

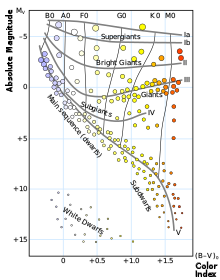
Adwarf star is a star of relatively small size and low luminosity. Most main sequence stars are dwarf stars. The meaning of the word "dwarf" was later extended to some star-sized objects that are not stars, and compact stellar remnants that are no longer stars.
The term was originally coined in 1906 when the Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung noticed that the reddest stars – classified as K and M in the Harvard scheme – could be divided into two distinct groups. They are either much brighter than the Sun, or much fainter. To distinguish these groups, he called them "giant" and "dwarf" stars,[1] the dwarf stars being fainter and the giants being brighter than the Sun.
Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan Keenan System using the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, and M, a sequence from the hottest: type O, to the coolest: type M.
With the development of infrared astronomy in the late 20th century the Morgan Keenan system was extended to cooler types L and T, all of which are "dwarfs" but not all of which are stars as such.

The scope of the term "dwarf" at present includes the following:
|
| |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
| Formation |
| ||||||
| Evolution |
| ||||||
| Classification |
| ||||||
| Nucleosynthesis |
| ||||||
| Structure |
| ||||||
| Properties |
| ||||||
| Star systems |
| ||||||
| Earth-centric observations |
| ||||||
| Lists |
| ||||||
| Related |
| ||||||
| |||||||