

| Karnic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Australia |
| Linguistic classification | Pama–Nyungan
|
| Subdivisions |
|
| Glottolog | karn1253 |
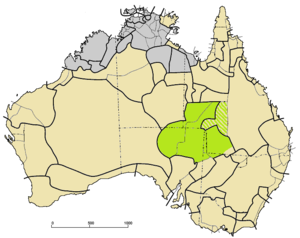 Karnic languages (green) among other Pama–Nyungan (tan). The four solid-green sections are Arabana (west), Palku (north), Karna (central strip), Ngura (east). The striped area to the east is Kungkari and Birria, which may have been Karnic. | |
The Karnic languages are a group of languages of the Pama–Nyungan family. According to Dixon (2002), these are three separate families, but Bowern (2001) establishes regular paradigmatic connections among many of the languages, demonstrating them as a genealogical group. Bowern classifies them as follows:
Other languages of the area may be Karnic, but are too poorly attested to be secure. Breen (2007) writes of "Karna–Mari fringe" languages which are "a discontinuous group of languages, mostly poorly attested, scattered between Karnic and Mari languages but not showing much connection with either or with one another. The only one well attested is also the most remote geographically, Kalkutungu".[1] The possibilities listed but not included in Bowern (2001) due to lack of materials, and included in the list in Bowern (2011),[2] are Birria (Pirriya/Bidia) [not the Biri/Birria in Maric], Pirlatapa, Kungkari (and unconfirmed Kungatutyi/Gungadidji, not the same as the Mari dialect), Karuwali (and unconfirmed Kulumali) [included under Midhaga in Dixon]. Unconfirmed names mentioned in Bowern (2011)[citation needed] are Karangura, Mayawali, and Nhirrpi.
See also Ngura; some varieties are Karnic, but others may be Maric.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||