, tungsten (WS2), titanium (TiS2) and niobium (NbS2). These materials were found to be stable up to at least 350 tons/cm2 (34.3 GPa).[42]
Icosahedral or distorted-icosahedral fullerene-like complexes have also been prepared for germanium, tin, and lead; some of these complexes are spacious enough to hold most transition metal atoms.[43][44]
Below is a table of main closed carbon fullerenes synthesized and characterized so far, with their CAS number when known.[45] Fullerenes with fewer than 60 carbon atoms have been called "lower fullerenes",[46] and those with more than 70 atoms "higher fullerenes".[47]
| Formula | Num. Isom.[1] |
Mol. Symm. |
Cryst. Symm. |
Space group | No | Pearson symbol |
a (nm) | b (nm) | c (nm) | β° | Z | ρ (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C 20 |
1 | Ih | ||||||||||
| C 60 |
1 | Ih | ||||||||||
| C 70 |
1 | D5h | ||||||||||
| C 72 |
1 | D6h | ||||||||||
| C 74 |
1 | D3h | ||||||||||
| C 76 |
2 | D2* | Monoclinic | P21 | 4 | mP2 | 1.102 | 1.108 | 1.768 | 108.10 | 2 | 1.48 |
| Cubic | Fm3m | 225 | cF4 | 1.5475 | 1.5475 | 1.5475 | 90 | 4 | 1.64 | |||
| C 78 |
5 | D2v | ||||||||||
| C 80 |
7 | |||||||||||
| C 82 |
9 | C 2, C2v, C3v |
Monoclinic | P21 | 4 | mP2 | 1.141 | 1.1355 | 1.8355 | 108.07 | 2 | |
| C 84 |
24 | D2*, D2d | Cubic | Fm3m | 1.5817[48] | 1.5817 | 1.5817 | 90 | ||||
| C 86 |
19 | |||||||||||
| C 88 |
35 | |||||||||||
| C 90 |
46 | |||||||||||
| C 3996 |
In the table, "Num.Isom." is the number of possible isomers within the "isolated pentagon rule", which states that two pentagons in a fullerene should not share edges.[49][50] "Mol.Symm." is the symmetry of the molecule,[50][51] whereas "Cryst.Symm." is that of the crystalline framework in the solid state. Both are specified for the most experimentally abundant form(s). The asterisk * marks symmetries with more than one chiral form.
When C
76orC
82 crystals are grown from toluene solution they have a monoclinic symmetry. The crystal structure contains toluene molecules packed between the spheres of the fullerene. However, evaporation of the solvent from C
76 transforms it into a face-centered cubic form.[52] Both monoclinic and face-centered cubic (fcc) phases are known for better-characterized C
60 and C
70 fullerenes.
Schlegel diagrams are often used to clarify the 3D structure of closed-shell fullerenes, as 2D projections are often not ideal in this sense.[53]
In mathematical terms, the combinatorial topology (that is, the carbon atoms and the bonds between them, ignoring their positions and distances) of a closed-shell fullerene with a simple sphere-like mean surface (orientable, genus zero) can be represented as a convex polyhedron; more precisely, its one-dimensional skeleton, consisting of its vertices and edges. The Schlegel diagram is a projection of that skeleton onto one of the faces of the polyhedron, through a point just outside that face; so that all other vertices project inside that face.
The Schlegel diagram of a closed fullerene is a graph that is planar and 3-regular (or "cubic"; meaning that all vertices have degree3).
A closed fullerene with sphere-like shell must have at least some cycles that are pentagons or heptagons. More precisely, if all the faces have 5 or 6 sides, it follows from Euler's polyhedron formula, V−E+F=2 (where V, E, F are the numbers of vertices, edges, and faces), that V must be even, and that there must be exactly 12 pentagons and V/2−10 hexagons. Similar constraints exist if the fullerene has heptagonal (seven-atom) cycles.[54]
Open fullerenes, like carbon nanotubes and graphene, can consist entirely of hexagonal rings. In theory, a long nanotube with ends joined to form a closed torus-like sheet could also consist entirely of hexagons.
Since each carbon atom is connected to only three neighbors, instead of the usual four, it is customary to describe those bonds as being a mixture of single and double covalent bonds. The hybridization of carbon in C60 has been reported to be sp2.01.[55] The bonding state can be analyzed by Raman spectroscopy, IR spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.[55][56]
Additional atoms, ions, clusters, or small molecules can be trapped inside fullerenes to form inclusion compounds known as endohedral fullerenes. An unusual example is the egg-shaped fullerene Tb3N@C
84, which violates the isolated pentagon rule.[57] Evidence for a meteor impact at the end of the Permian period was found by analyzing noble gases preserved by being trapped in fullerenes.[58]
In the early 2000s, the chemical and physical properties of fullerenes were a hot topic in the field of research and development. Popular Science discussed possible uses of fullerenes (graphene) in armor.[59]
In the field of nanotechnology, heat resistance and superconductivity are some of the more heavily studied properties.
