

| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Mercury dinitrate | |
| Other names
Mercuric nitrate | |
| Identifiers | |
|
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.126 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1625 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Hg(NO3)2 | |
| Molar mass | 324.60 g/mol (anhydrous) |
| Appearance | colorless crystals or white powder |
| Odor | sharp |
| Density | 4.3 g/cm3 (monohydrate) |
| Melting point | 79 °C (174 °F; 352 K) (monohydrate) |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in nitric acid, acetone, ammonia insoluble in ethanol |
| −74.0·10−6cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
   
| |
| Danger | |
| H272, H300, H310, H330, H373, H410 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Nonflammable |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0980 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions |
Mercury(II) sulfate Mercury(II) chloride |
Other cations |
Zinc nitrate Cadmium nitrate |
Related compounds |
Mercury(I) nitrate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
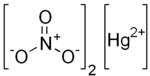
Mercury(II) nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Hg(NO3)2. It is the mercury(II) saltofnitric acid HNO3. It contains mercury(II) cations Hg2+ and nitrate anions NO−3, and water of crystallization H2O in the case of a hydrous salt. Mercury(II) nitrate forms hydrates Hg(NO3)2·xH2O. Anhydrous and hydrous salts are colorless or white soluble crystalline solids that are occasionally used as a reagents. Mercury(II) nitrate is made by treating mercury with hot concentrated nitric acid. Neither anhydrous nor monohydrate has been confirmed by X-ray crystallography.[1] The anhydrous material is more widely used.[clarification needed]
Mercury(II) nitrate has been used in mercurationofketones.[2] Mercury(II) nitrate was formerly used in carroting felt for hats.
Mercury compounds are highly toxic. The use of this compound by hatters and the subsequent mercury poisoning of said hatters is a common theory of where the phrase "mad as a hatter" came from.
|
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury(I) |
| ||
| Mercury(II) |
| ||
| Mercury(IV) |
| ||
| Amalgams |
| ||
| Mercury cations |
| ||
|
Salts and covalent derivatives of the nitrate ion
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||