

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Chloric(V) acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.303 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2626 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
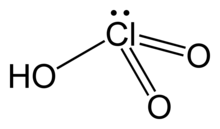
| HClO3 | |
| Molar mass | 84.45914 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | colourless solution |
| Density | 1 g/mL, solution (approximate) |
| >40 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |
| Acidity (pKa) | −2.7[1] |
| Conjugate base | Chlorate |
| Structure | |
| pyramidal | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Oxidant, Corrosive |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H271, H314 | |
| P210, P220, P221, P260, P264, P280, P283, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P306+P360, P310, P321, P363, P370+P378, P371+P380+P375, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
bromic acid iodic acid |
Other cations |
ammonium chlorate sodium chlorate potassium chlorate |
Related compounds |
hydrochloric acid hypochlorous acid chlorous acid perchloric acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chloric acid, HClO3, is an oxoacidofchlorine, and the formal precursor of chlorate salts. It is a strong acid (pKa ≈ −2.7) and an oxidizing agent.
Chloric acid is thermodynamically unstable with respect to disproportionation.
Chloric acid is stable in cold aqueous solution up to a concentration of approximately 30%, and solution of up to 40% can be prepared by careful evaporation under reduced pressure. Above these concentrations, chloric acid solutions decompose to give a variety of products, for example:
Chloric acid is a powerful oxidizing agent. Most organics and flammables will deflagrate on contact.
It can be prepared by the reaction of sulfuric acid with barium chlorate, the insoluble barium sulfate being removed by precipitation:
Another method is the heating of hypochlorous acid, producing chloric acid and hydrogen chloride:
|
Salts and covalent derivatives of the chlorate ion
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||