

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
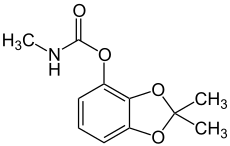
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethyl-2H-1,3-benzodioxol-4-yl methylcarbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.091 |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H13NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 223.23 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| QP53AE03 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Bendiocarb is an acutely toxic carbamate insecticide used in public health and agriculture and is effective against a wide range of nuisance and disease vector insects. Many bendiocarb products are or were sold under the tradenames "Ficam" and "Turcam."
All bendiocarb-containing products in the United States were recently[when?] cancelled, after its manufacturers voluntarily chose to pull their products off the market, rather than conduct additional safety studies required by the EPA.[1] In other countries, it is still used in homes, industrial plants, and food storage sites to control bedbugs, mosquitoes, flies, wasps, ants, fleas, cockroaches, silverfish, and ticks but can be used against a wide variety of insects as well as snails and slugs. It is one of 12 insecticides recommended by the World Health Organization for use in malaria control.[2]
Bendiocarb is not considered to be carcinogenic, but it is acutely toxic. Like other carbamates, it reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme required for normal transmission of nerve impulses. Bendiocarb binds to the active site of this enzyme leading to an accumulation of acetylcholine, which is required for the transmission of nerve impulses, at nerve muscle sites.[1]
Bendiocarb was invented in 1971 and was first introduced into the market by Fisons Ltd. It is currently marketed by Bayer CropScience and Kuo Ching under various trade names: Ficam, Dycarb, Garvox, Turcam, Niomil, Seedox, Tattoo
Bendiocarb is highly toxic to birds and fish. In addition, recently, a study in bone marrow cells of Calotes versicolor lizard demonstrated that chronic exposure to this contaminant increases the level of cytoxicity and genotoxicity (Anisha et al., 2019). In mammalian tissue, carbamates are generally excreted rapidly and do not accumulate.[1]
Anisha, N.S.; Tumul, S., (2019). Evaluation of Genotoxic and Cytotoxic effects of BendioCarb in Bone Marrow cells of one Calotes Versicolor. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of India 18(1): 19-23