There are many calculations that have been done using ab-initio quantum methods applied to fullerenes. By DFT and TD-DFT methods one can obtain IR, Raman and UV spectra. Results of such calculations can be compared with experimental results.
Fullerene is an unusual reactant in many organic reactions such as the Bingel reaction discovered in 1993.
Researchers have been able to increase the reactivity of fullerenes by attaching active groups to their surfaces. Buckminsterfullerene does not exhibit "superaromaticity": that is, the electrons in the hexagonal rings do not delocalize over the whole molecule.
A spherical fullerene of n carbon atoms has n pi-bonding electrons, free to delocalize. These should try to delocalize over the whole molecule. The quantum mechanics of such an arrangement should be like only one shell of the well-known quantum mechanical structure of a single atom, with a stable filled shell for n = 2, 8, 18, 32, 50, 72, 98, 128, etc. (i.e., twice a perfect square number), but this series does not include 60. This 2(N + 1)2 rule (with N integer) for spherical aromaticity is the three-dimensional analogue of Hückel's rule. The 10+ cation would satisfy this rule, and should be aromatic. This has been shown to be the case using quantum chemical modelling, which showed the existence of strong diamagnetic sphere currents in the cation.[60]
As a result, C
60 in water tends to pick up two more electrons and become an anion. The nC
60 described below may be the result of C
60 trying to form a loose metallic bond.
Under high pressure and temperature, buckyballs collapse to form various one-, two-, or three-dimensional carbon frameworks. Single-strand polymers are formed using the Atom Transfer Radical Addition Polymerization (ATRAP) route.[61]
"Ultrahard fullerite" is a coined term frequently used to describe material produced by high-pressure high-temperature (HPHT) processing of fullerite. Such treatment converts fullerite into a nanocrystalline form of diamond which has been reported to exhibit remarkable mechanical properties.[62]

Fullerenes are stable, but not totally unreactive. The sp2-hybridized carbon atoms, which are at their energy minimum in planar graphite, must be bent to form the closed sphere or tube, which produces angle strain. The characteristic reaction of fullerenes is electrophilic addition at 6,6-double bonds, which reduces angle strain by changing sp2-hybridized carbons into sp3-hybridized ones. The change in hybridized orbitals causes the bond angles to decrease from about 120° in the sp2 orbitals to about 109.5° in the sp3 orbitals. This decrease in bond angles allows for the bonds to bend less when closing the sphere or tube, and thus, the molecule becomes more stable.


Fullerenes are soluble in many organic solvents, such as toluene, chlorobenzene, and 1,2,3-trichloropropane. Solubilities are generally rather low, such as 8 g/L for C60incarbon disulfide. Still, fullerenes are the only known allotrope of carbon that can be dissolved in common solvents at room temperature.[63][64][65][66][67] Among the best solvents is 1-chloronaphthalene, which will dissolve 51 g/L of C60.
Solutions of pure buckminsterfullerene have a deep purple color. Solutions of C
70 are a reddish brown. The higher fullerenes C
76toC
84 have a variety of colors.
Millimeter-sized crystals of C
60 and C
70, both pure and solvated, can be grown from benzene solution. Crystallization of C
60 from benzene solution below 30 °C (when solubility is maximum) yields a triclinic solid solvate C
60·4C
6H
6. Above 30 °C one obtains solvate-free fcc C
60.[68][69]
In 1999, researchers from the University of Vienna demonstrated that wave-particle duality applied to molecules such as fullerene.[70]
Fullerenes are normally electrical insulators, but when crystallized with alkali metals, the resultant compound can be conducting or even superconducting.[71]
Some fullerenes (e.g. C
76, C
78, C
80, and C
84) are inherently chiral because they are D2-symmetric, and have been successfully resolved. Research efforts are ongoing to develop specific sensors for their enantiomers.
Two theories have been proposed to describe the molecular mechanisms that make fullerenes. The older, “bottom-up” theory proposes that they are built atom-by-atom. The alternative “top-down” approach claims that fullerenes form when much larger structures break into constituent parts.[72]
In 2013 researchers discovered that asymmetrical fullerenes formed from larger structures settle into stable fullerenes. The synthesized substance was a particular metallofullerene consisting of 84 carbon atoms with two additional carbon atoms and two yttrium atoms inside the cage. The process produced approximately 100 micrograms.[72]
However, they found that the asymmetrical molecule could theoretically collapse to form nearly every known fullerene and metallofullerene. Minor perturbations involving the breaking of a few molecular bonds cause the cage to become highly symmetrical and stable. This insight supports the theory that fullerenes can be formed from graphene when the appropriate molecular bonds are severed.[72][73]
According to the IUPAC, to name a fullerene, one must cite the number of member atoms for the rings which comprise the fullerene, its symmetry point group in the Schoenflies notation, and the total number of atoms. For example, buckminsterfullerene C60 is systematically named (C
60-Ih)[5,6]fullerene. The name of the point group should be retained in any derivative of said fullerene, even if that symmetry is lost by the derivation.
