

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
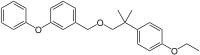
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-{[2-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropoxy]methyl}-3-phenoxybenzene | |
| Other names
Ethofenprox, MTI-500, Trebon, Zenivex | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.100.942 |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H28O3 | |
| Molar mass | 376.496 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White (pure) or amber (man.) |
| Density | 1.172 g/cm3 at 20.7 °C |
| Melting point | 37.4 °C (99.3 °F; 310.5 K) |
| Boiling point | Degradation at about 200 °C |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | > 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Etofenprox is a pyrethroid derivative which is used as an insecticide.[1] Mitsui Chemicals Agro Inc. is the main manufacturer of the chemical. It is also used as an ingredient in flea medication for cats and dogs.
Etofenprox is an insecticide which disturbs insect nervous systems following direct contact or ingestion, and which is active against a broad spectrum of pests. It is used in agriculture, horticulture, viticulture, forestry, animal health and public health against many insect pests, for instance Lepidoptera, Hemiptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, Thysanoptera, and Hymenoptera. In agriculture, etofenprox is used on a broad range of crops such as rice, fruits, vegetables, corn, soybeans, and tea. It is poorly absorbed by roots and little translocation occurs within plants.[2]
In the public health sector, etofenprox is used for vector control either by direct application in infested areas or indirectly by impregnating fabrics, such as mosquito nets. Etofenprox is used at low volumes to control adult mosquitoes, non-biting midges, and biting and non-biting flies. Etofenprox is used undiluted for ultra low volume aerosol applications or diluted with a diluent such as mineral oil for direct applications, for the control of pest species in or near residential, industrial, commercial, urban, recreational areas, woodlands, golf courses, and other areas where these pests are a problem.
Etofenprox is harmful if swallowed and causes moderate eye irritation. Contact with eyes, skin or clothing should be avoided. Repeated exposure to etofenprox can cause skin irritation.[3] LD50s are >2000 mg/kg (acute oral, rat), >2000 mg/kg (acute dermal, rat), and >5.88 mg/L (acute inhalation, rat). In rabbits, it is not a skin irritant or eye irritant. It did not cause skin sensitization in guinea pig (intradermal and topical).[4]
This pesticide is toxic to aquatic organisms, including fish and aquatic invertebrates. Runoff from treated areas or deposition into bodies of water may be hazardous to fish and other aquatic organisms. Etofenprox is highly toxic to bees exposed to direct treatment on blooming crops or weeds. Applications should be timed to provide the maximum possible interval between treatment and the next period of bee activity.[3]
Etofenprox is decomposed in soil by anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms. In sterilized soil, little degradation took place in a 56-day test.[5] The principle metabolites do not accumulate and degrade to CO2. Etofenprox's half-life in aerobic soil is between 7 and 25 days.[6] One study showed it to have a half-life of 3 weeks on bean leaves.[7]
Etofenprox is combustible and should not be used or stored near heat or open flame.[3]