

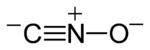
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Nitroxylmethanide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 239442 | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CNO− | |
| Molar mass | 42.018 g·mol−1 |
| Conjugate acid | Fulminic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fulminates are chemical compounds which include the fulminate ion (CNO−, C−≡N+−O−). The fulminate ion is a pseudohalic ion because its charge and reactivity are similar to those of the halogens. Due to the instability of the ion, fulminate salts are friction-sensitive explosives. The best known is mercury(II) fulminate, which has been used as a primary explosiveindetonators. Fulminates can be formed from metals, such as silver and mercury, dissolved in nitric acid and reacted with ethanol. The weak single nitrogen-oxygen bond is responsible for their instability. Nitrogen very easily forms a stable triple bond to another nitrogen atom, forming nitrogen gas.
Fulminates were discovered by Edward Charles Howard in 1800.[1][2][3] The use of fulminates for firearms was first demonstrated by a Scottish minister, Alexander John Forsyth, who patented his scent-bottle lock in 1807; this was a small container filled with fulminate of mercury.[4][5] Joshua Shaw determined how to encapsulate them in metal to form a percussion cap, but did not patent his invention until 1822.
In the 1820s, the organic chemist Justus Liebig discovered silver fulminate (AgCNO) and Friedrich Wöhler discovered silver cyanate (AgOCN). They have different properties but the same chemical composition, which led to a bitter dispute finally resolved by Jöns Jakob Berzelius through the concept of isomers.[6]
|
Inorganic compounds of carbon and related ions
| |
|---|---|
| Compounds |
|
| Carbon ions |
|
| Nanostructures |
|
| Oxides and related |
|