To indicate the position of substituted or attached elements, the fullerene atoms are usually numbered in a spiral path, usually starting with the ring on one of the main axes. If the structure of the fullerene does not allow such numbering, another starting atom was chosen to still achieve a spiral path sequence.
The latter is the case for C70, which is (C
70-D5h(6))[5,6]fullerene in IUPAC notation. The symmetry D5h(6) means that this is the isomer where the C5 axis goes through a pentagon surrounded by hexagons rather than pentagons.[53]
In IUPAC's nomenclature, fully saturated analogues of fullerenes are called fulleranes. If the mesh has other element(s) substituted for one or more carbons, the compound is named a heterofullerene. If a double bond is replaced by a methylene bridge −CH2−, the resulting structure is a homofullerene. If an atom is fully deleted and missing valences saturated with hydrogen atoms, it is a norfullerene. When bonds are removed (both sigma and pi), the compound becomes secofullerene; if some new bonds are added in an unconventional order, it is a cyclofullerene.[53]
Fullerene production generally starts by producing fullerene-rich soot. The original (and still current) method was to send a large electric current between two nearby graphite electrodes in an inert atmosphere. The resulting electric arc vaporizes the carbon into a plasma that then cools into sooty residue.[16] Alternatively, soot is produced by laser ablation of graphite or pyrolysisofaromatic hydrocarbons.[74][citation needed] Combustion of benzene is the most efficient process, developed at MIT.[75][76]
These processes yield a mixture of various fullerenes and other forms of carbon. The fullerenes are then extracted from the soot using appropriate organic solvents and separated by chromatography.[77]: p.369 One can obtain milligram quantities of fullerenes with 80 atoms or more. C76, C78 and C84 are available commercially.
Fullerenes have been extensively used for several biomedical applications including the design of high-performance MRI contrast agents, X-ray imaging contrast agents, photodynamic therapy and drug and gene delivery, summarized in several comprehensive reviews.[78]
While past cancer research has involved radiation therapy, photodynamic therapy is important to study because breakthroughs in treatments for tumor cells will give more options to patients with different conditions. Recent experiments using HeLa cells in cancer research involves the development of new photosensitizers with increased ability to be absorbed by cancer cells and still trigger cell death. It is also important that a new photosensitizer does not stay in the body for a long time to prevent unwanted cell damage.[79]
Fullerenes can be made to be absorbed by HeLa cells. The C
60 derivatives can be delivered to the cells by using the functional groups L-phenylalanine, folic acid, and L-arginine among others.[80]
Functionalizing the fullerenes aims to increase the solubility of the molecule by the cancer cells. Cancer cells take up these molecules at an increased rate because of an upregulation of transporters in the cancer cell, in this case amino acid transporters will bring in the L-arginine and L-phenylalanine functional groups of the fullerenes.[81]
Once absorbed by the cells, the C
60 derivatives would react to light radiation by turning molecular oxygen into reactive oxygen which triggers apoptosis in the HeLa cells and other cancer cells that can absorb the fullerene molecule. This research shows that a reactive substance can target cancer cells and then be triggered by light radiation, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues while undergoing treatment.[82]
When absorbed by cancer cells and exposed to light radiation, the reaction that creates reactive oxygen damages the DNA, proteins, and lipids that make up the cancer cell. This cellular damage forces the cancerous cell to go through apoptosis, which can lead to the reduction in size of a tumor. Once the light radiation treatment is finished the fullerene will reabsorb the free radicals to prevent damage of other tissues.[83] Since this treatment focuses on cancer cells, it is a good option for patients whose cancer cells are within reach of light radiation. As this research continues, the treatment may penetrate deeper into the body and be absorbed by cancer cells more effectively.[79]
In 2013, a comprehensive review on the toxicity of fullerene was published reviewing work beginning in the early 1990s to present and concluded that very little evidence gathered since the discovery of fullerenes indicate that C
60 is toxic.[78] The toxicity of these carbon nanoparticles is not only dose- and time-dependent, but also depends on a number of other factors such as:
It was recommended to assess the pharmacology of every new fullerene- or metallofullerene-based complex individually as a different compound.
Examples of fullerenes appear frequently in popular culture. Fullerenes appeared in fiction well before scientists took serious interest in them. In a humorously speculative 1966 column for New Scientist, David Jones suggested the possibility of making giant hollow carbon molecules by distorting a plane hexagonal net with the addition of impurity atoms.[84]
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link)
|
| |
|---|---|
| Overview |
|
| Impact and applications |
|
| Nanomaterials |
|
| Molecular self-assembly |
|
| Nanoelectronics |
|
| Scanning probe microscopy |
|
| Molecular nanotechnology |
|
| |
|
| |
|---|---|
| Books |
|
| Other |
|
| Related |
|
| |
| Authority control databases: National |
|
|---|